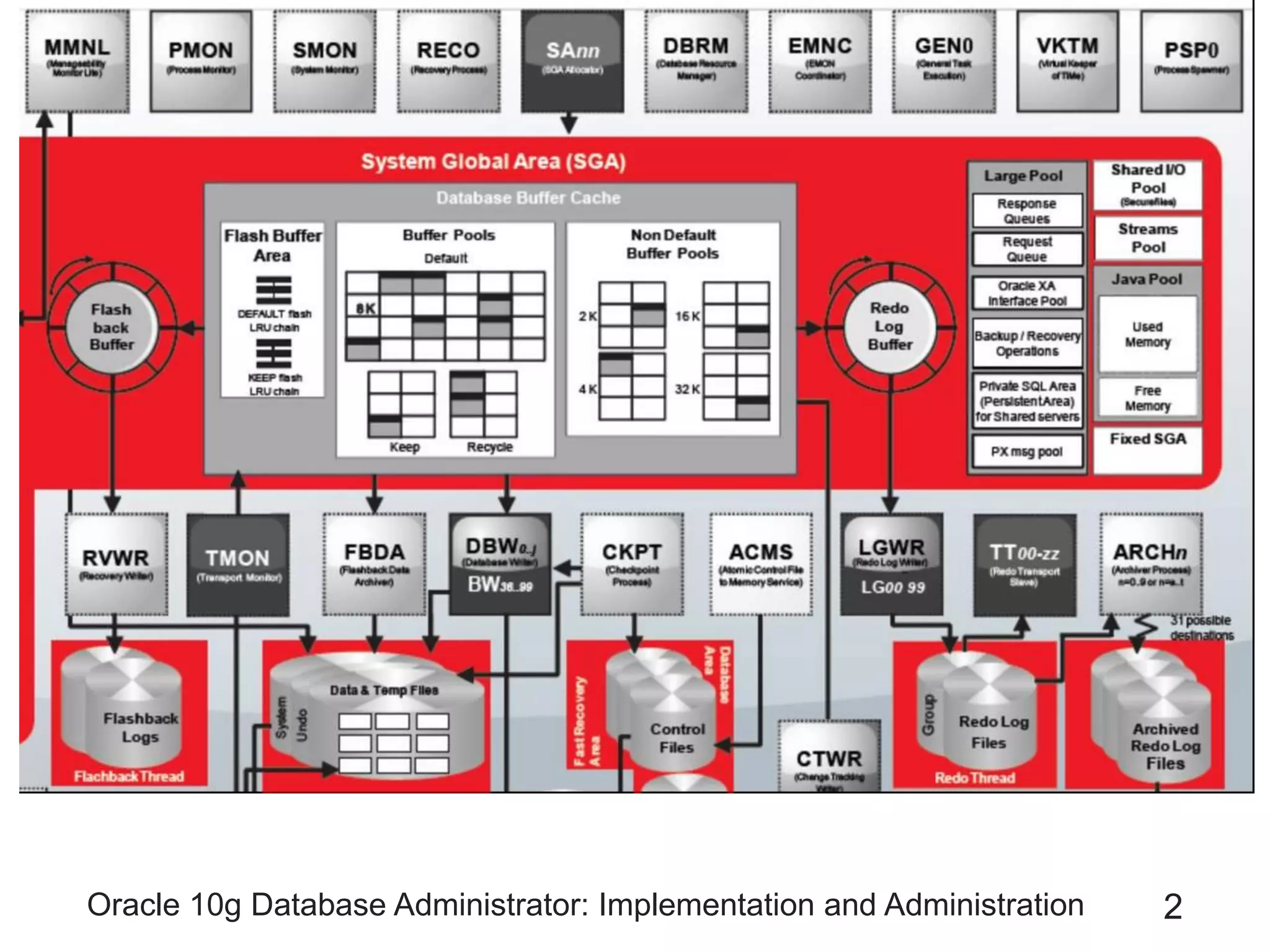
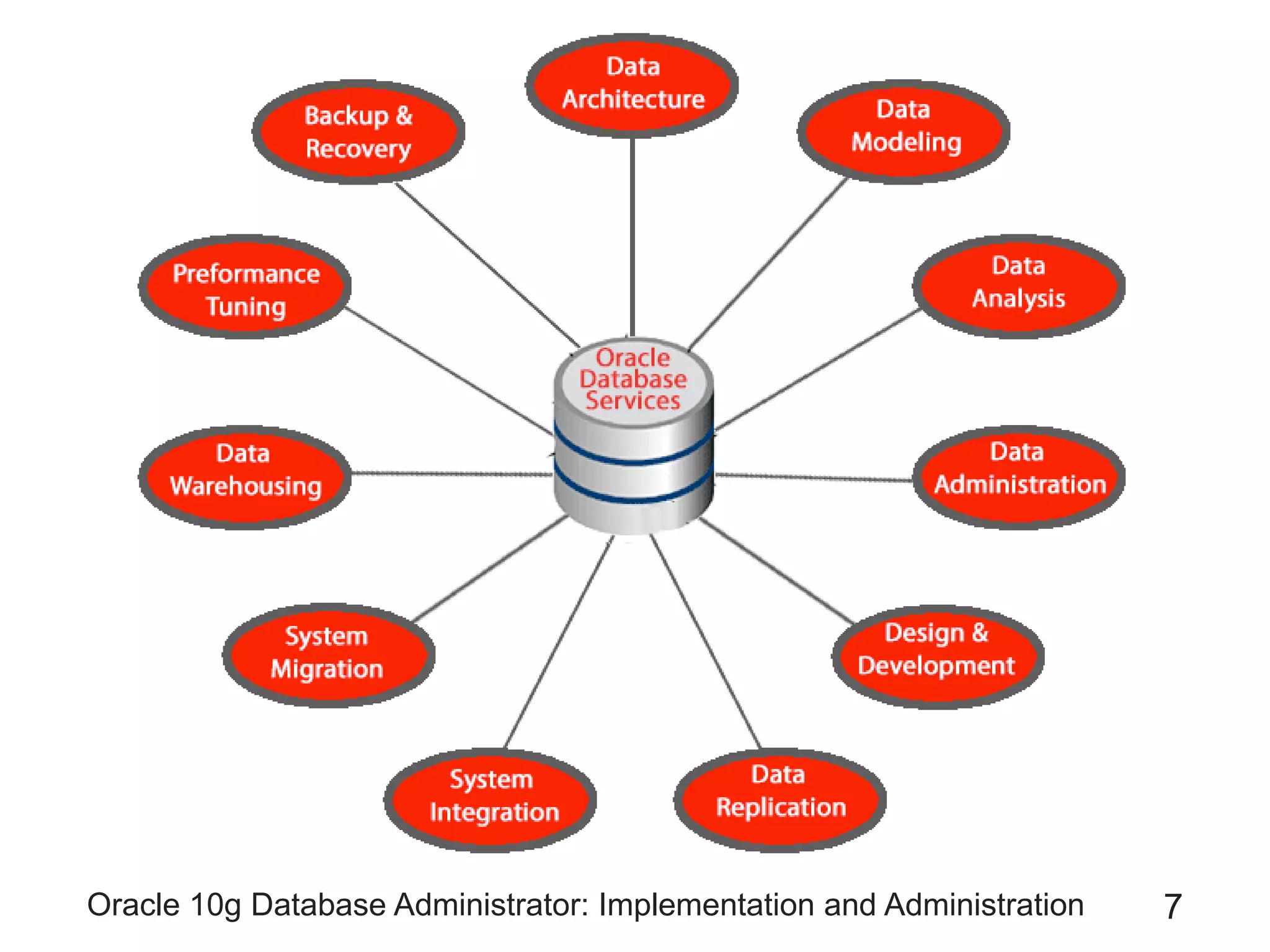
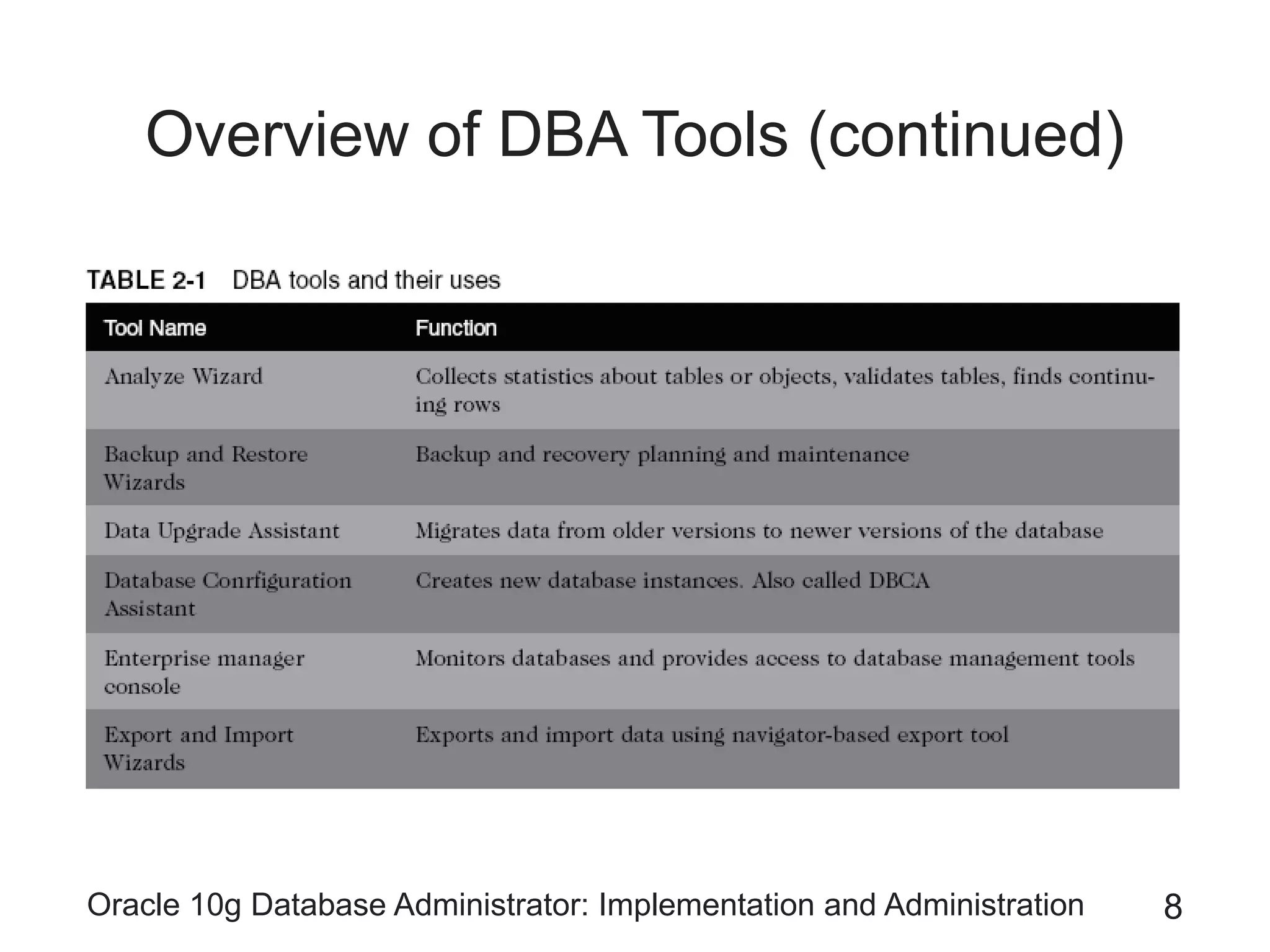
