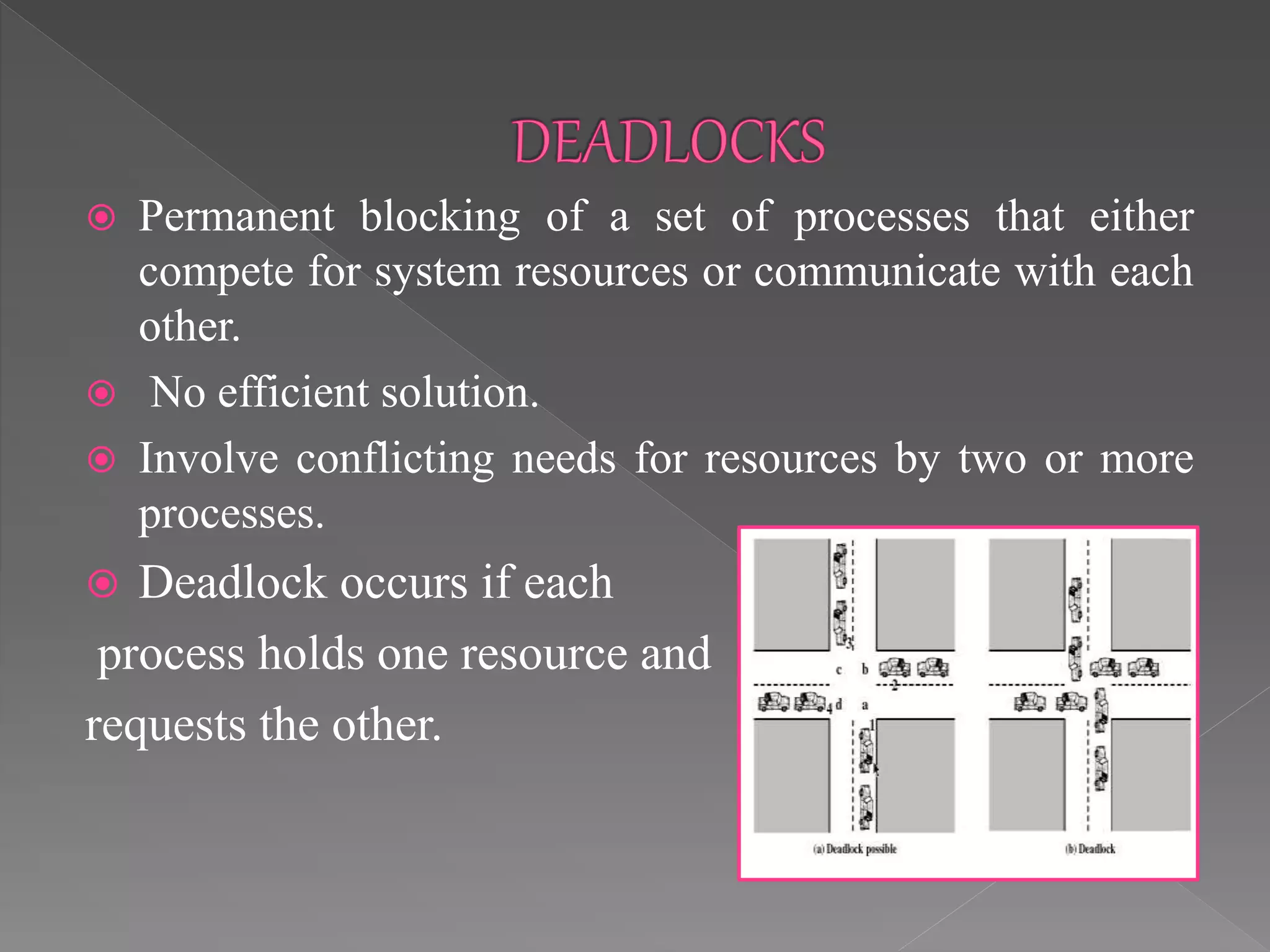
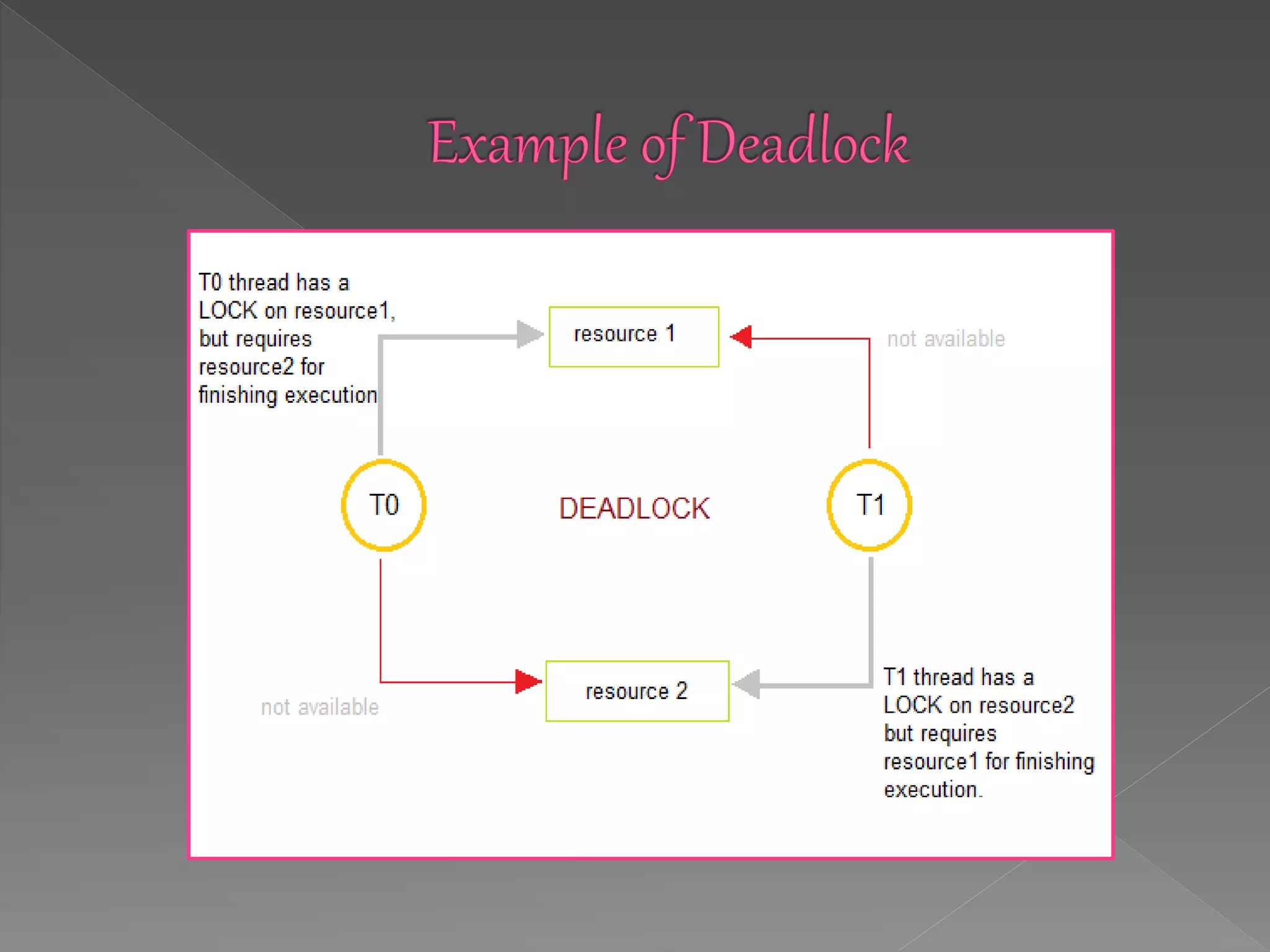
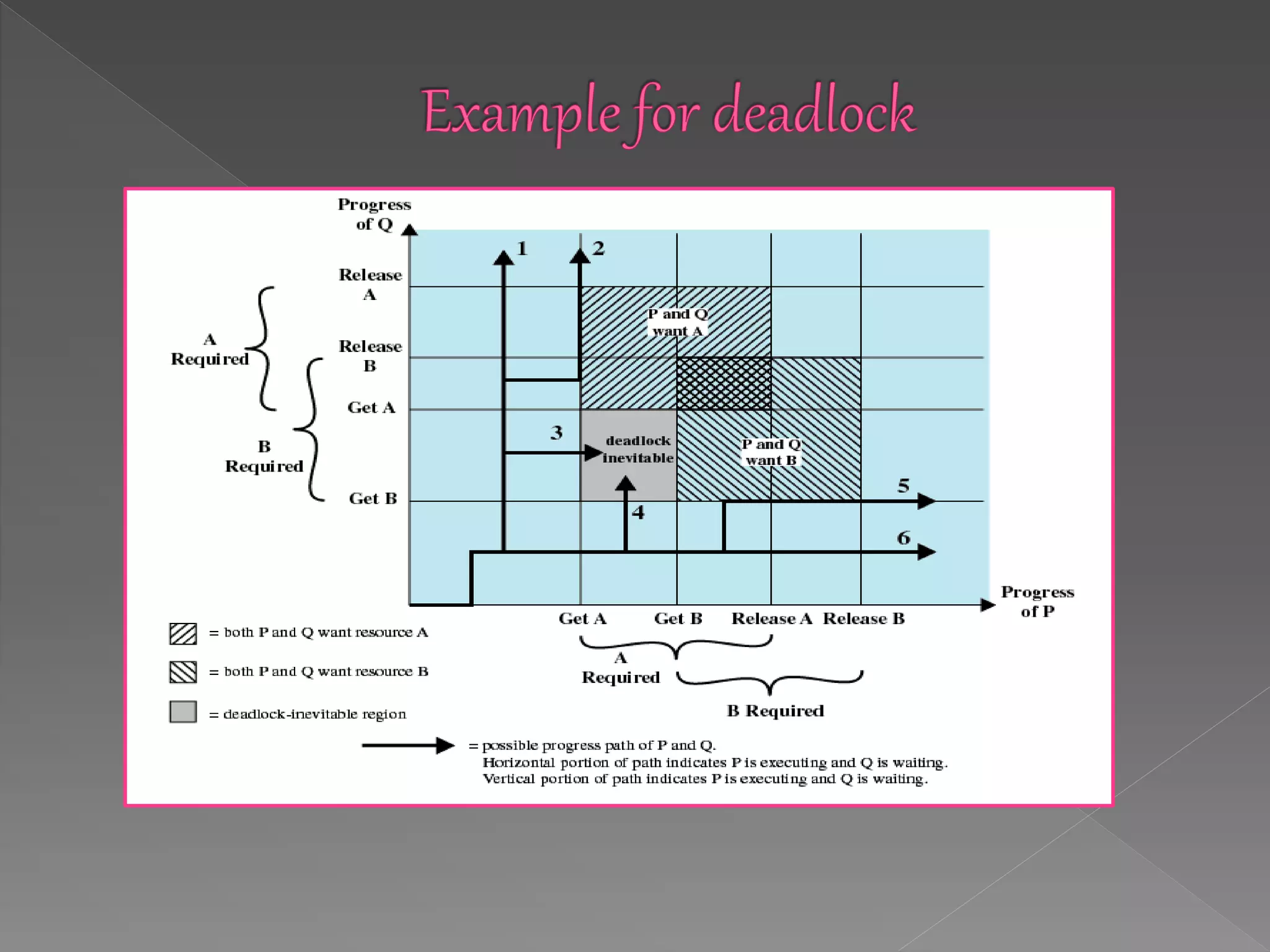
