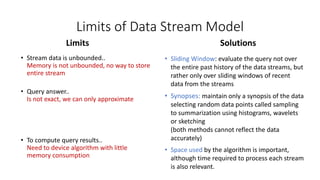
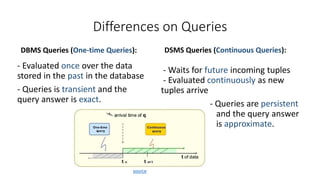
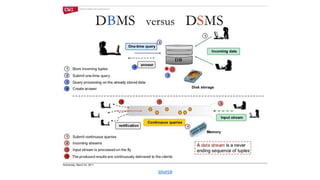
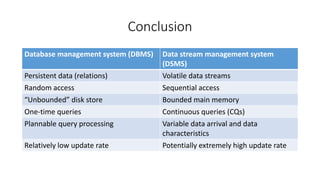
DBMS is used to manage stored data in databases while DSMS is used to manage continuous, real-time data streams. Key differences are that DBMS works with stored, persistent data that can be randomly accessed, while DSMS works with volatile data streams that arrive sequentially and must be processed in limited memory. DBMS supports one-time queries on stored data, while DSMS supports continuous queries that must adapt to the unpredictable nature and high update rate of streaming data.