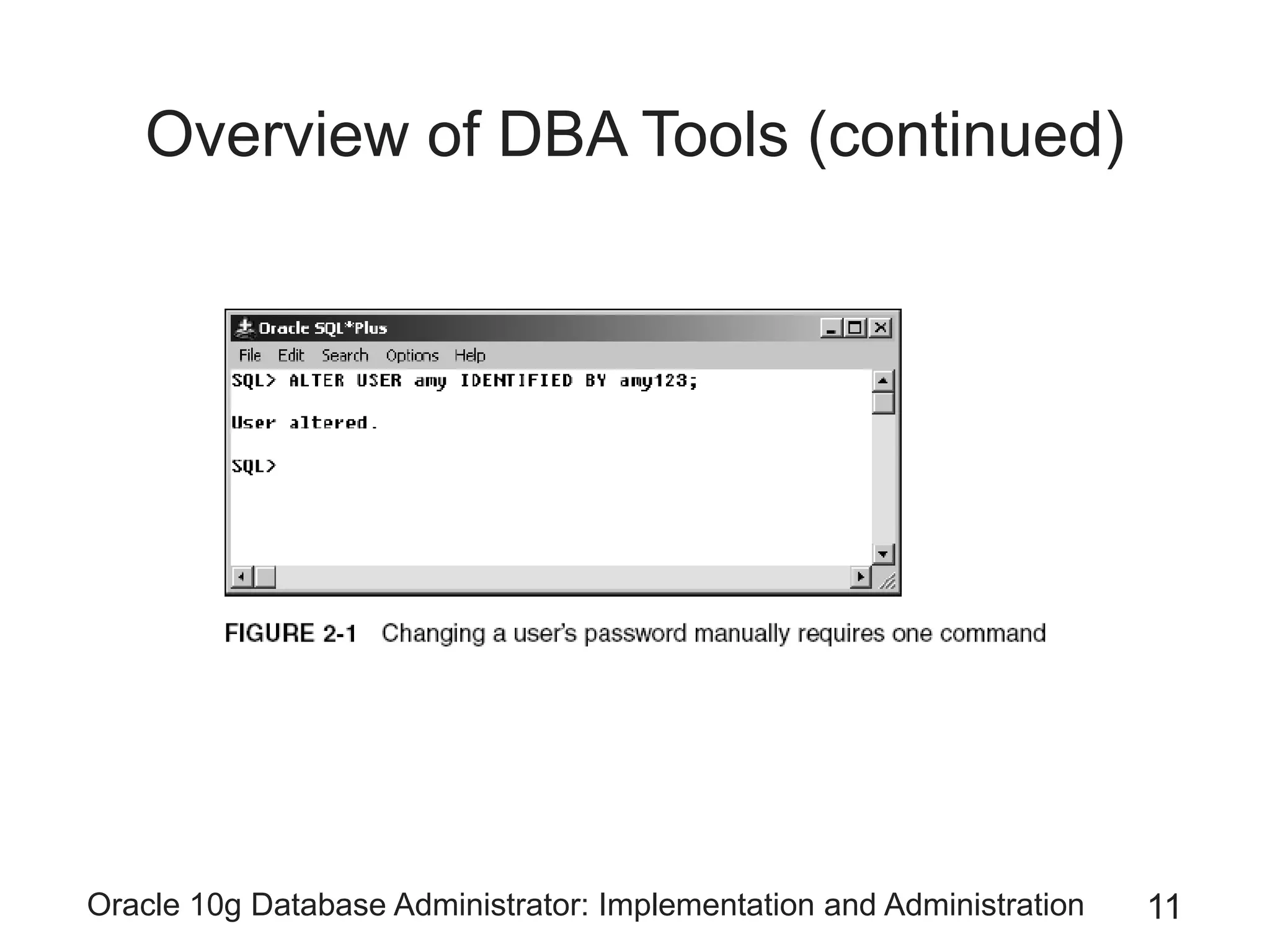
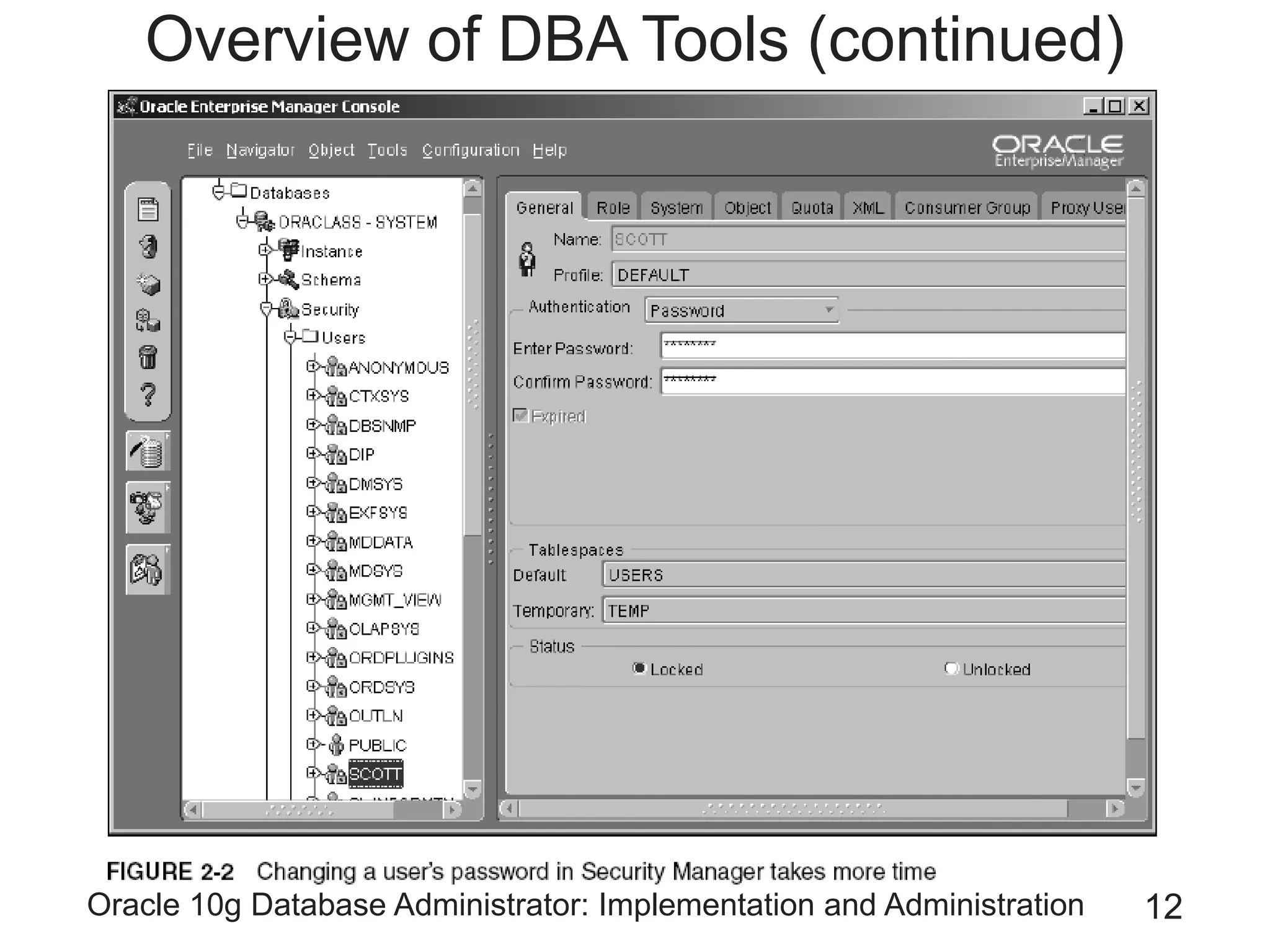
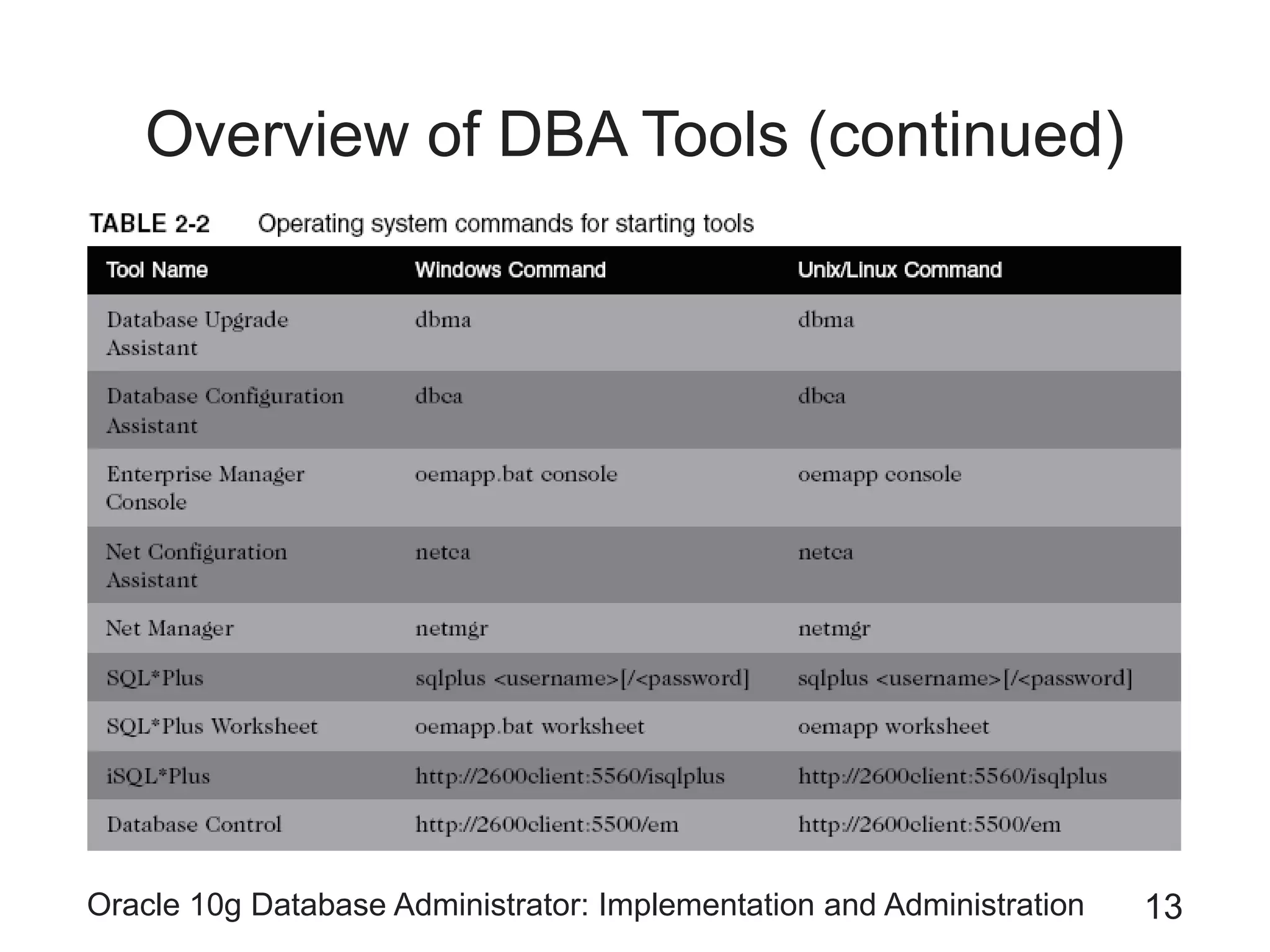