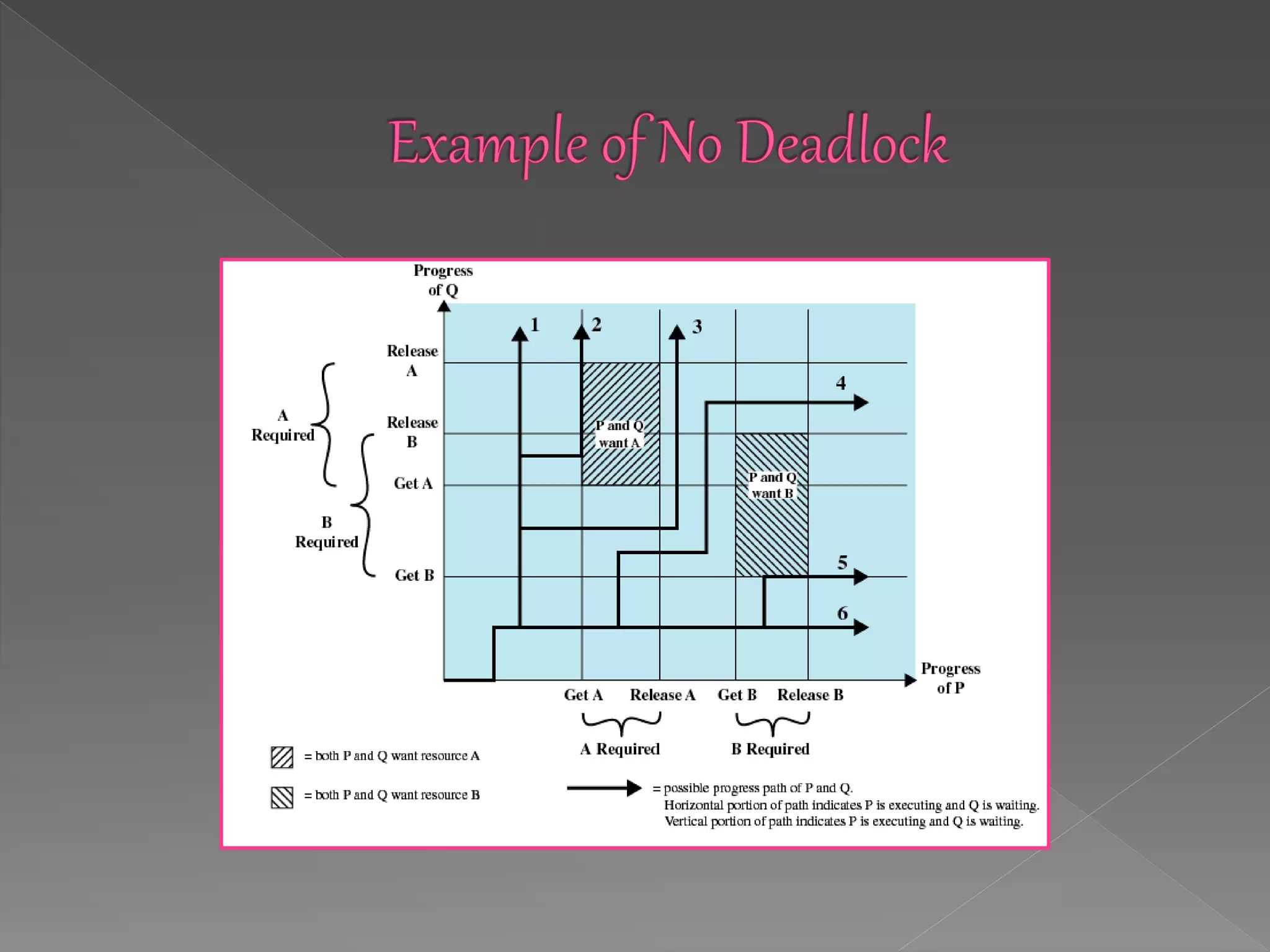
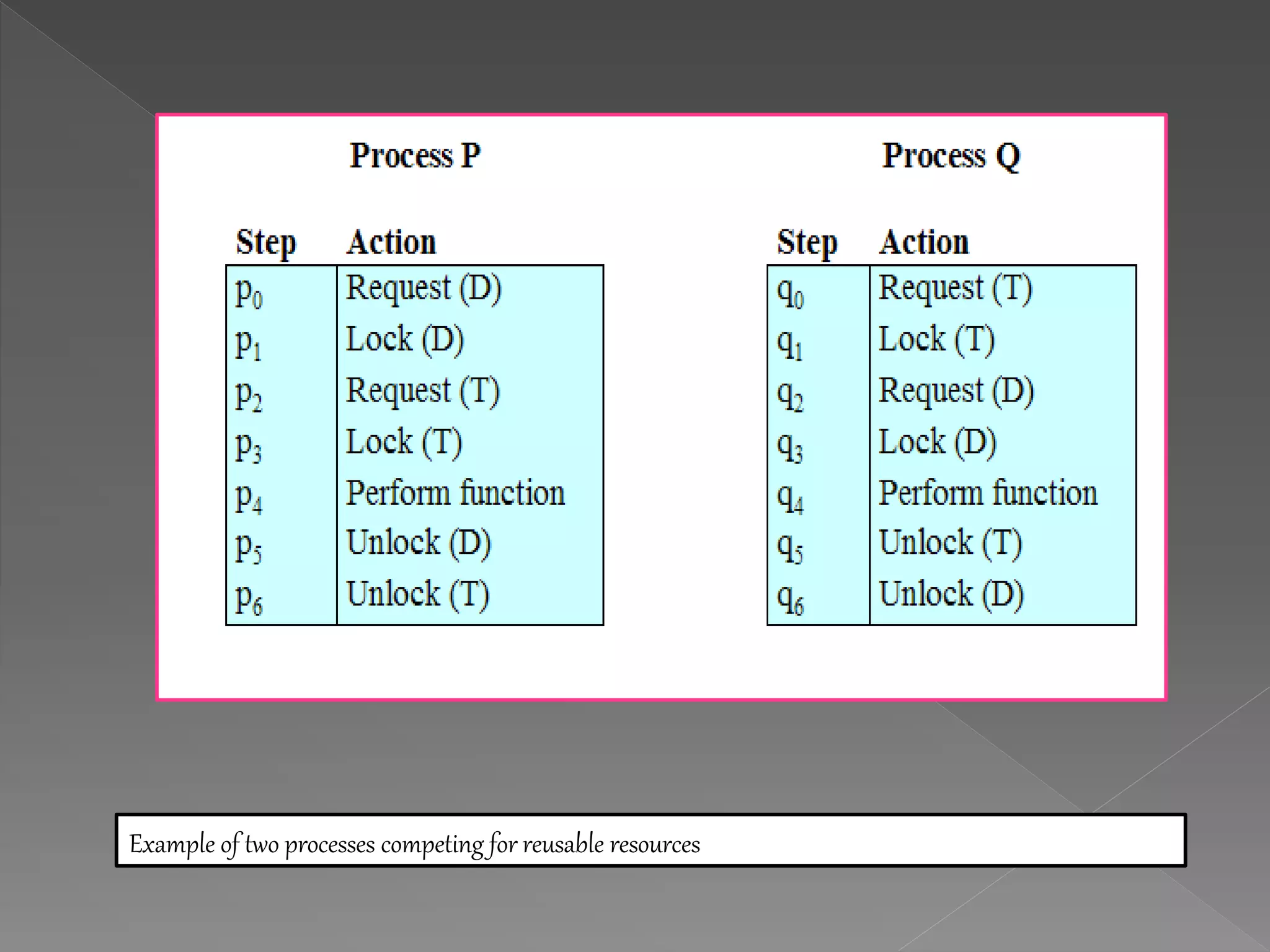
