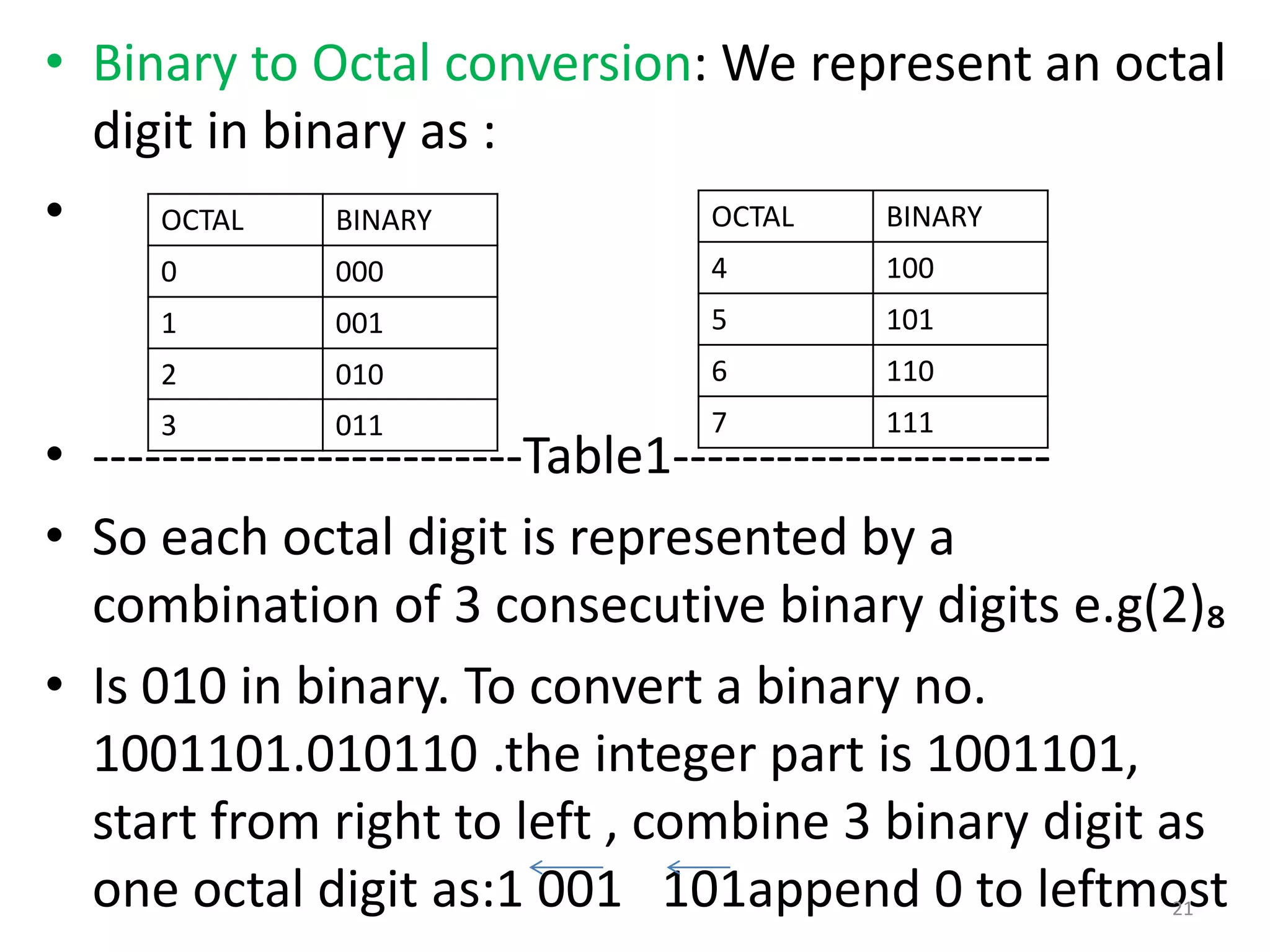
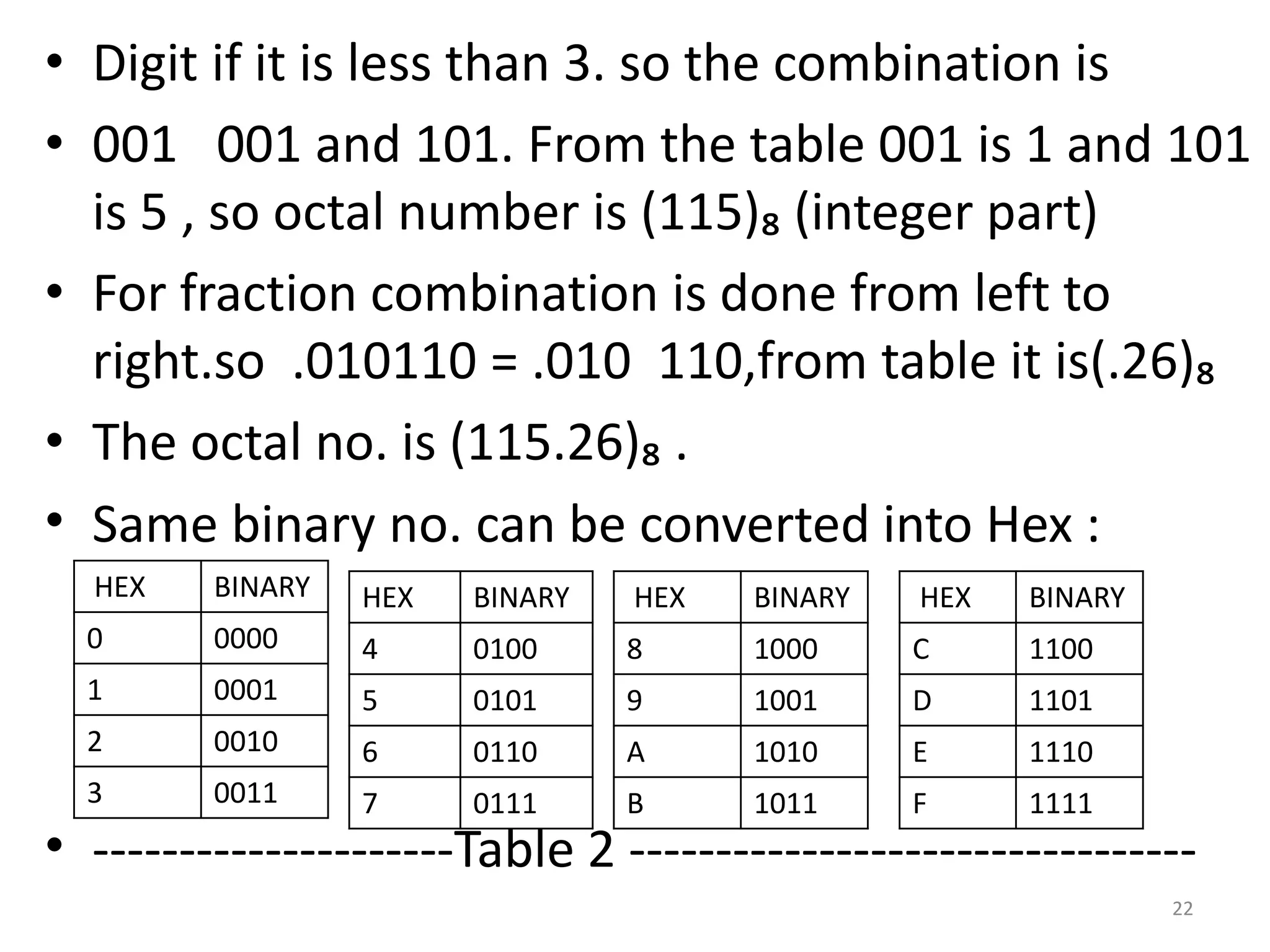
This document discusses different number systems including binary, octal, decimal, and hexadecimal. It provides examples of how to represent a number in each system and how to convert between them. The key points covered are:
1) Positional number systems assign a place value to digits based on their position, while non-positional systems do not.
2) Binary uses digits 0 and 1. Octal uses digits 0-7. Hexadecimal uses digits 0-9 and A-F.
3) To convert a decimal number to another base, it is repeatedly divided by the new base and the remainders are used to build the number in the target base from right to left.