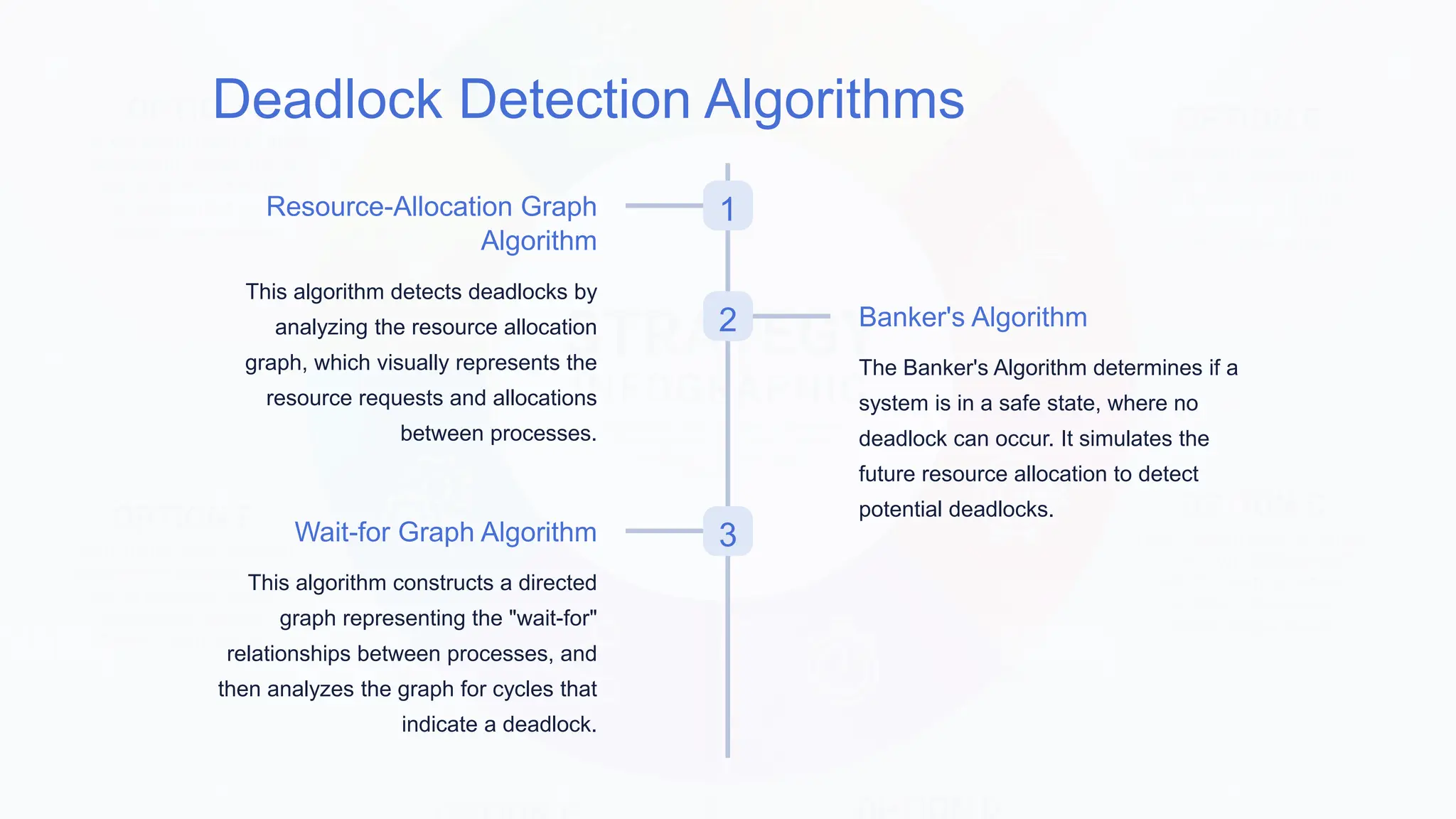
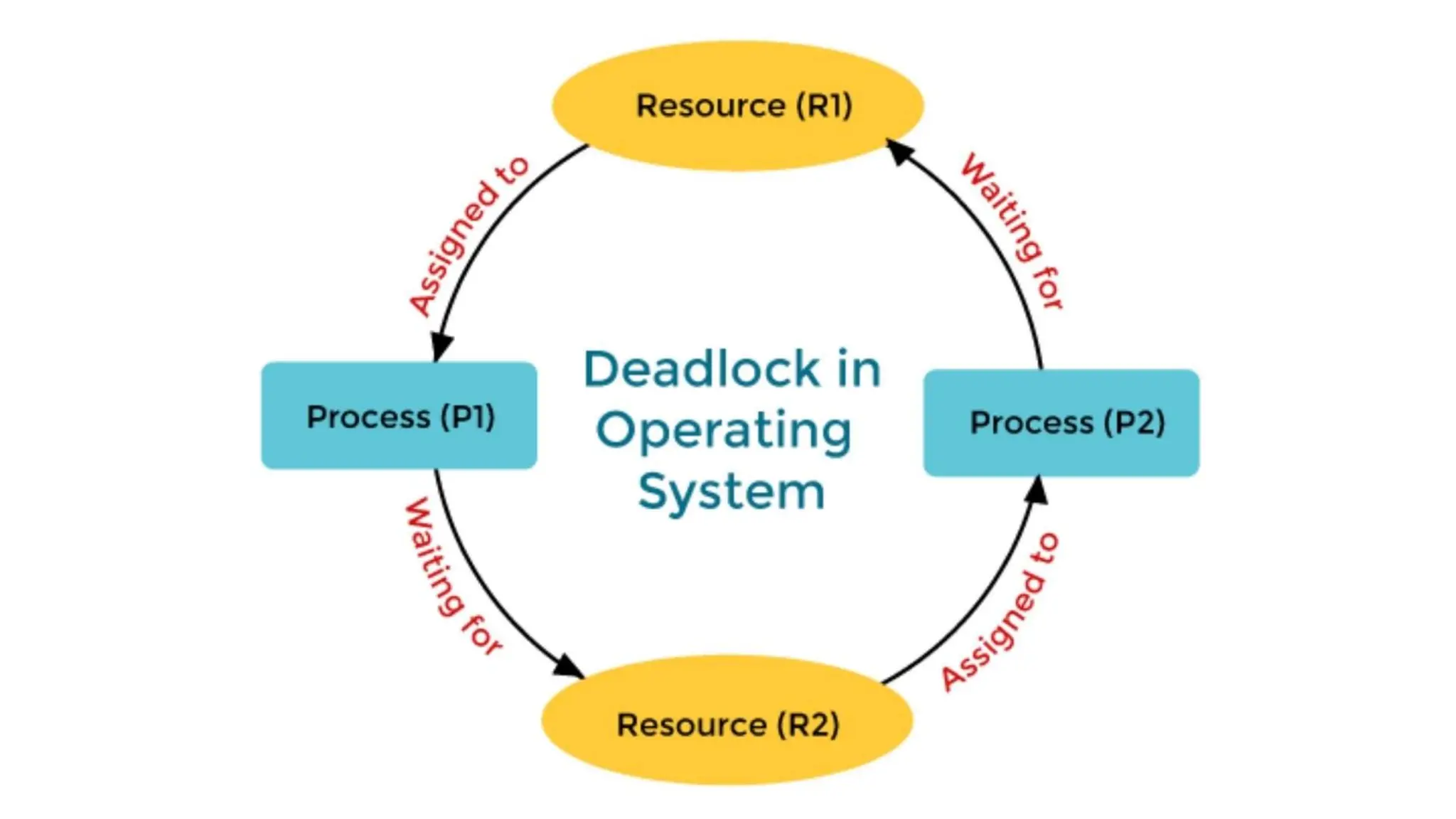
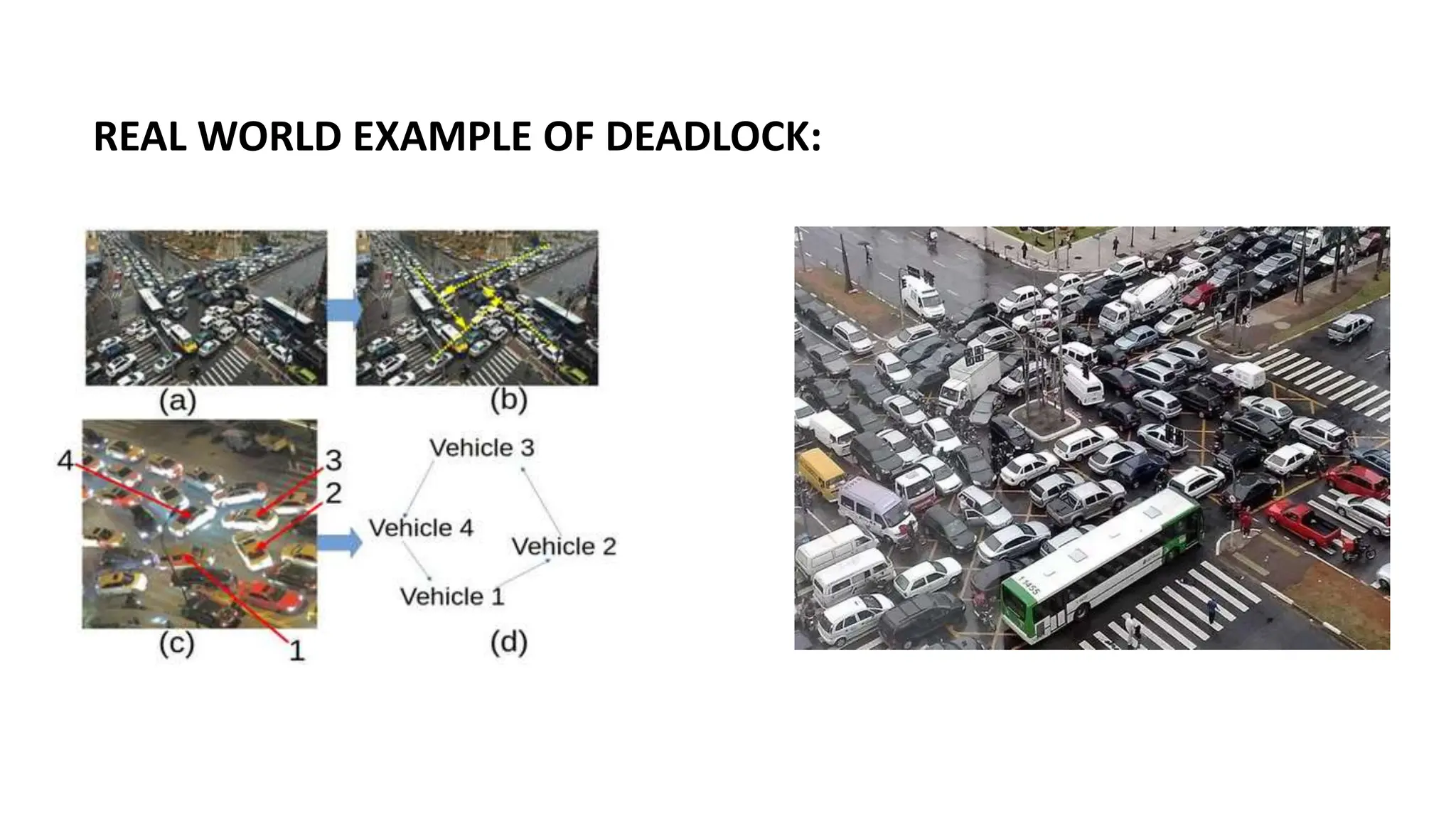
The document discusses deadlocks, which occur when two or more processes block each other by holding resources that the other needs, leading to system standstill. It outlines necessary conditions for deadlocks, such as mutual exclusion and circular wait, and describes various detection and prevention techniques, including resource allocation and process termination. Additionally, it highlights real-world examples of deadlocks and emphasizes the importance of understanding and mitigating such issues in software systems.