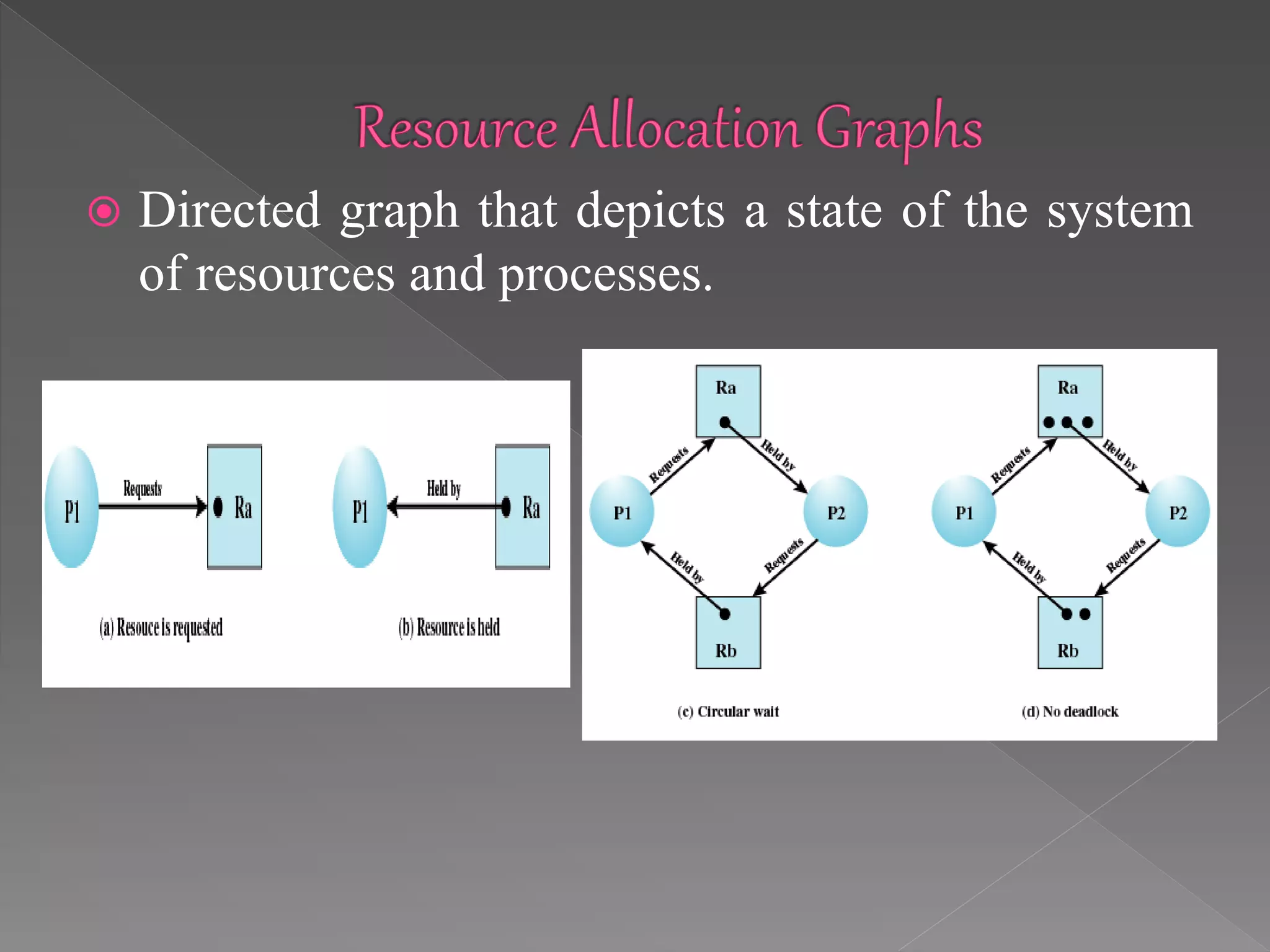
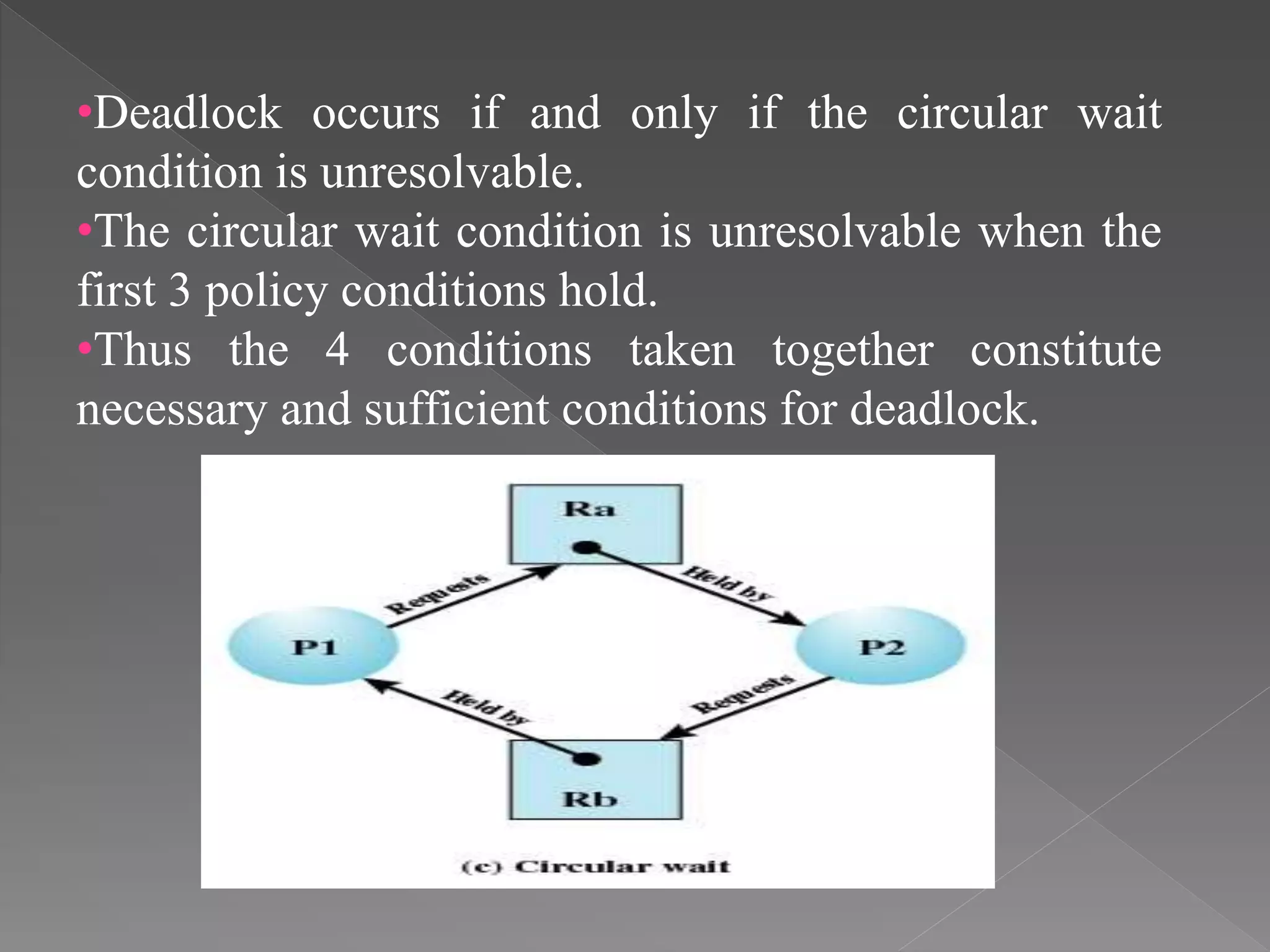
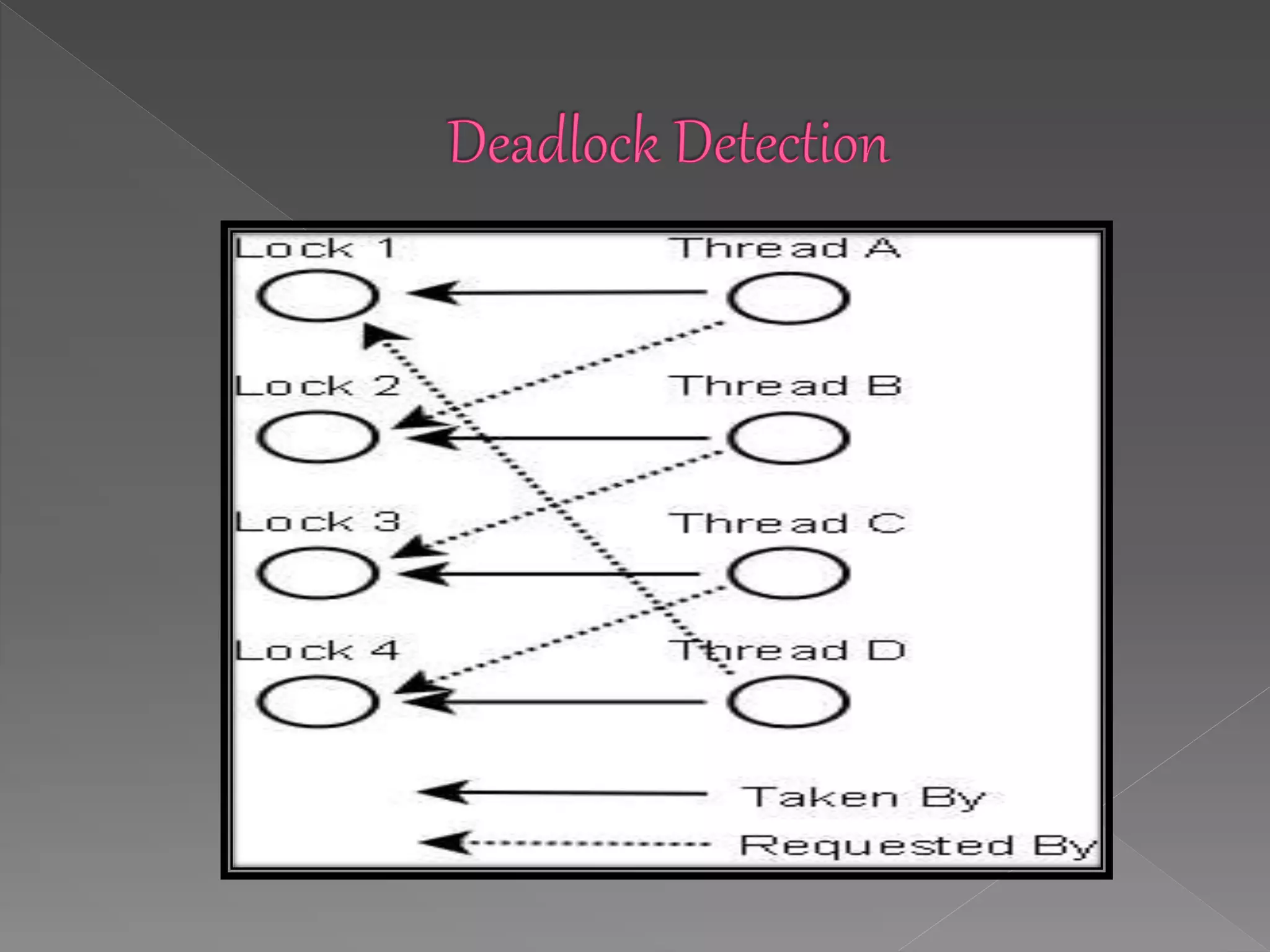