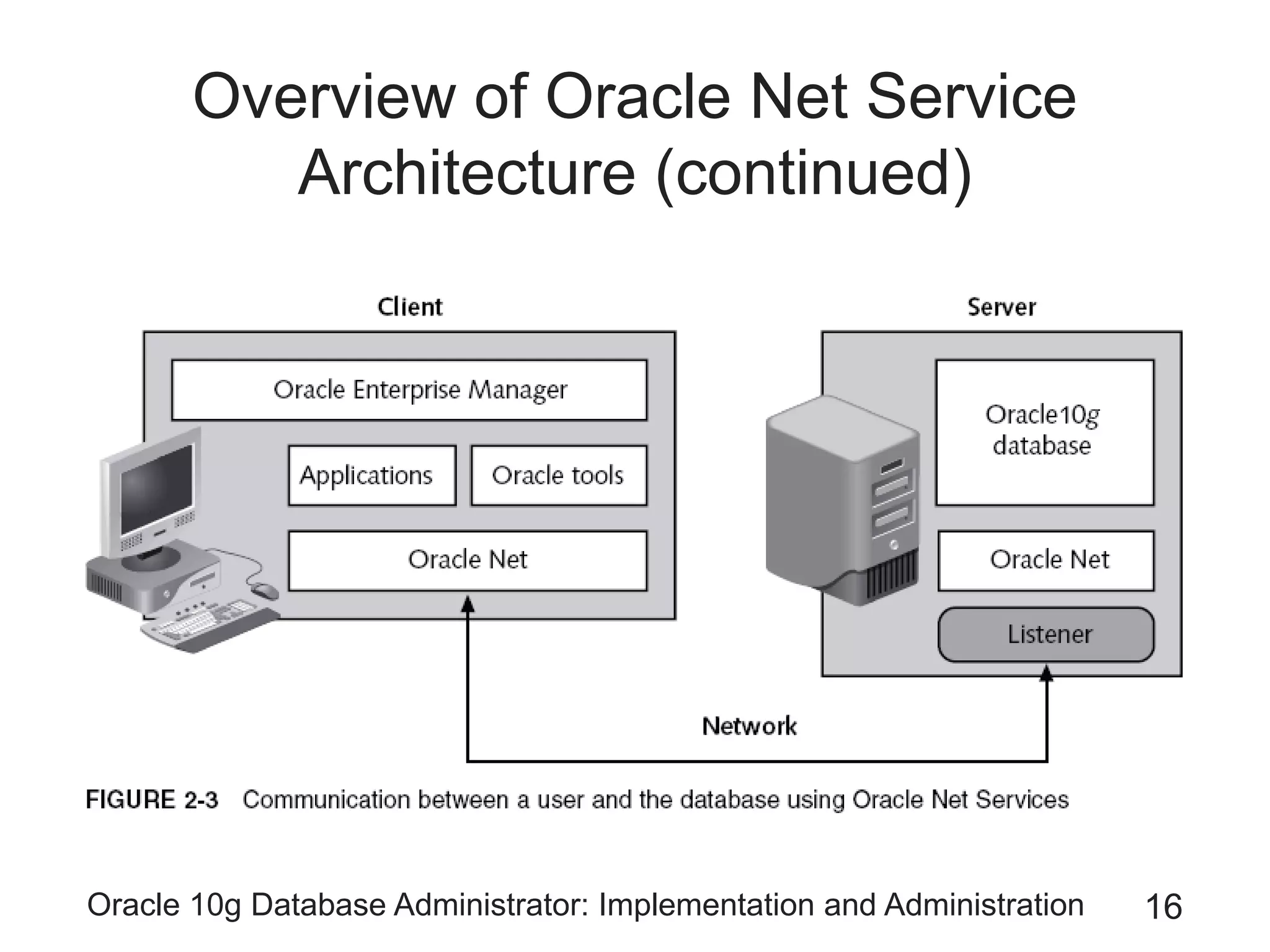
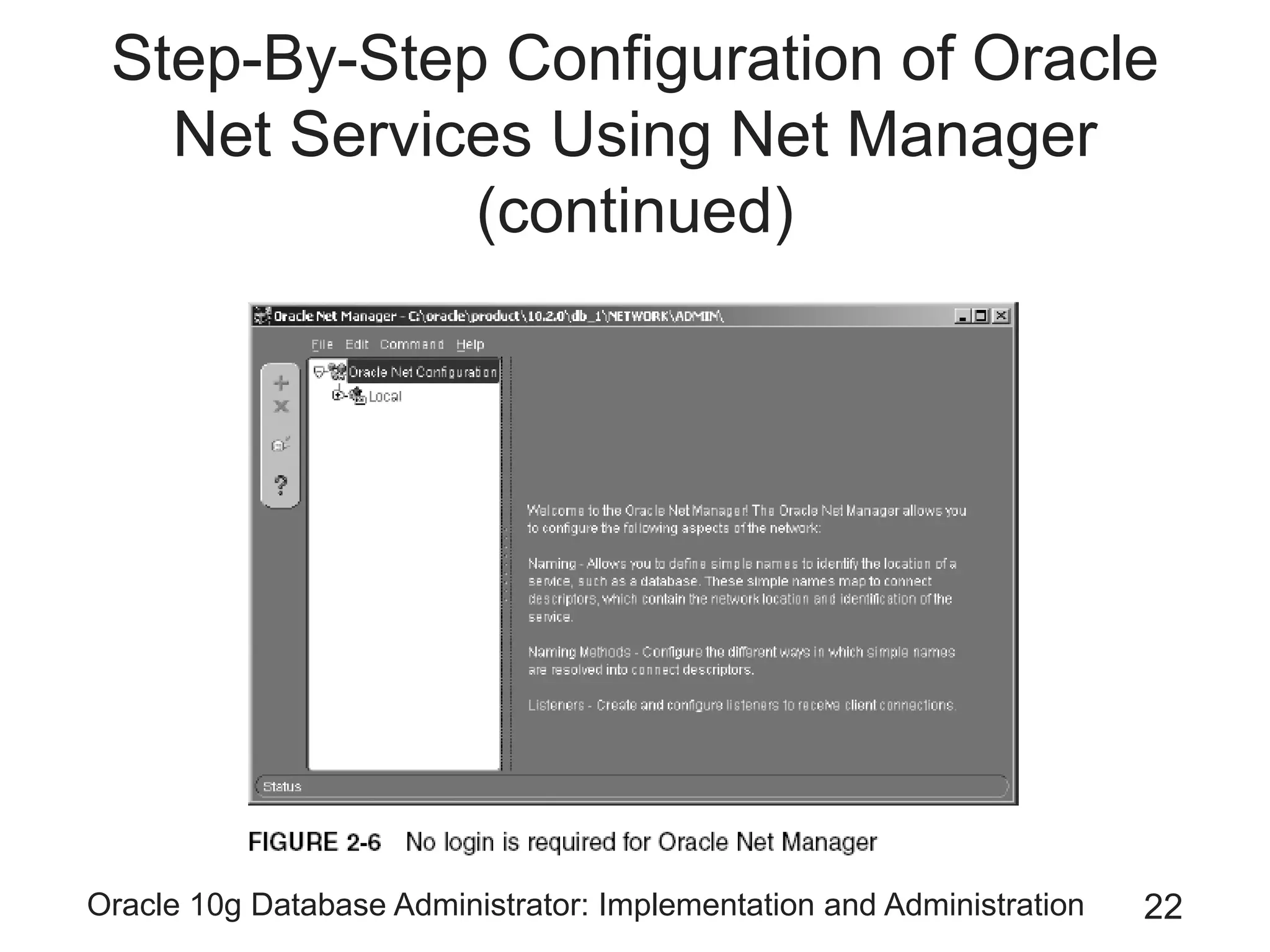
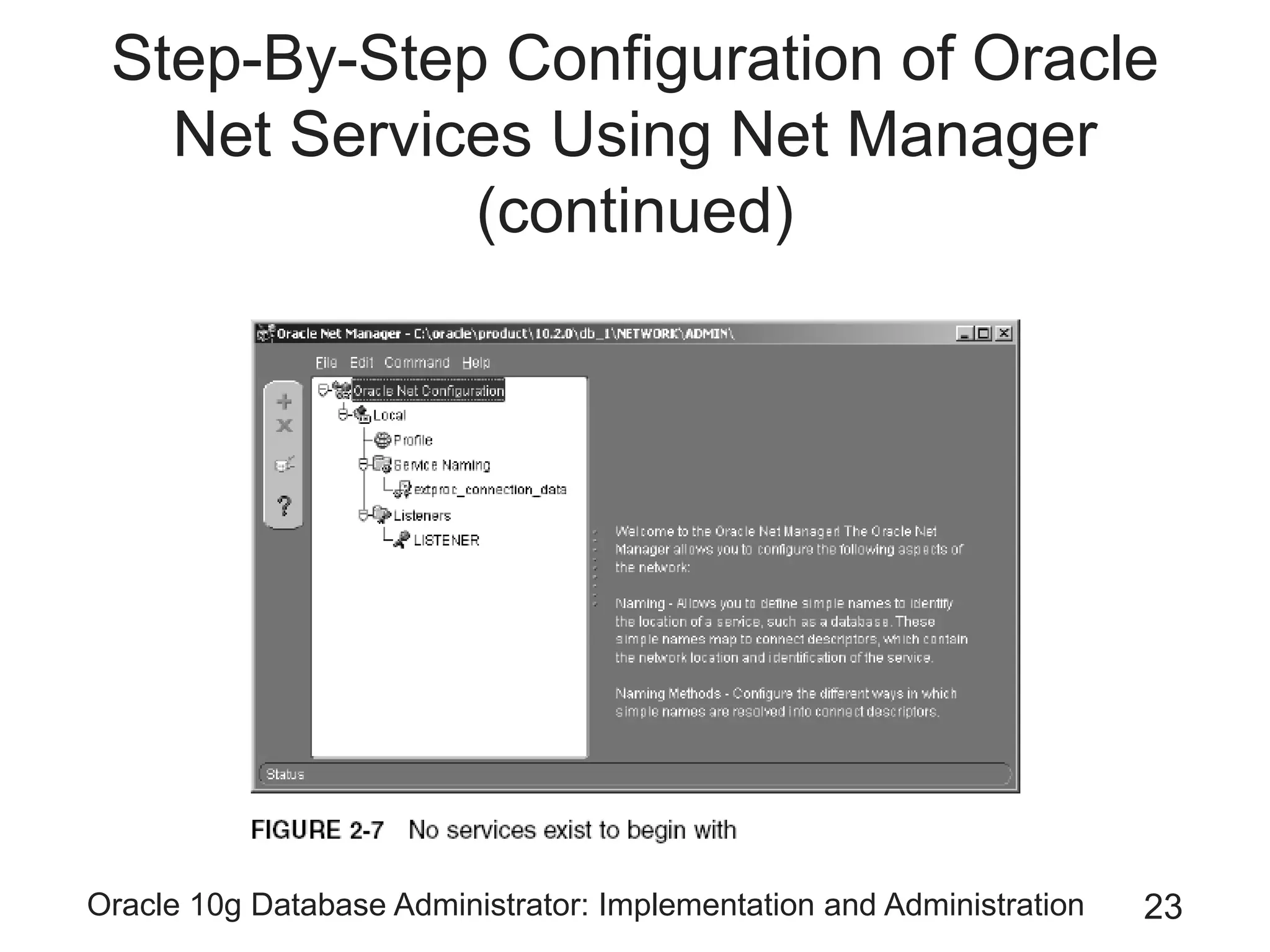
