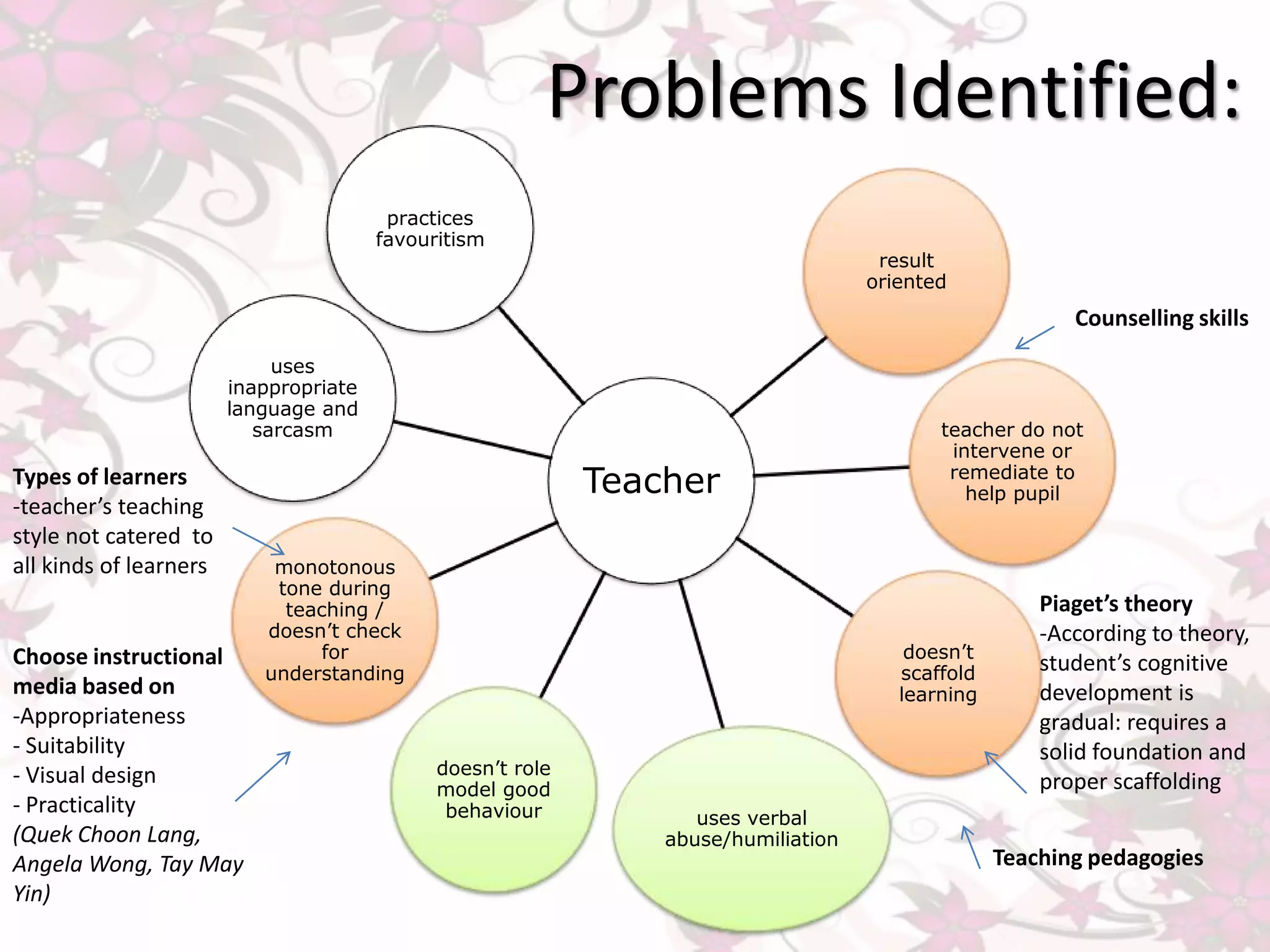
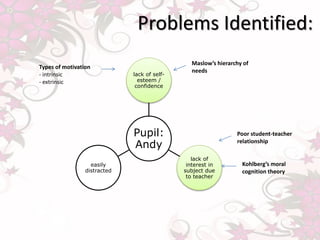
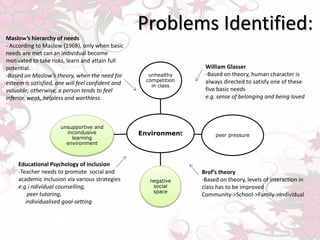
The document discusses issues with a teacher's practices including favoritism, lack of intervention or scaffolding for students, verbal abuse, and inappropriate language use. It also discusses problems with the learning environment including unhealthy competition, peer pressure, and a lack of support. Drawing from educational psychology theories, it suggests the teacher's style does not cater to different types of learners, the importance of meeting students' basic needs for learning, and improving interactions and inclusion in the classroom.