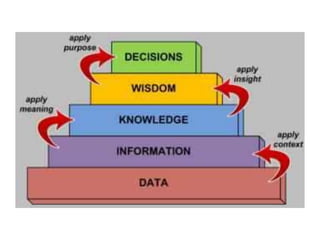
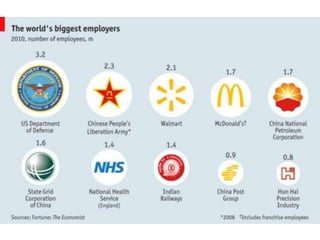
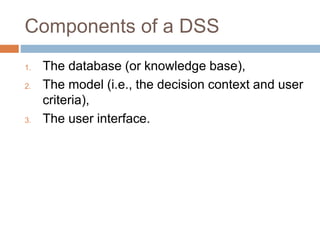
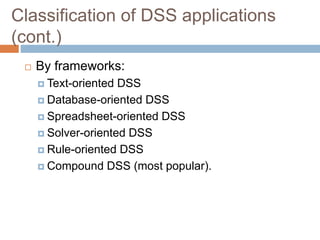
The document outlines a training session on decision support systems (DSS), covering their history, components, types, and benefits, while emphasizing the importance of decision-making within organizations. It discusses various classical and modern methods of decision-making, the evolution of DSS technology, and classified applications of DSS. The session also features case studies demonstrating the practical use of DSS in areas such as environmental monitoring, healthcare, and traffic management.