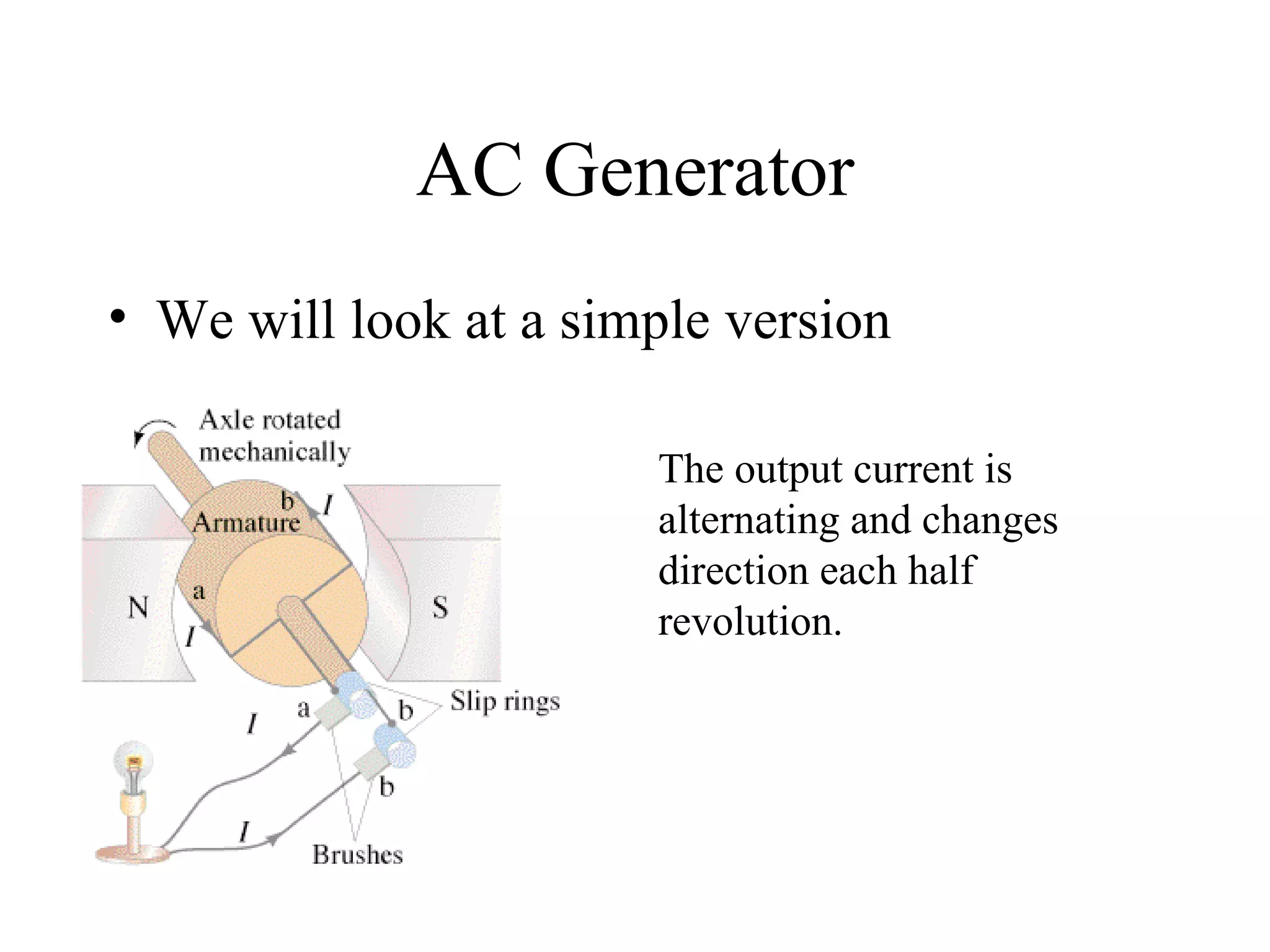
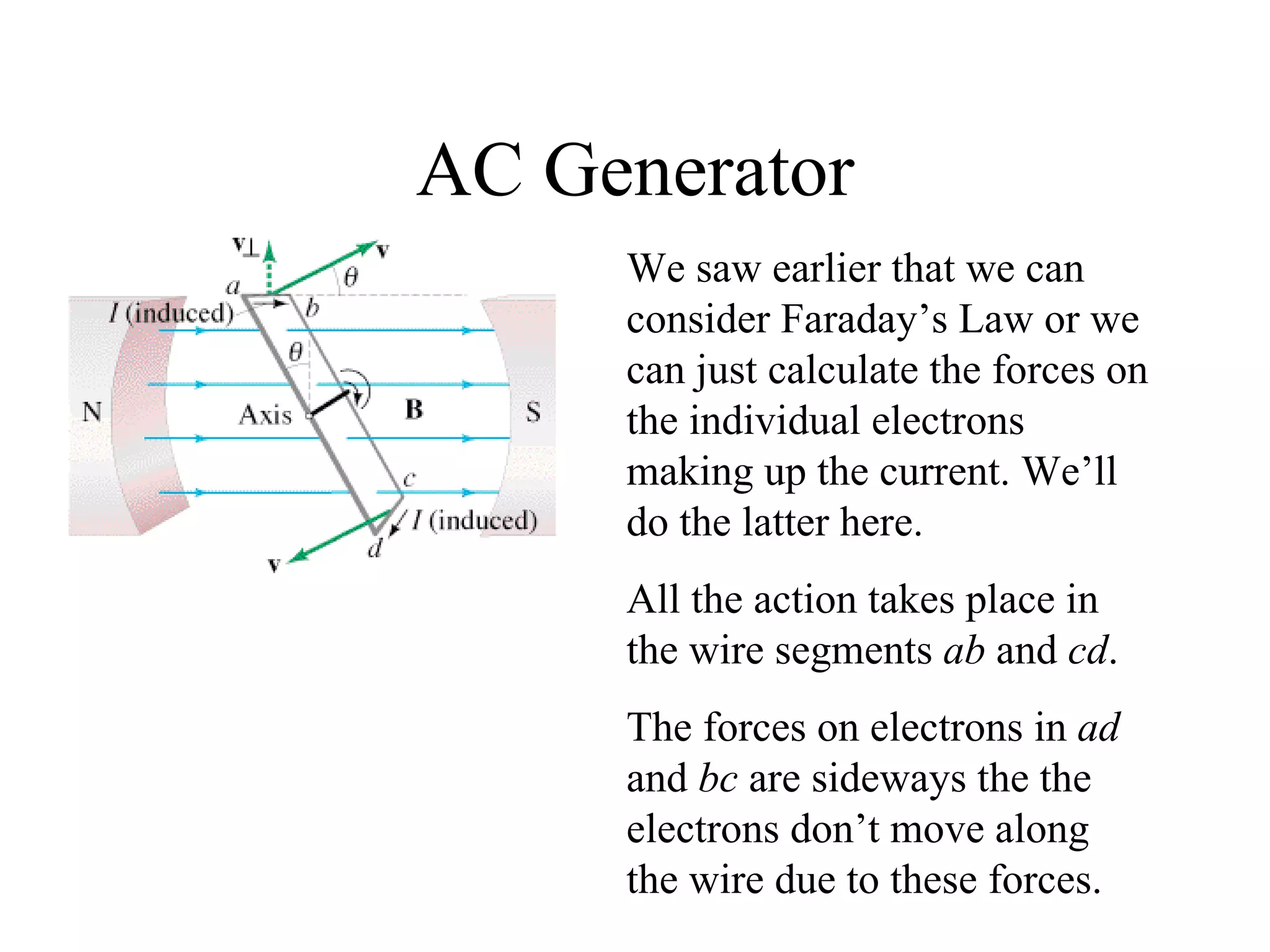
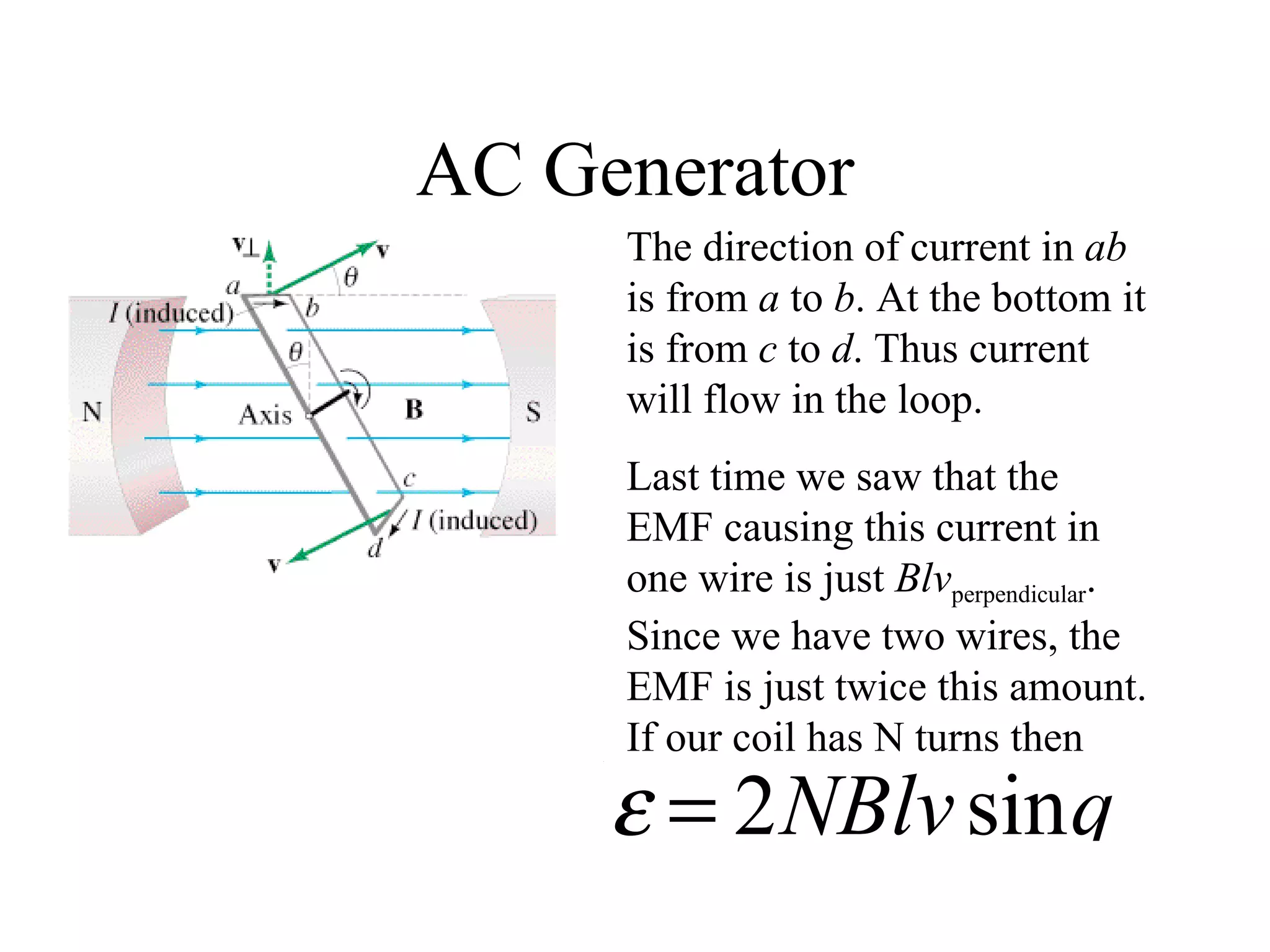
