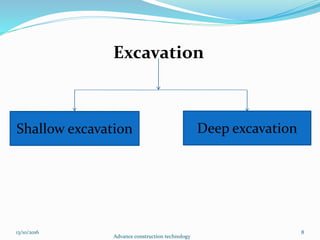
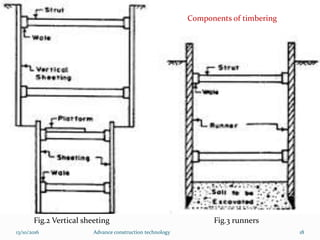
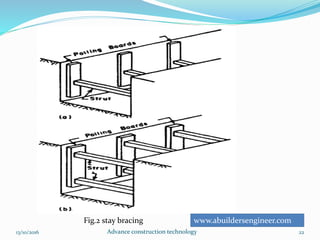
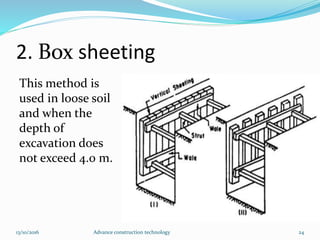
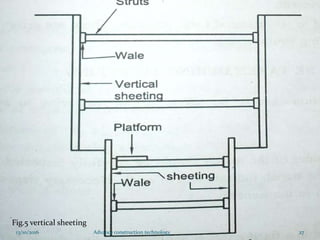
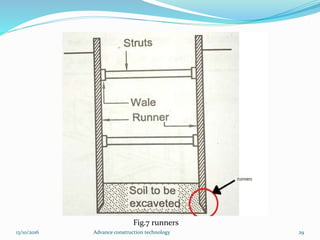
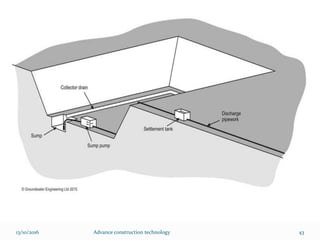
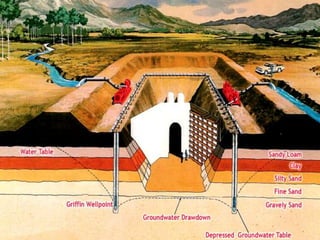
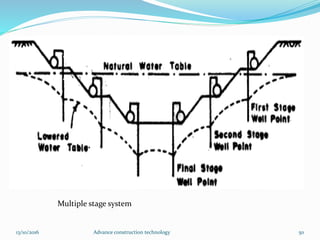
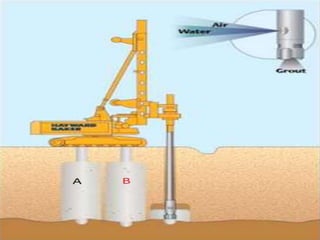
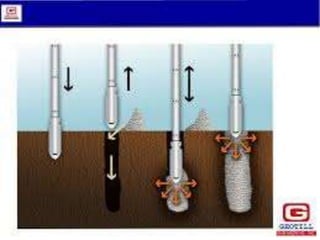
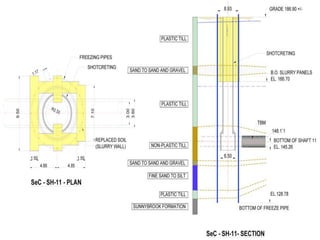
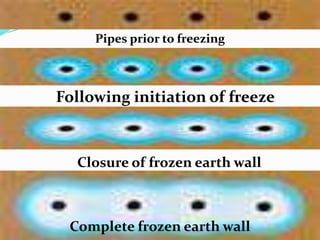
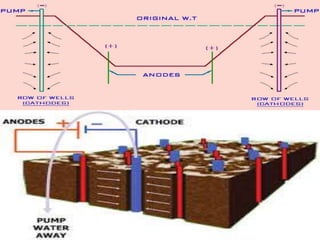
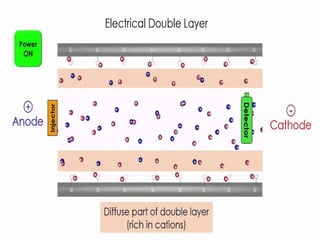
The document discusses advanced construction technology focusing on excavation methods, timbering of trenches, and dewatering techniques. It outlines shallow and deep excavation, detailing the necessity and methods of timbering to ensure safety and structural integrity. Additionally, various dewatering methods are presented for managing groundwater during excavation processes.