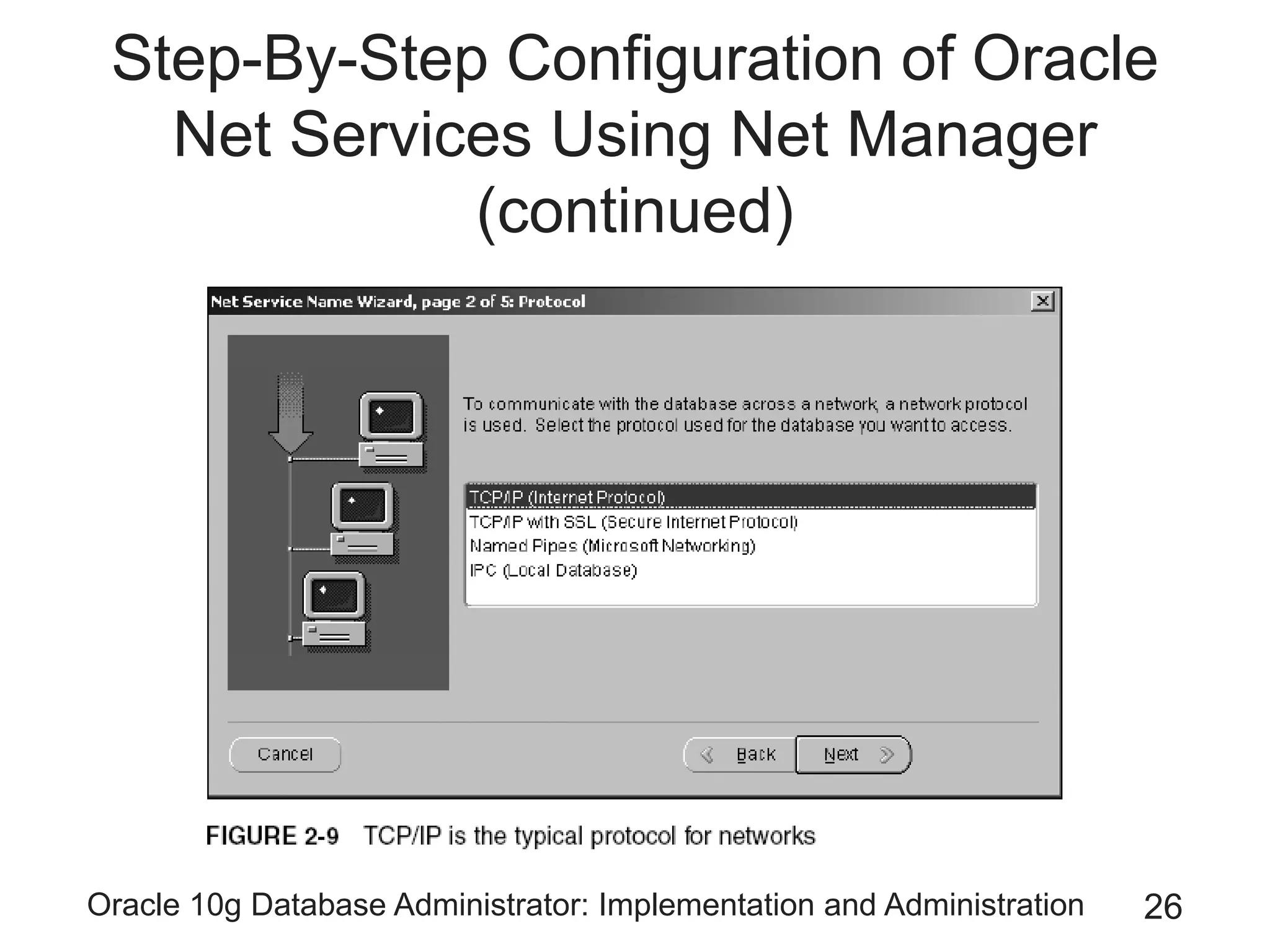
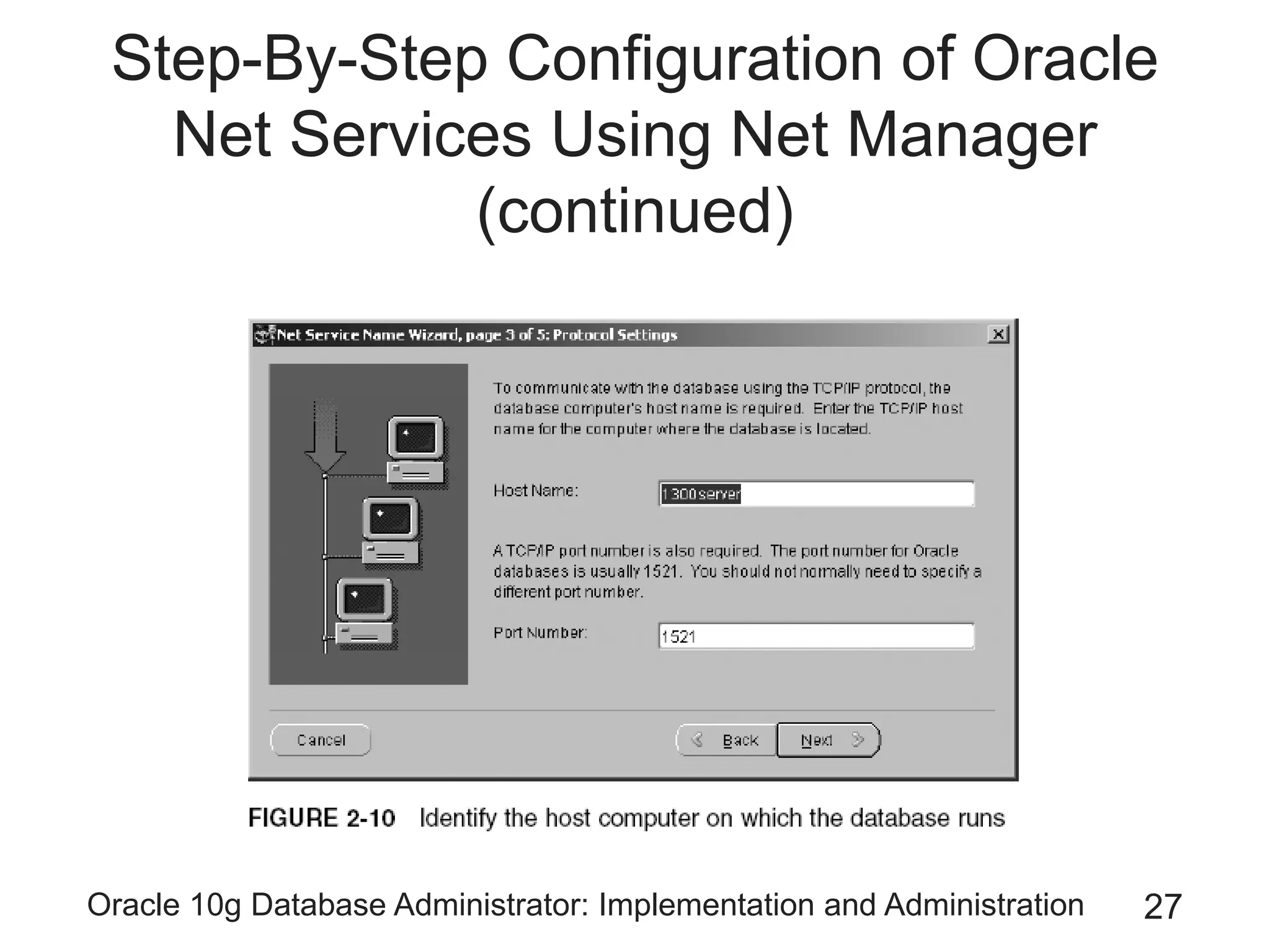
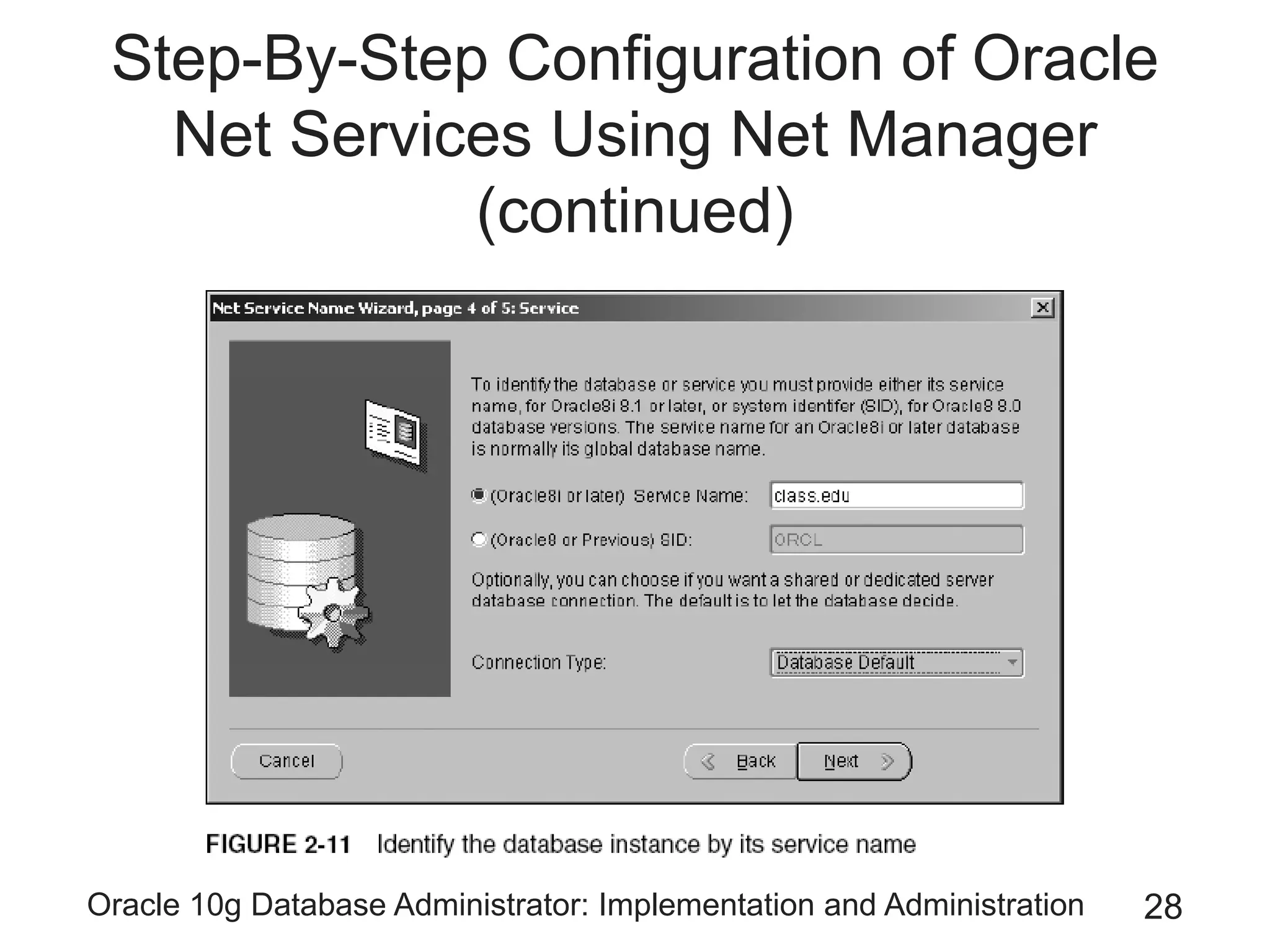
