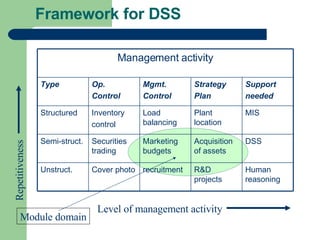
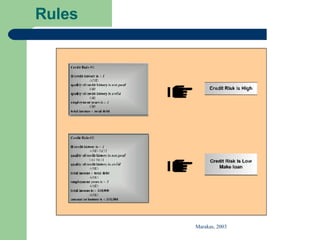
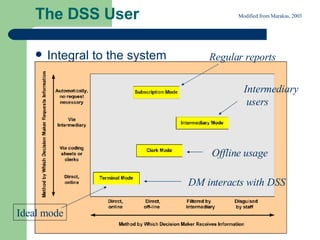
This document provides an overview of a module on decision support systems. It discusses what decision support systems are designed to do, which is to facilitate and support the human decision making process, not replace human decision makers. It outlines the learning outcomes, assessment components, lecture and lab schedule, and software that will be used. It also summarizes some of the key topics that will be covered, including decision modeling, knowledge acquisition and elicitation, and the components and characteristics of decision support systems.