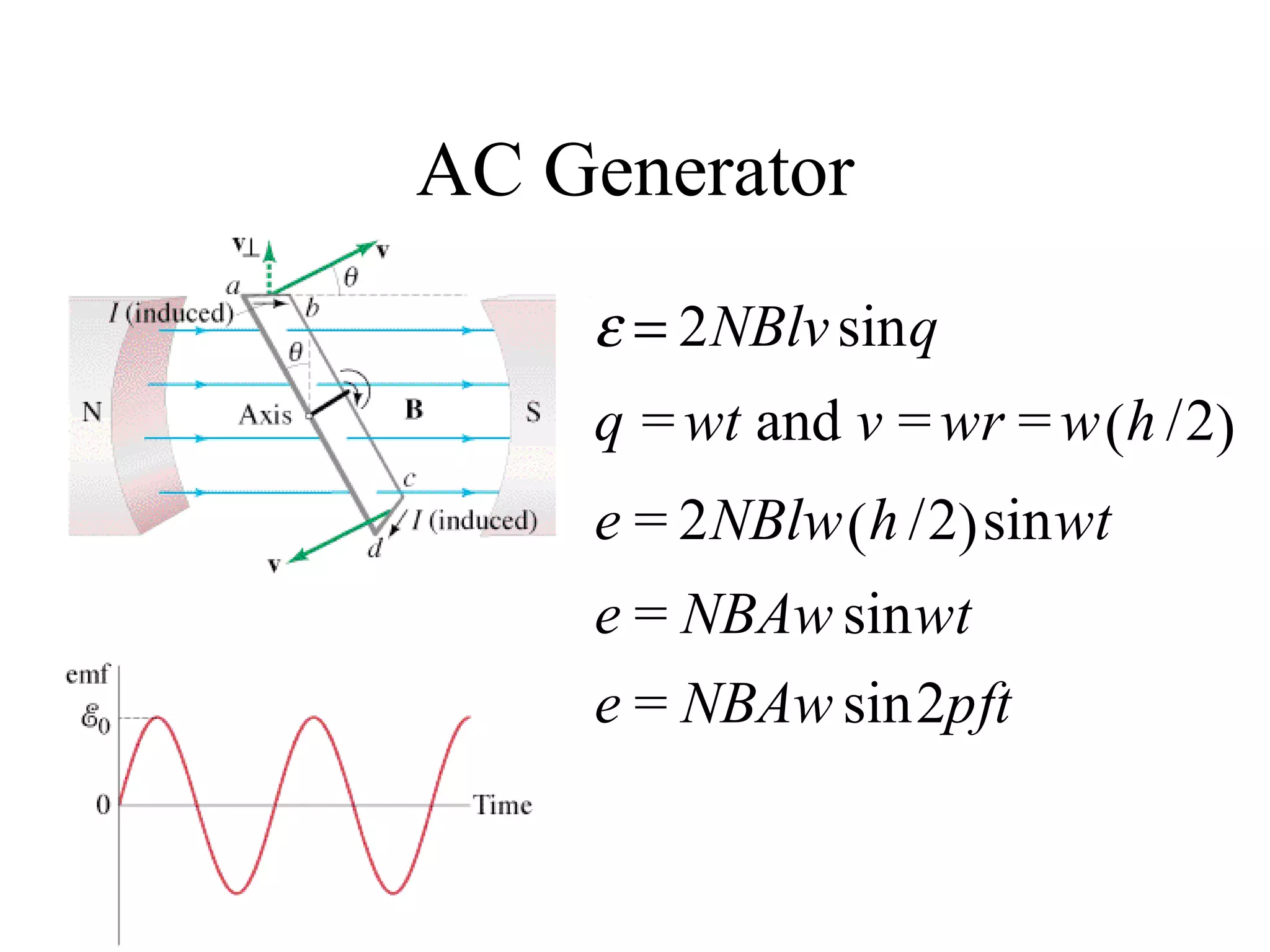
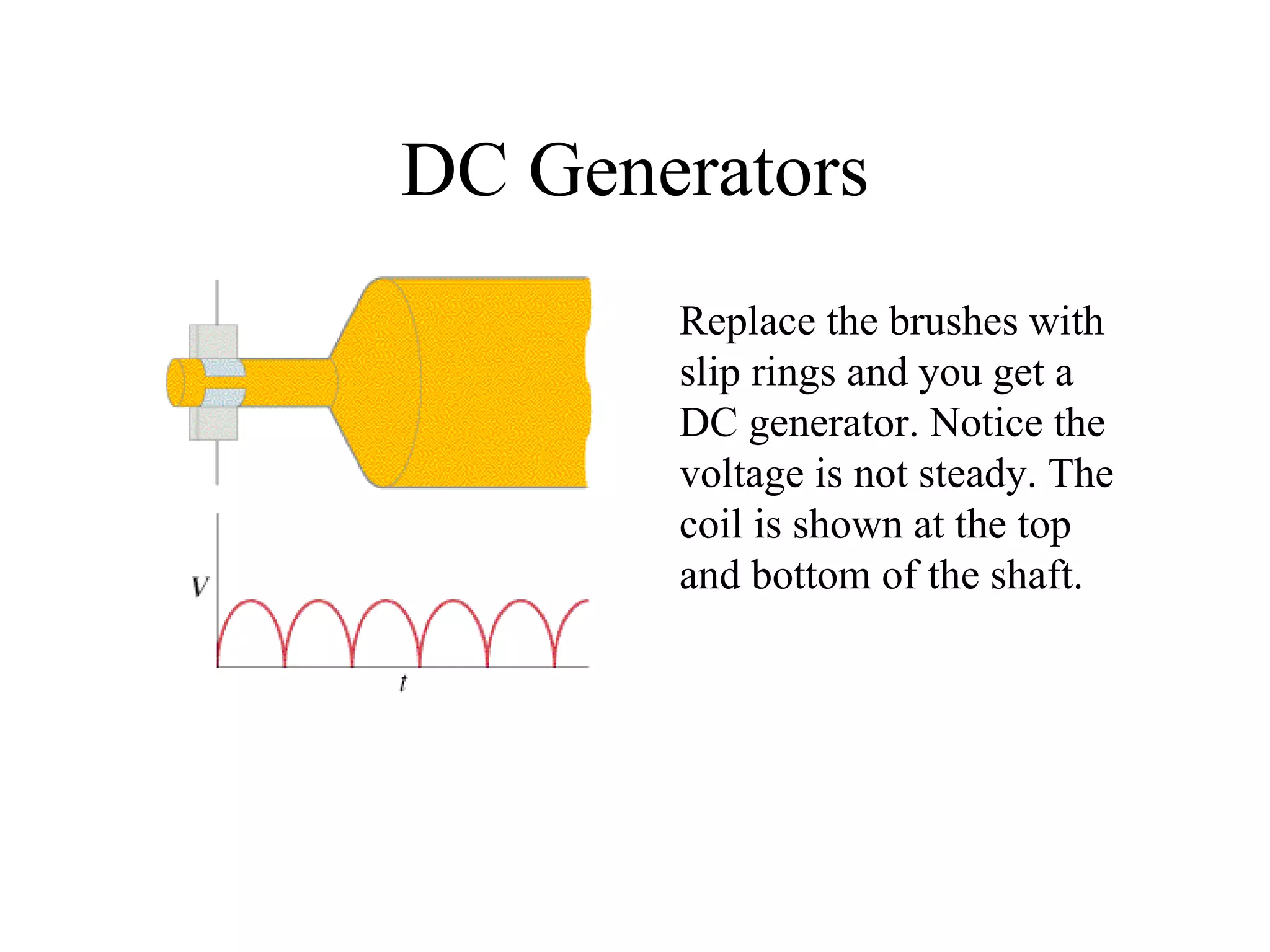