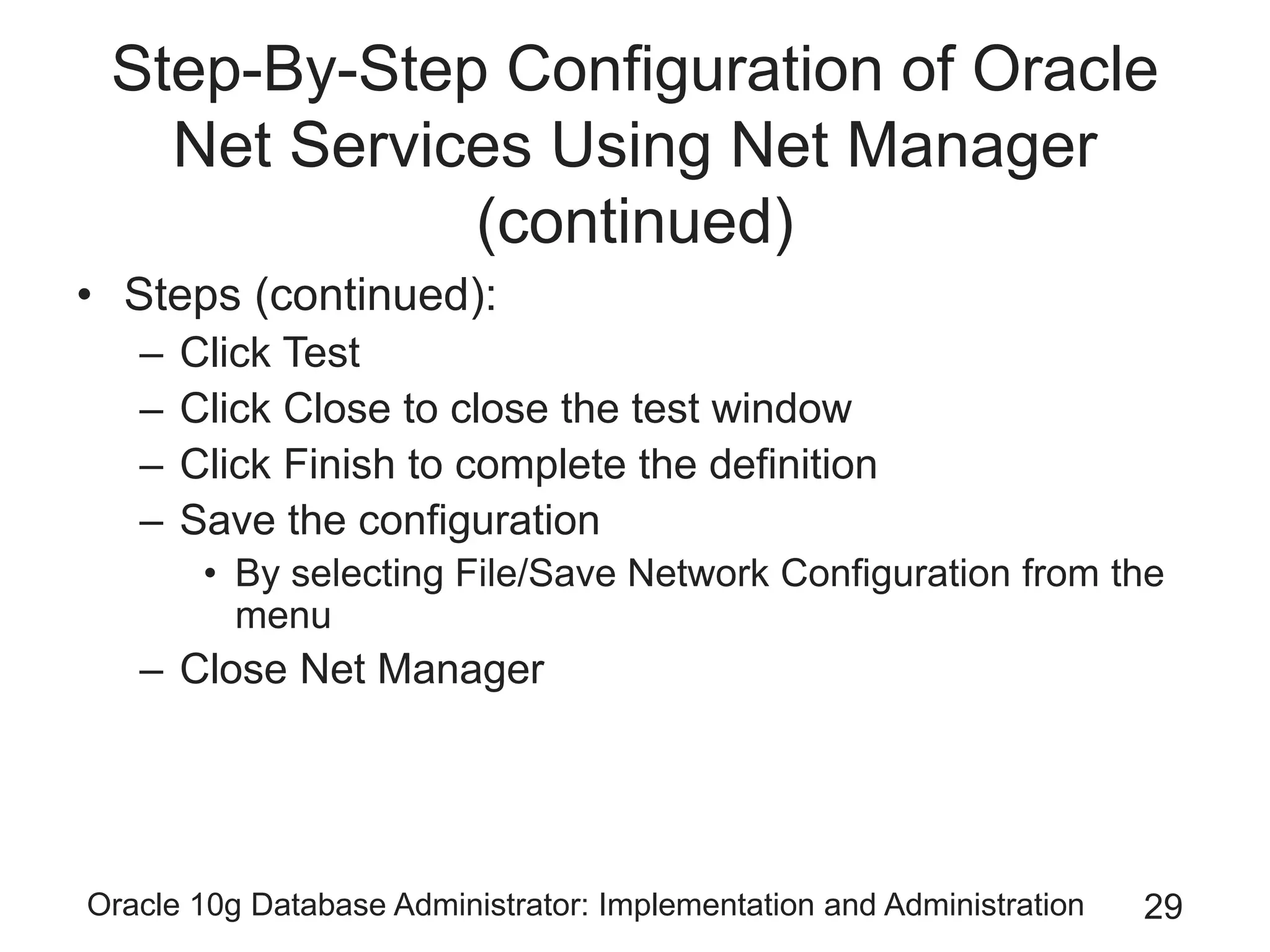
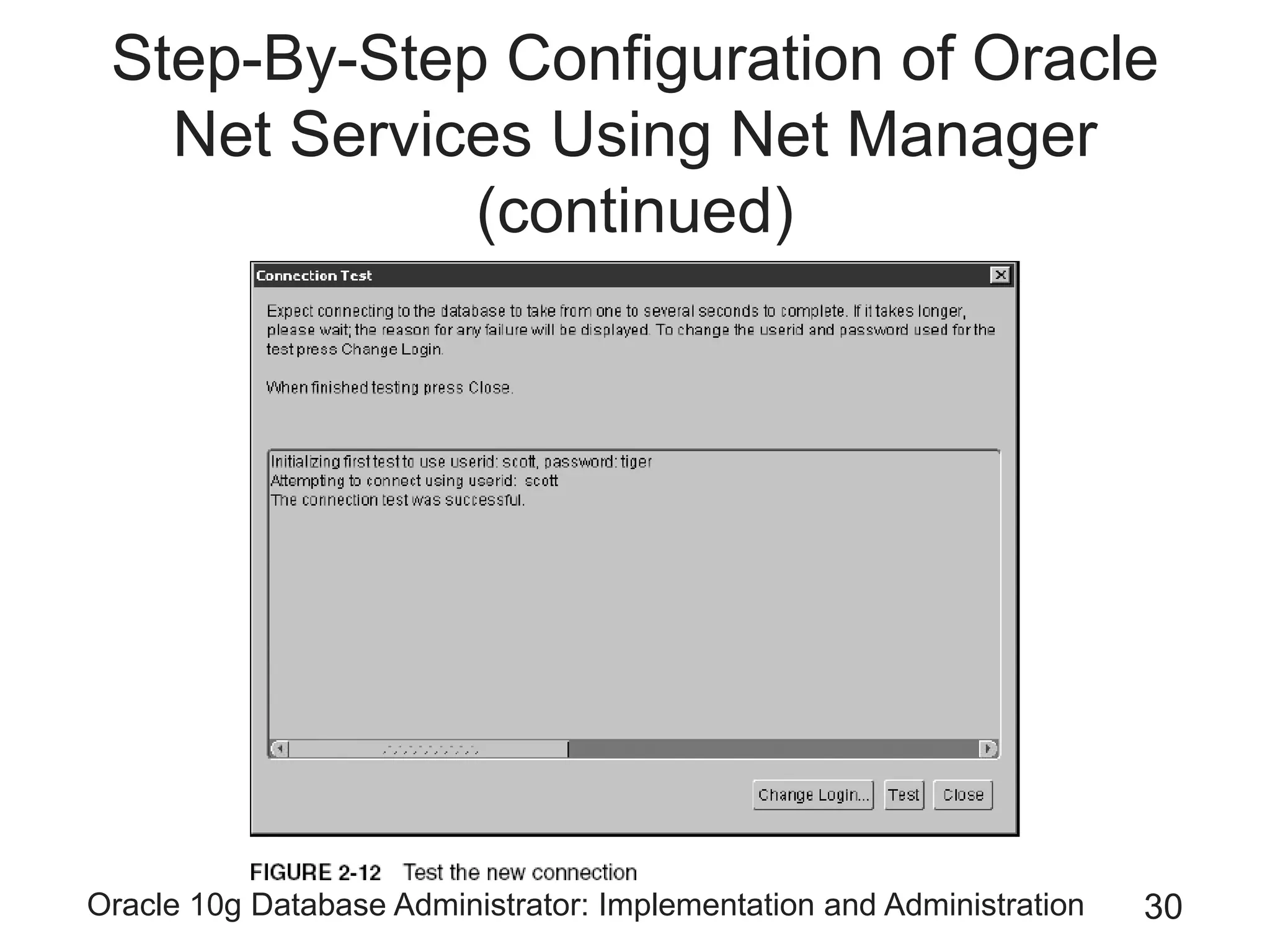
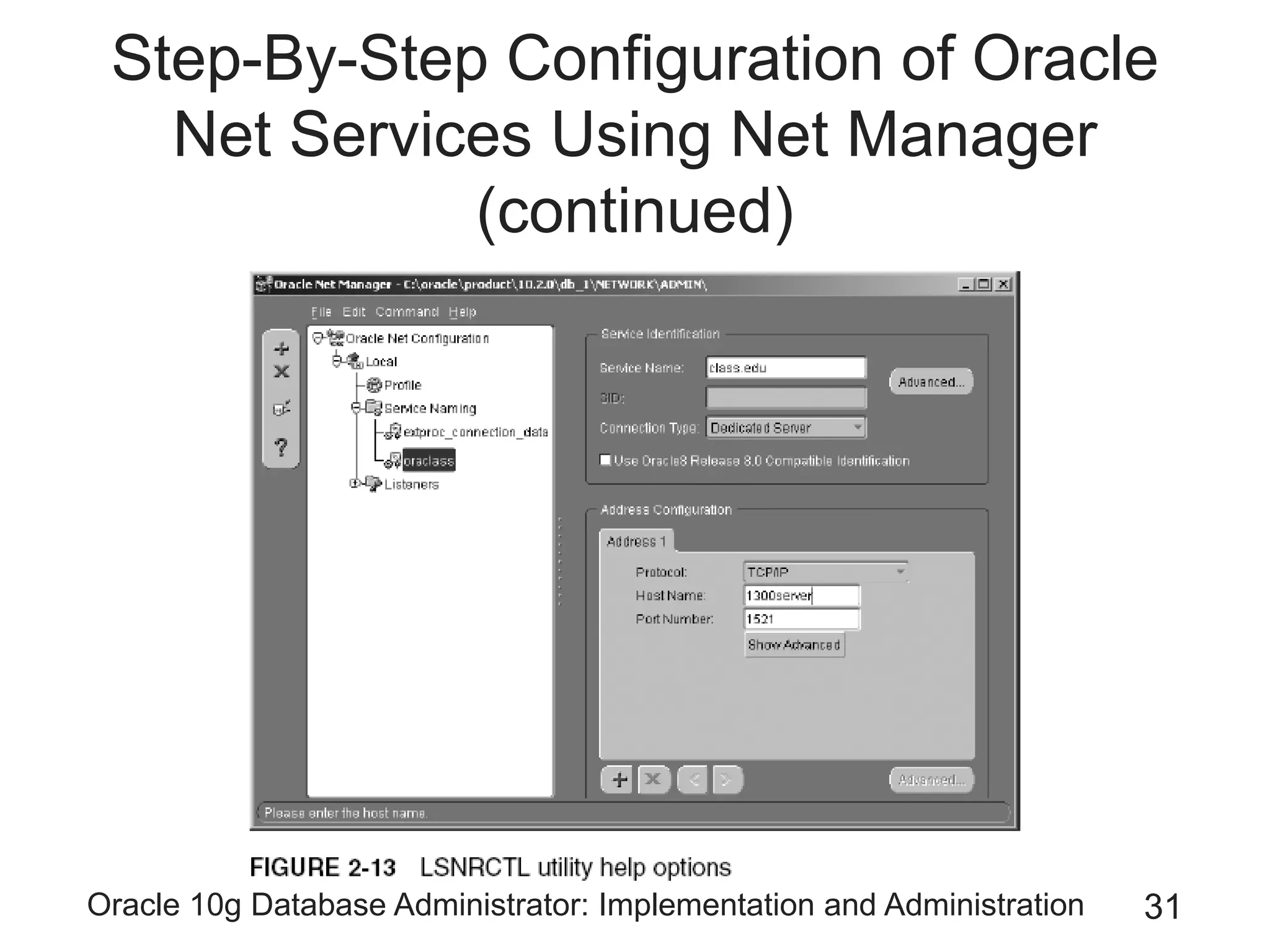