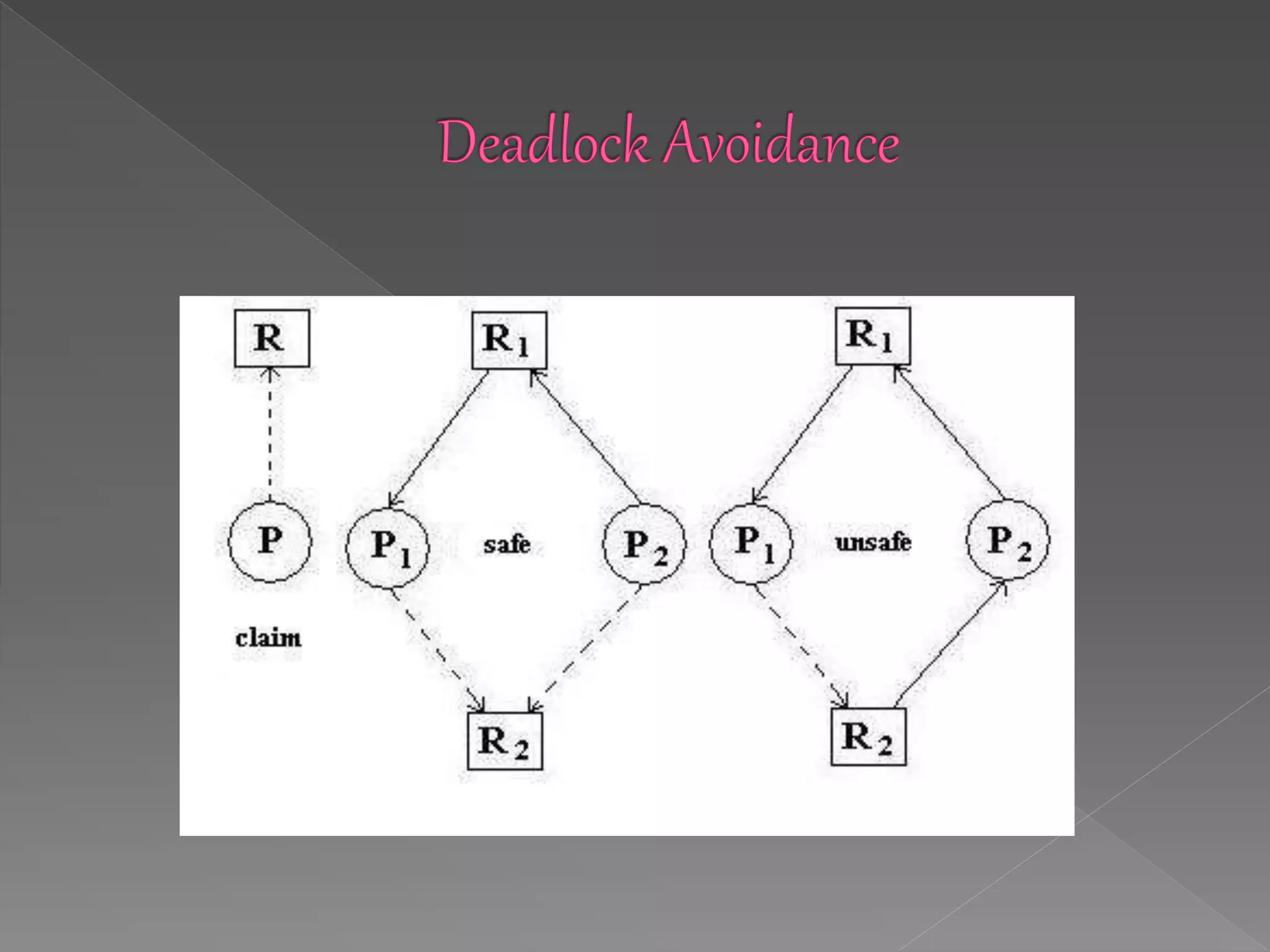
This document discusses deadlock in computer systems. It defines deadlock as when a set of processes are blocked waiting for resources held by other processes in the set. Four necessary conditions for deadlock to occur are outlined: mutual exclusion, hold and wait, no preemption, and circular wait. Strategies to handle deadlock such as prevention, detection, avoidance, and an integrated approach combining multiple strategies are also discussed. Examples of different resource types that can be involved in deadlock are provided.