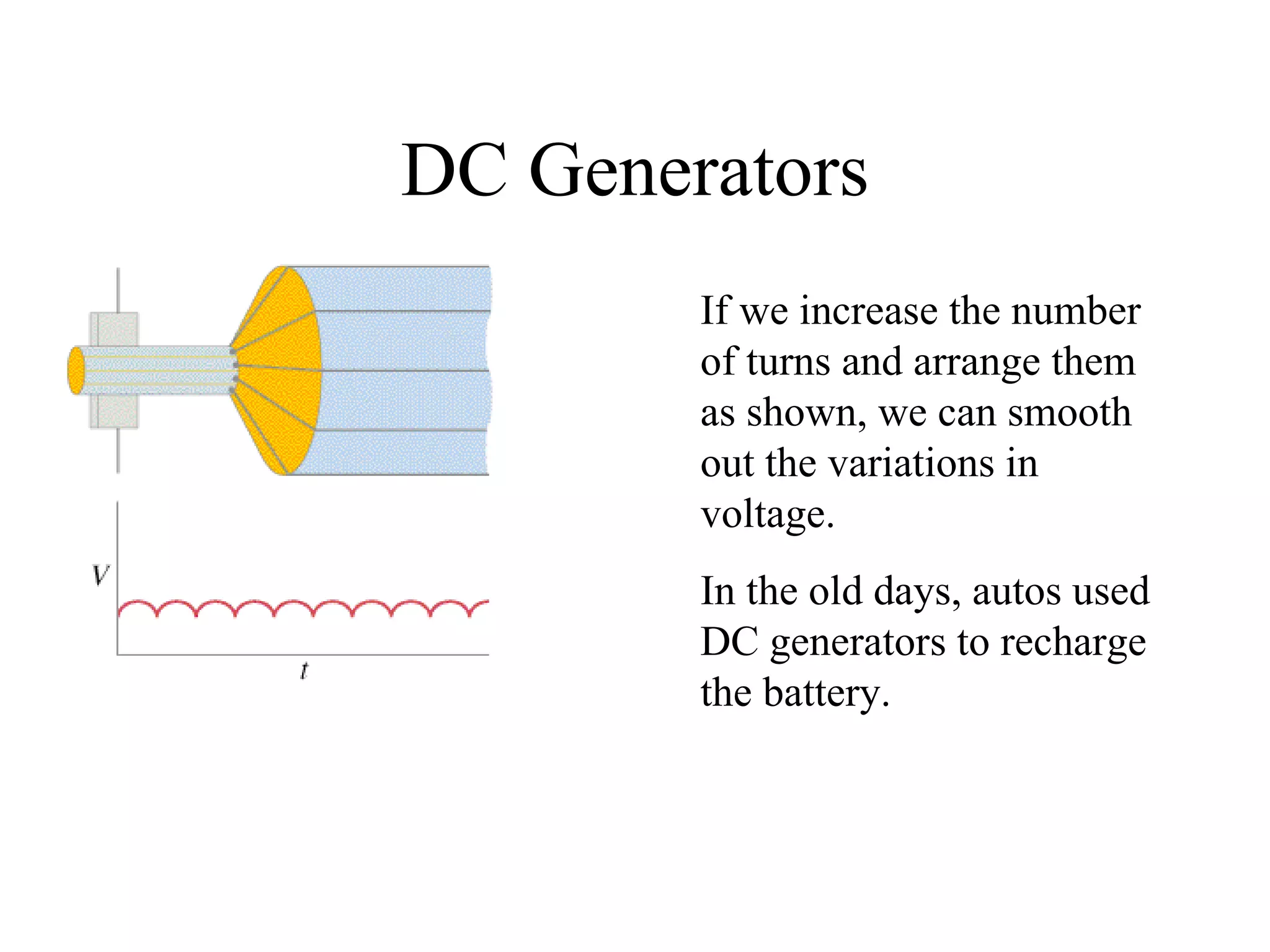
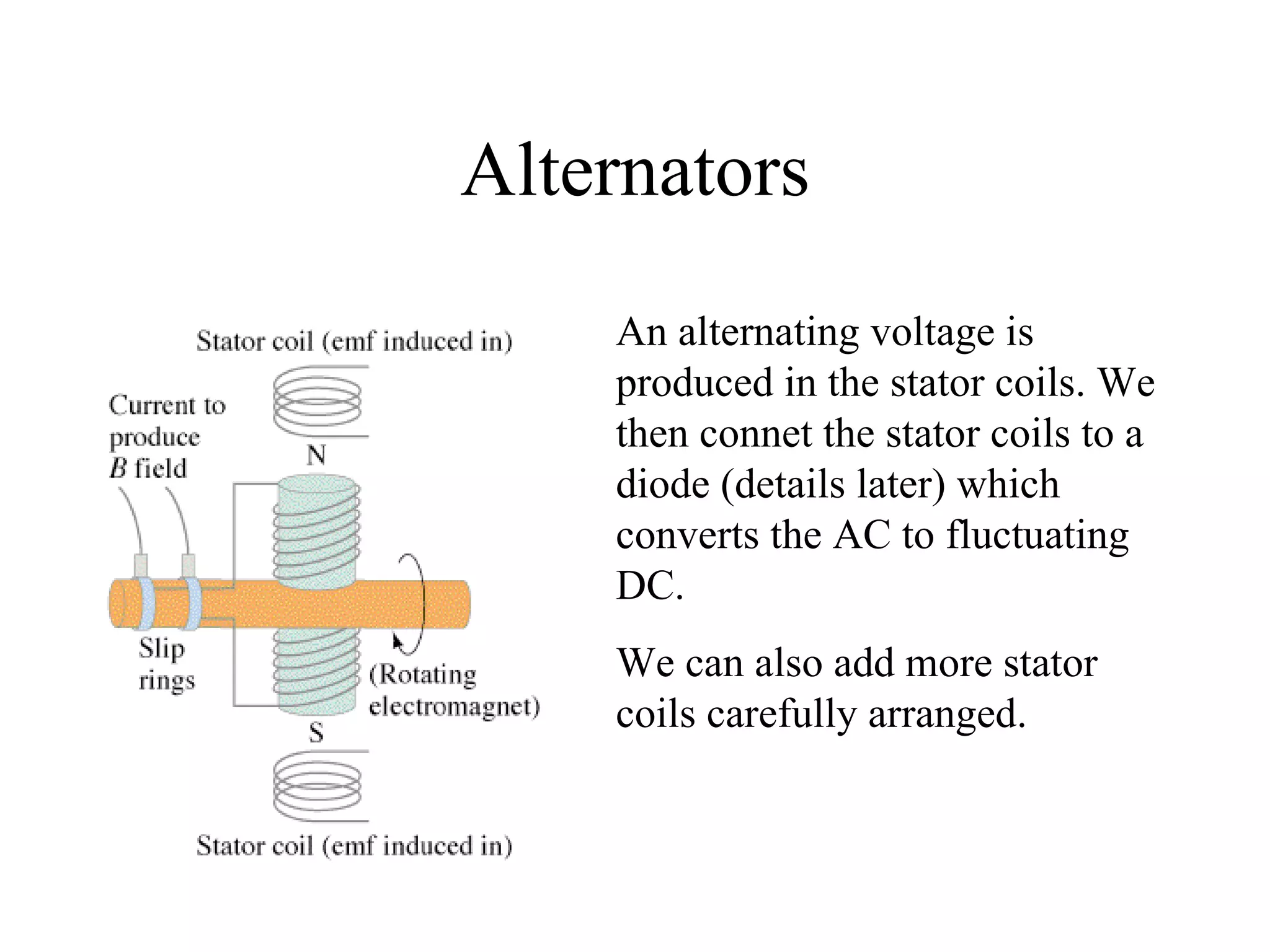
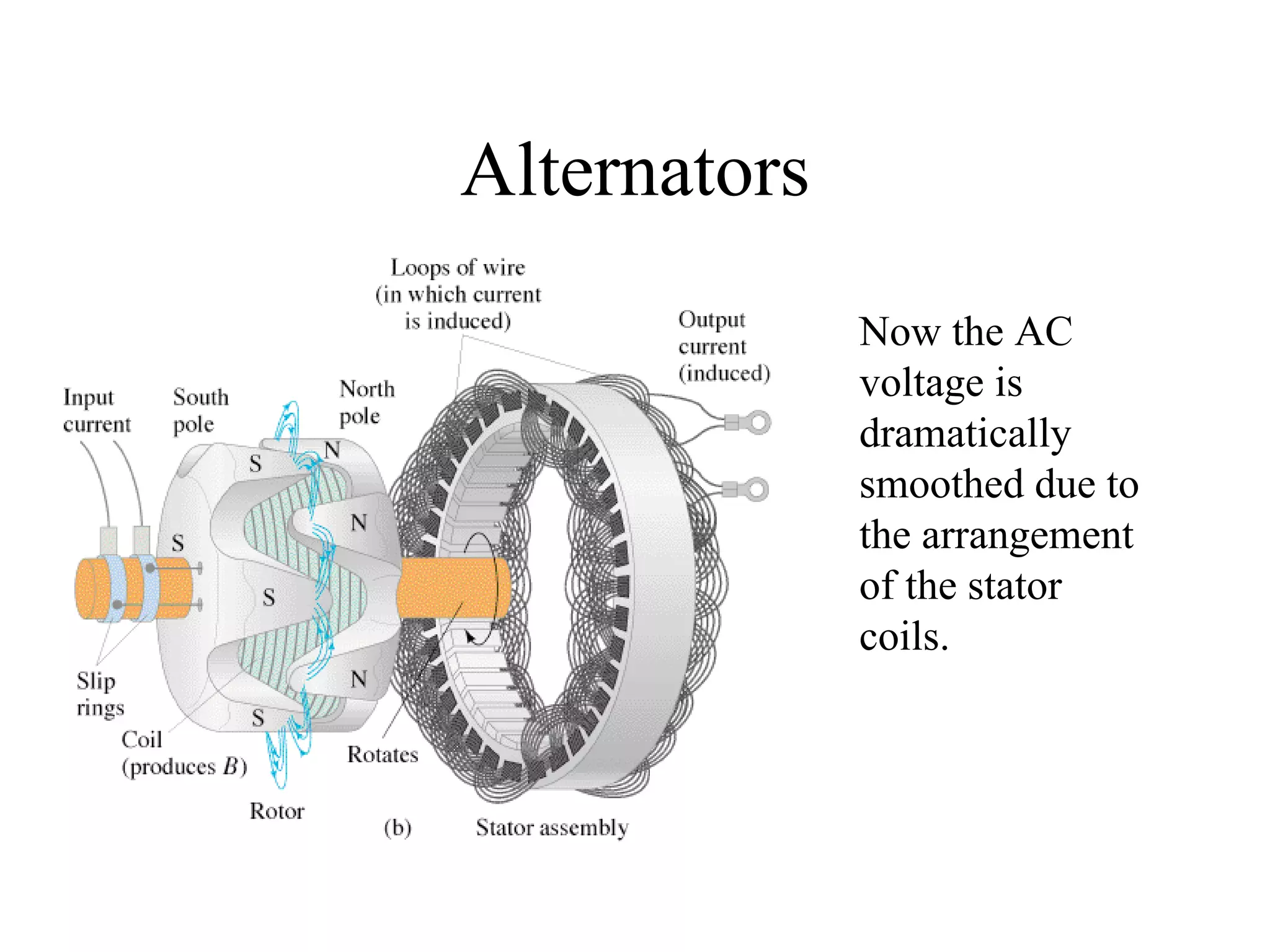