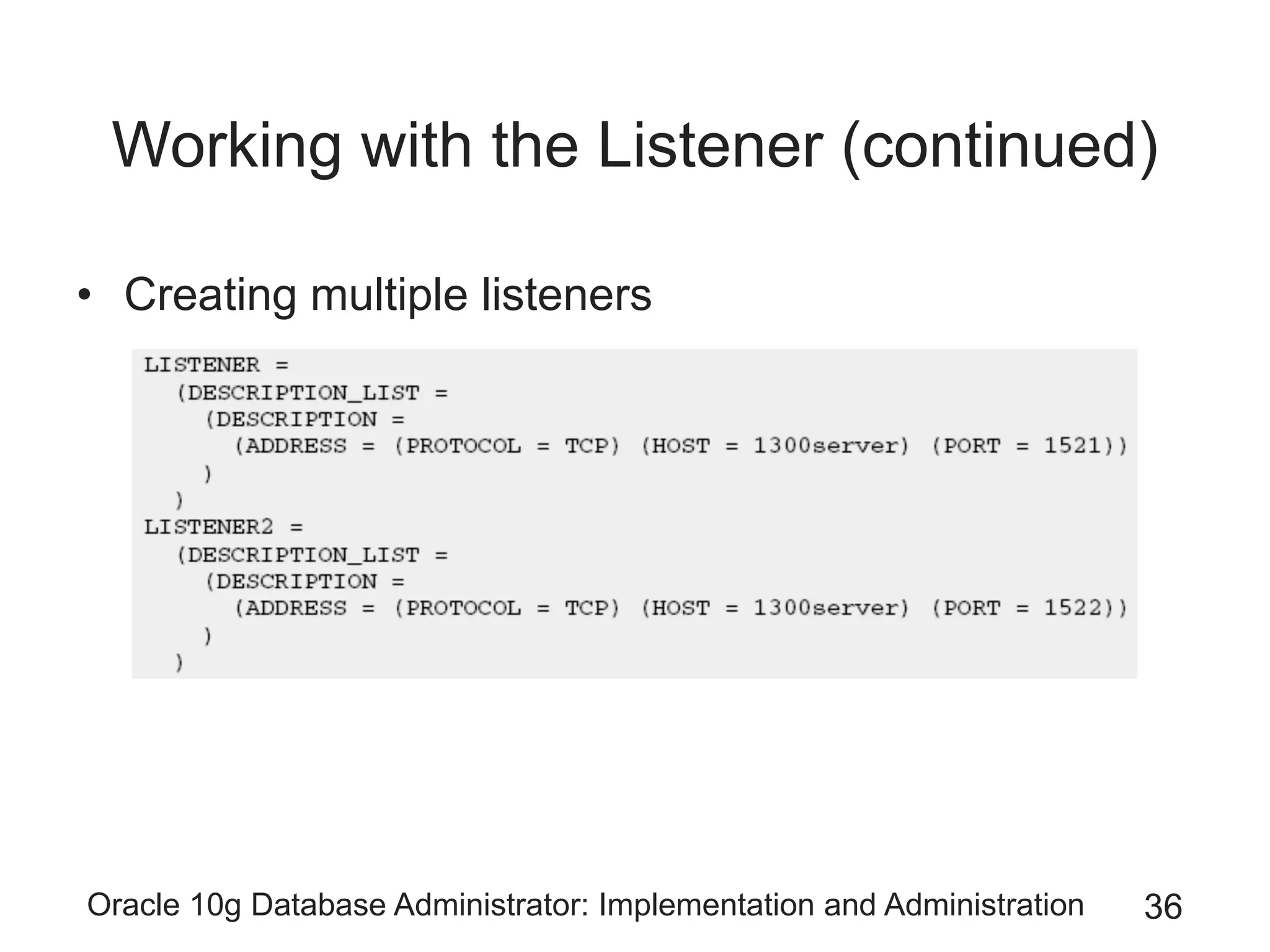
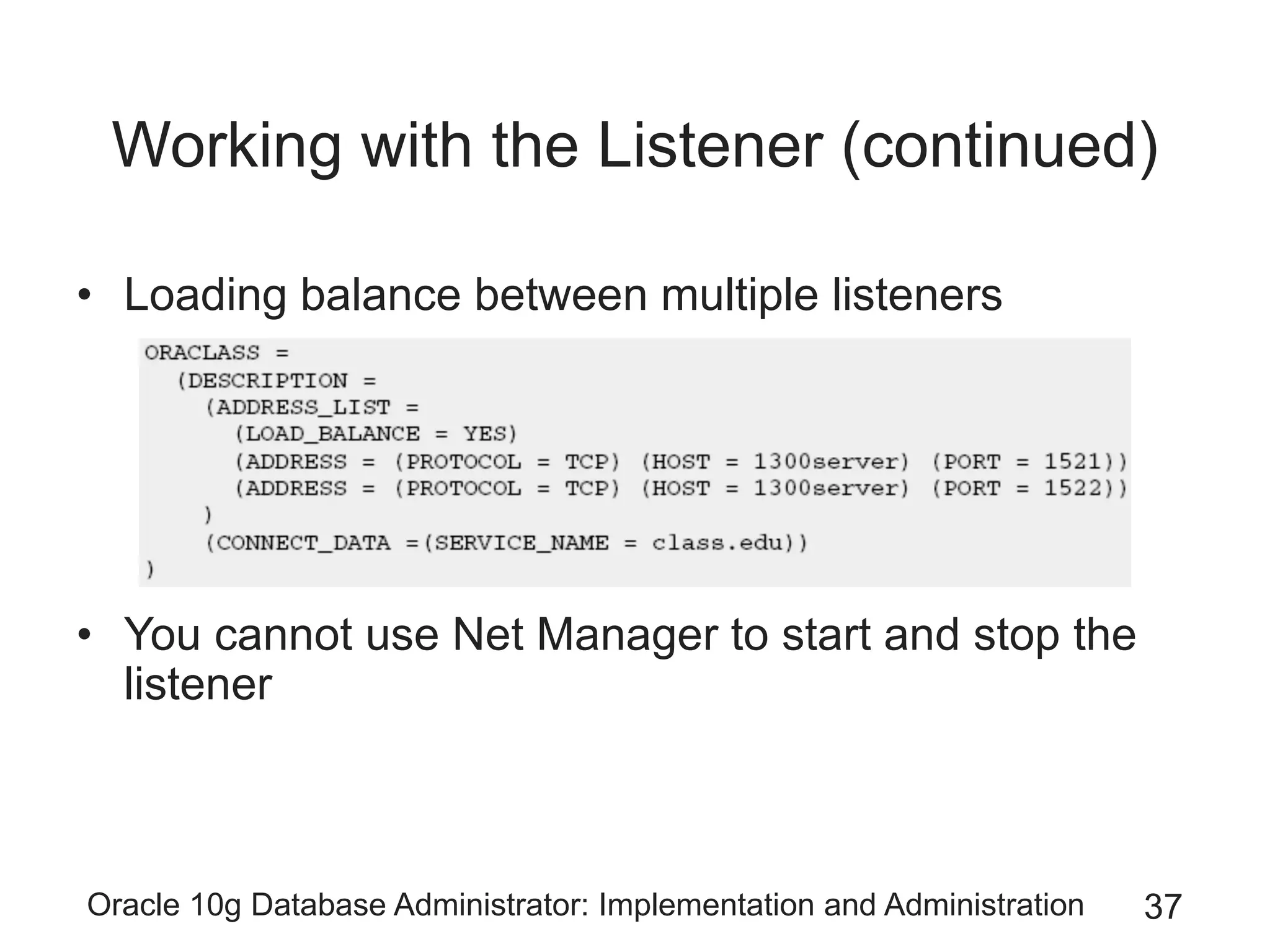
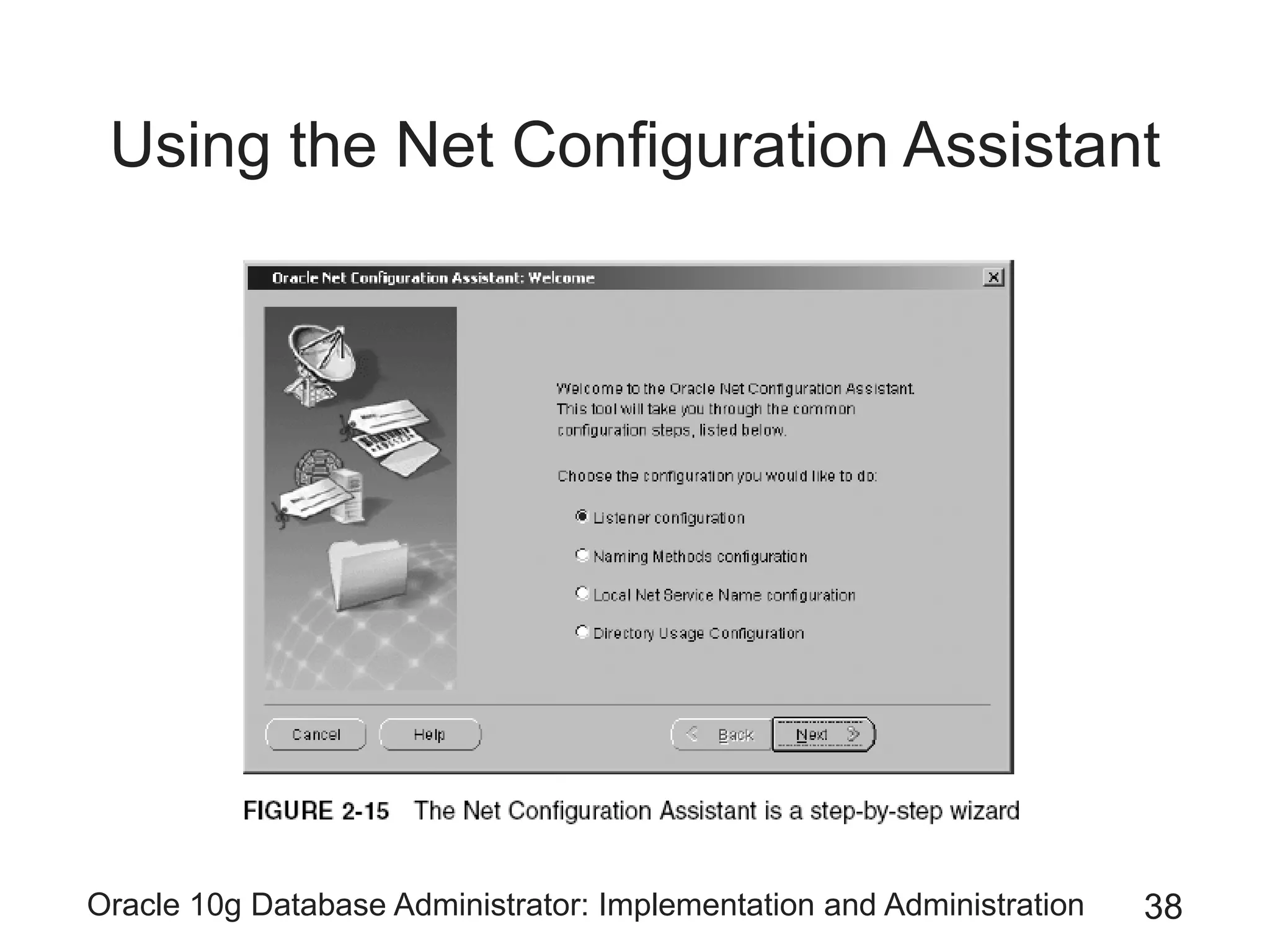
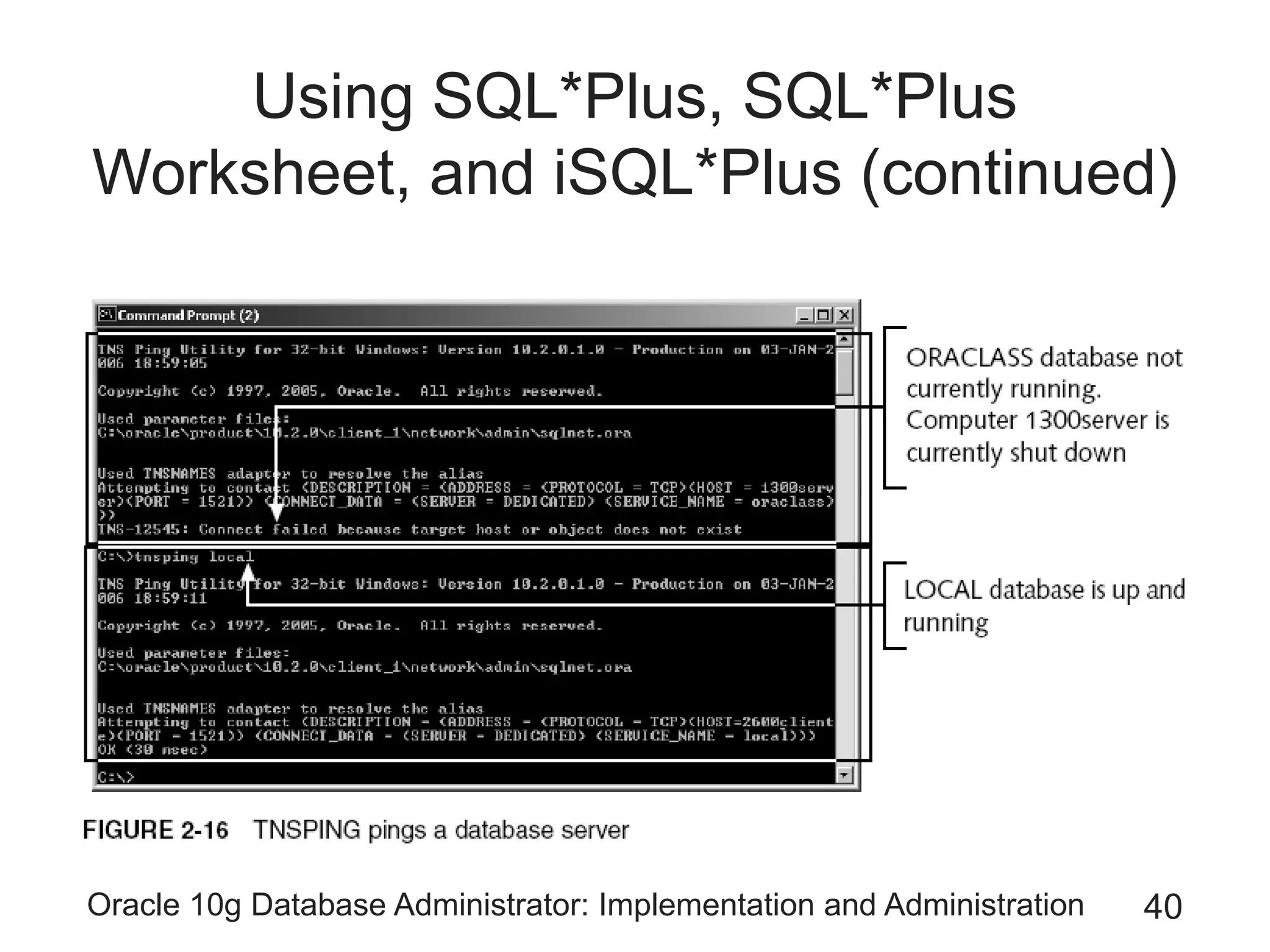
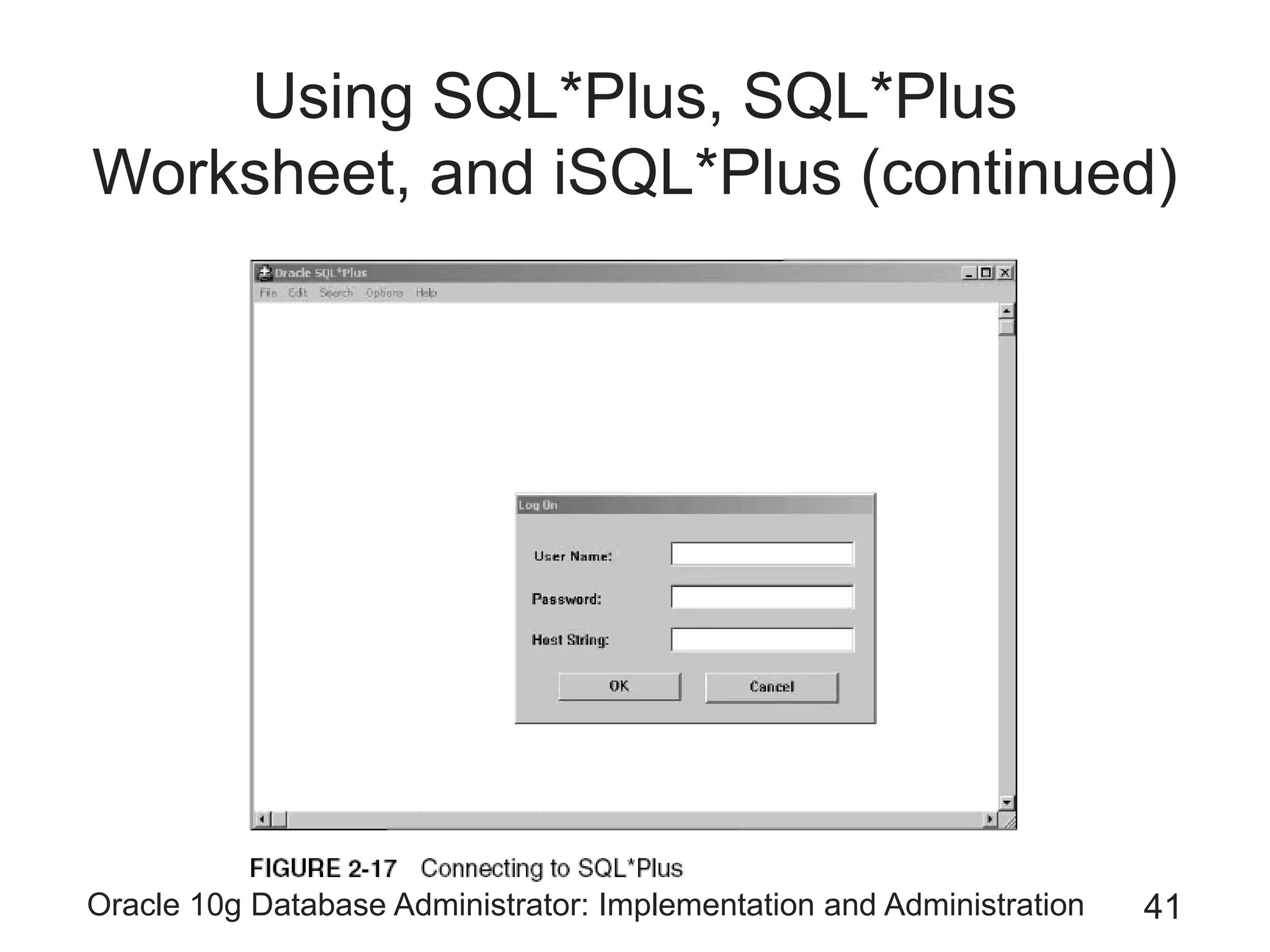
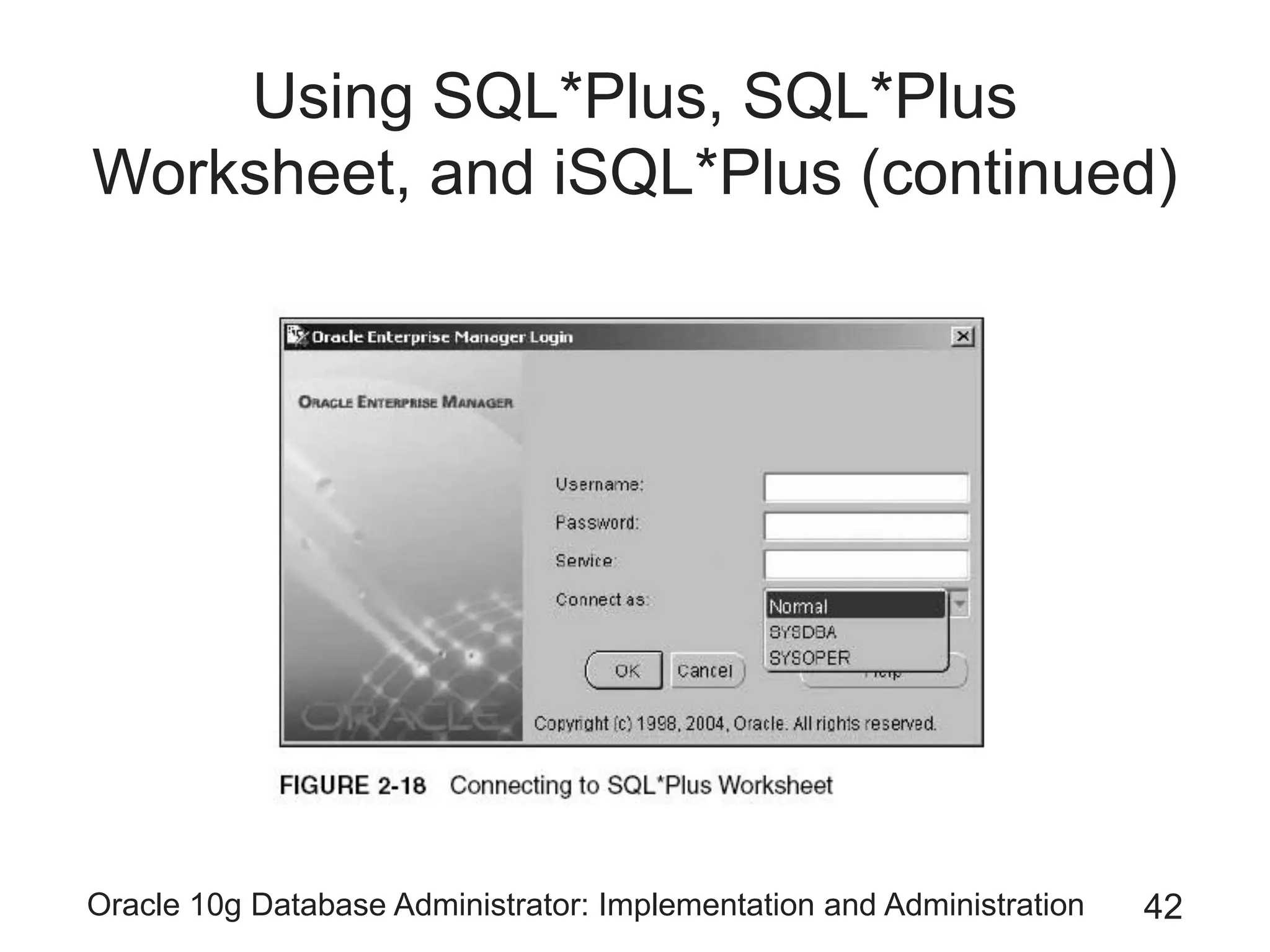