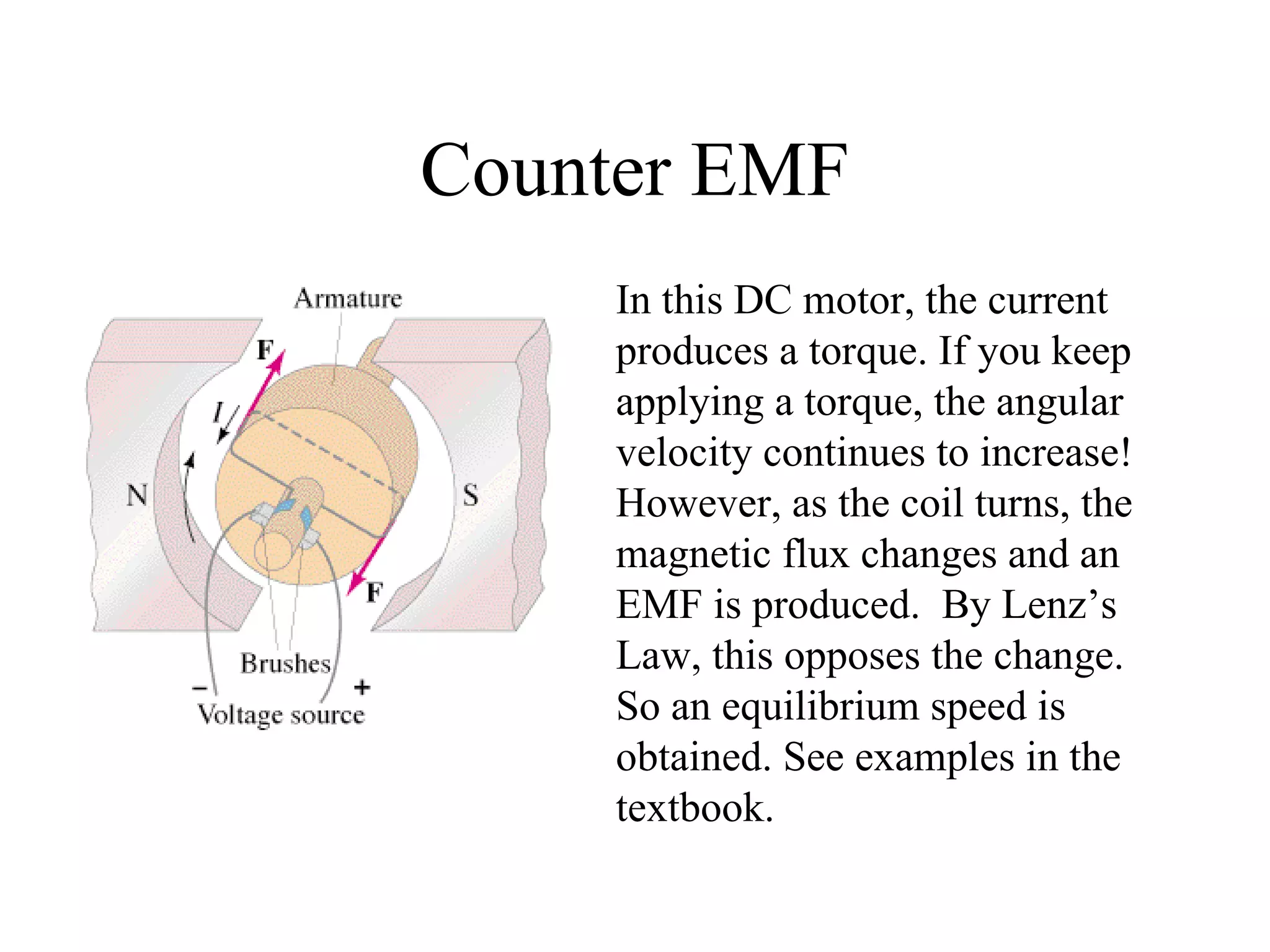
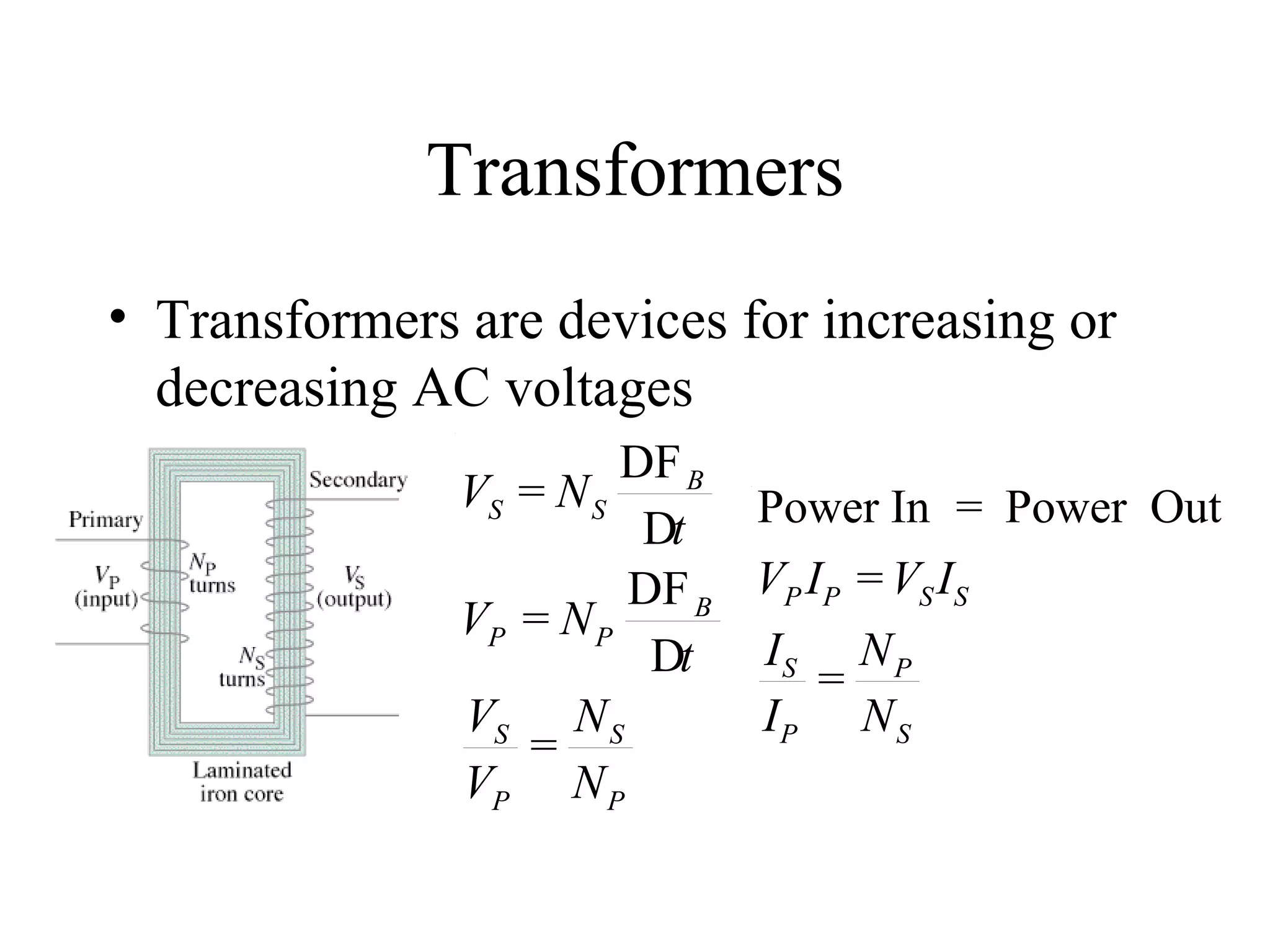
Electric generators convert mechanical energy into electrical energy through the process of electromagnetic induction described by Faraday's law. A generator works by spinning a coil of wire between the poles of a magnet, which induces an electric current in the wire that alternates based on the coil's orientation to the magnetic field. The faster the coil spins, the greater the induced voltage that is generated.