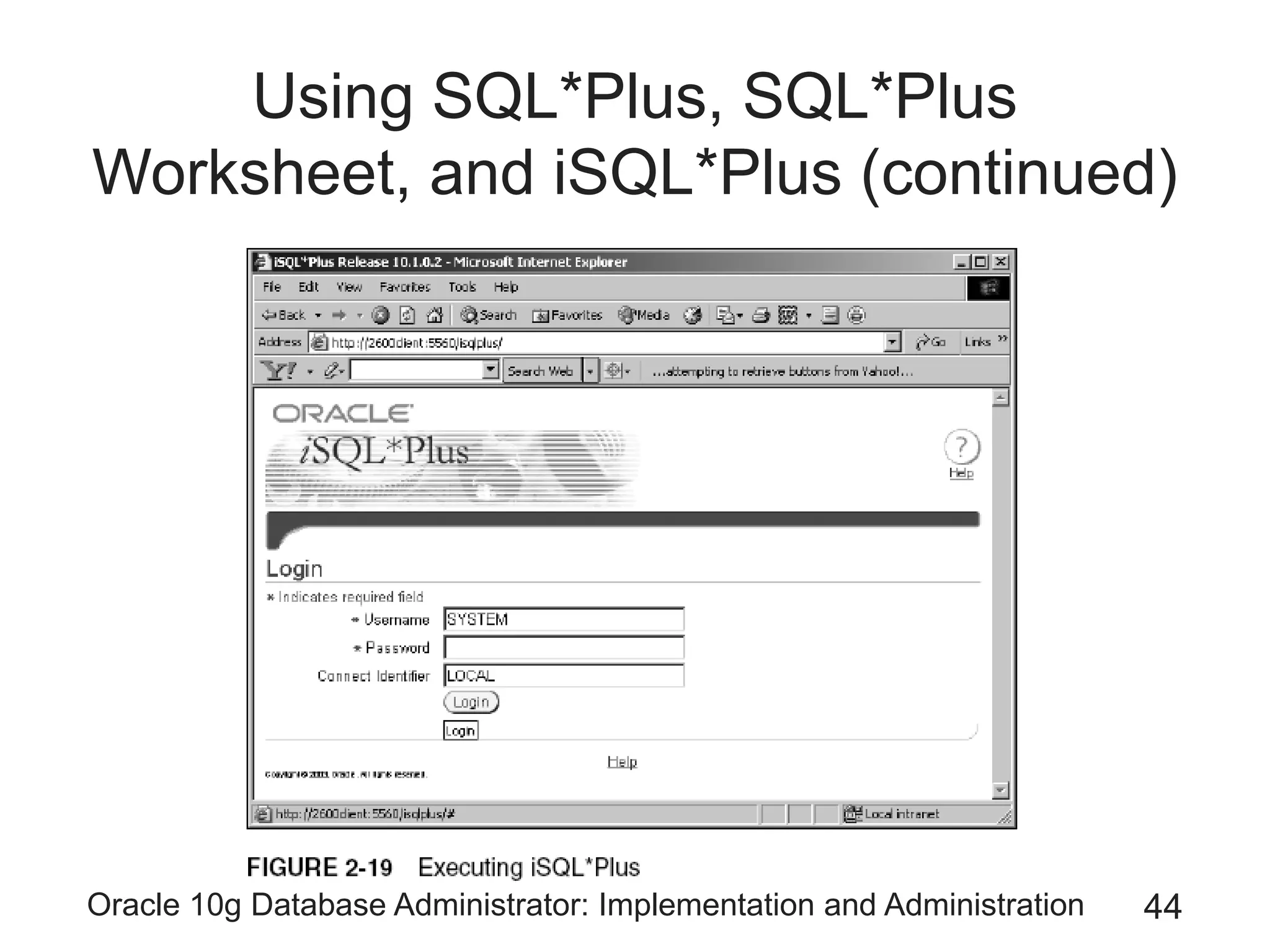
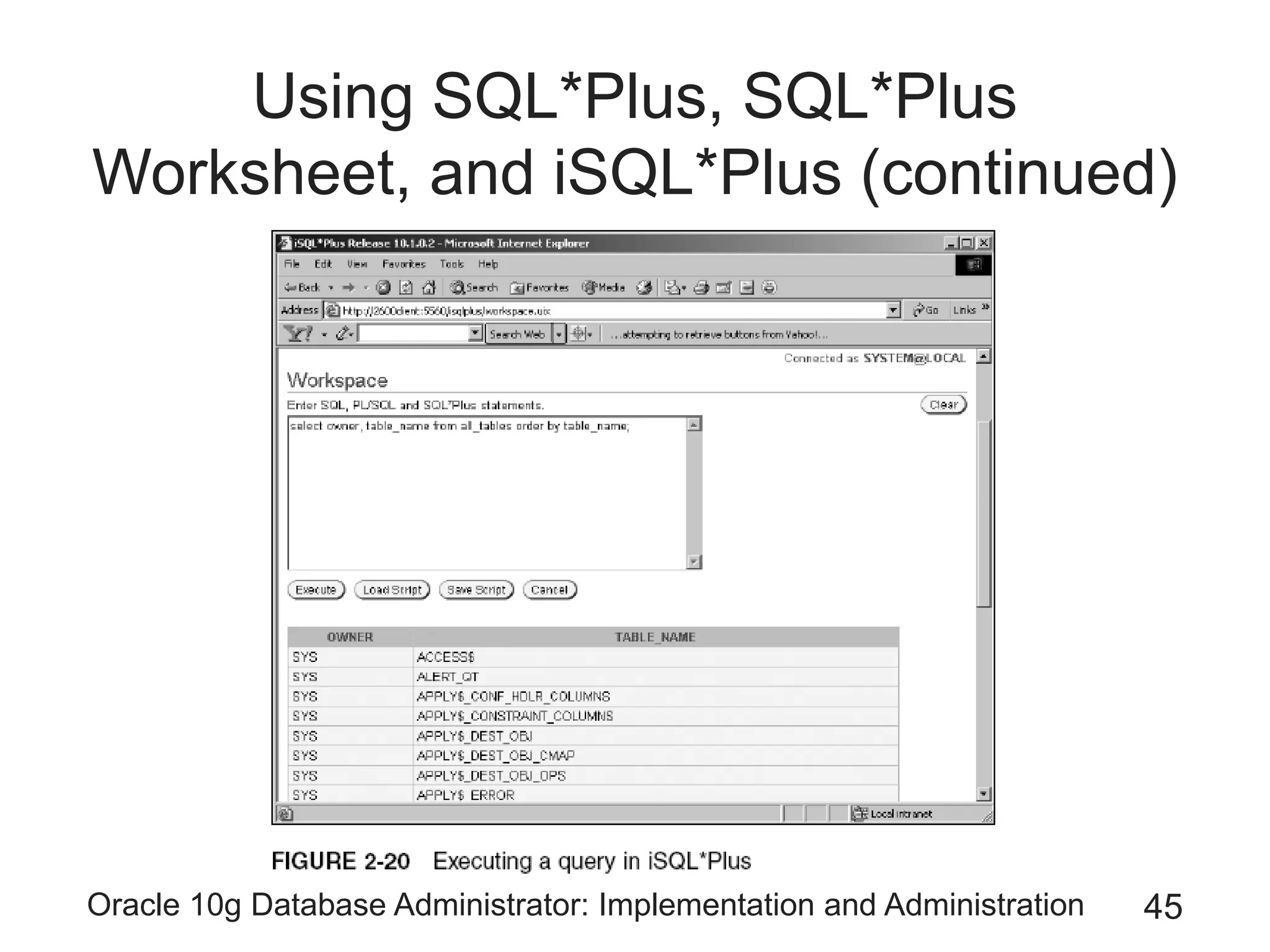
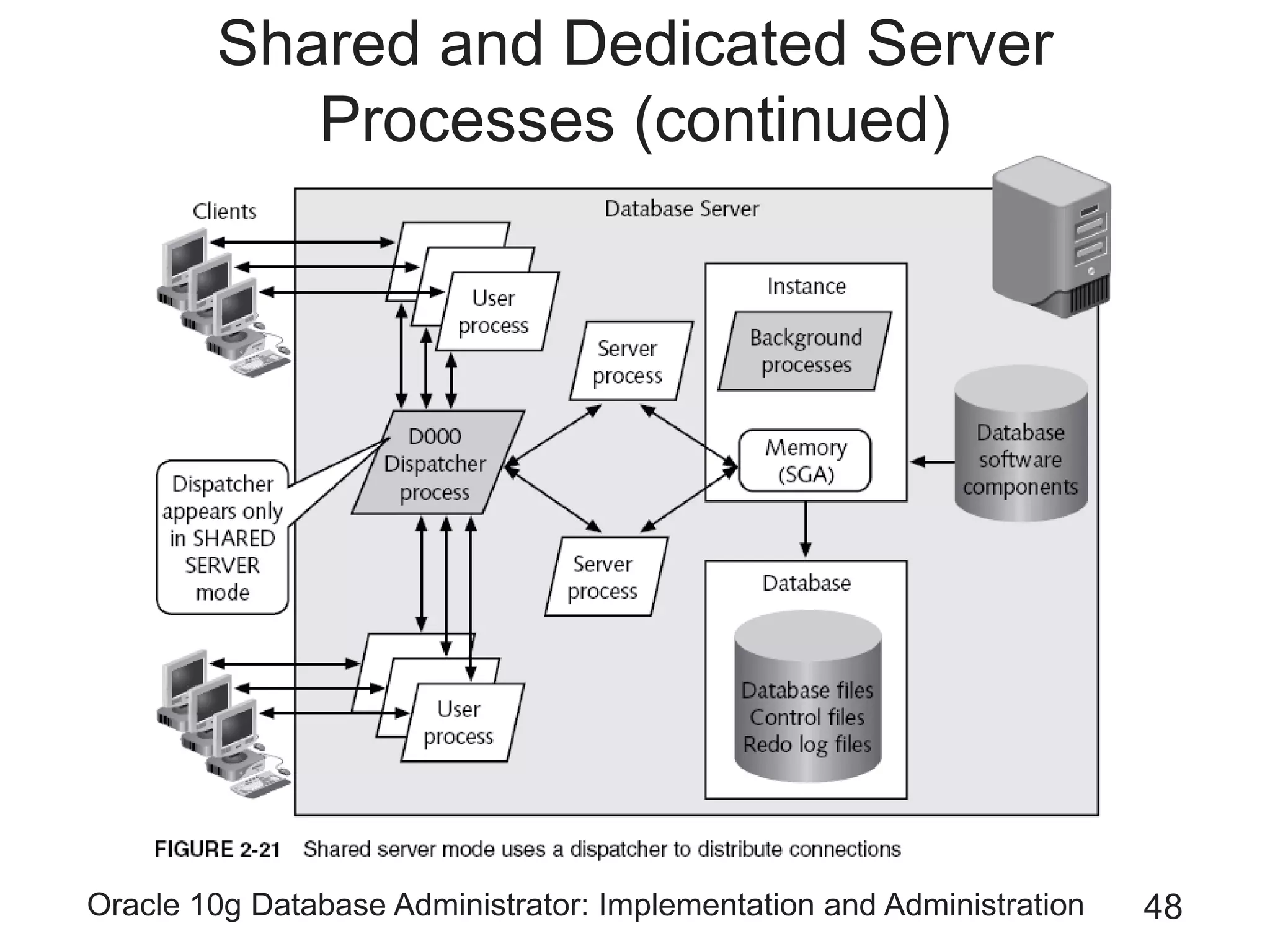
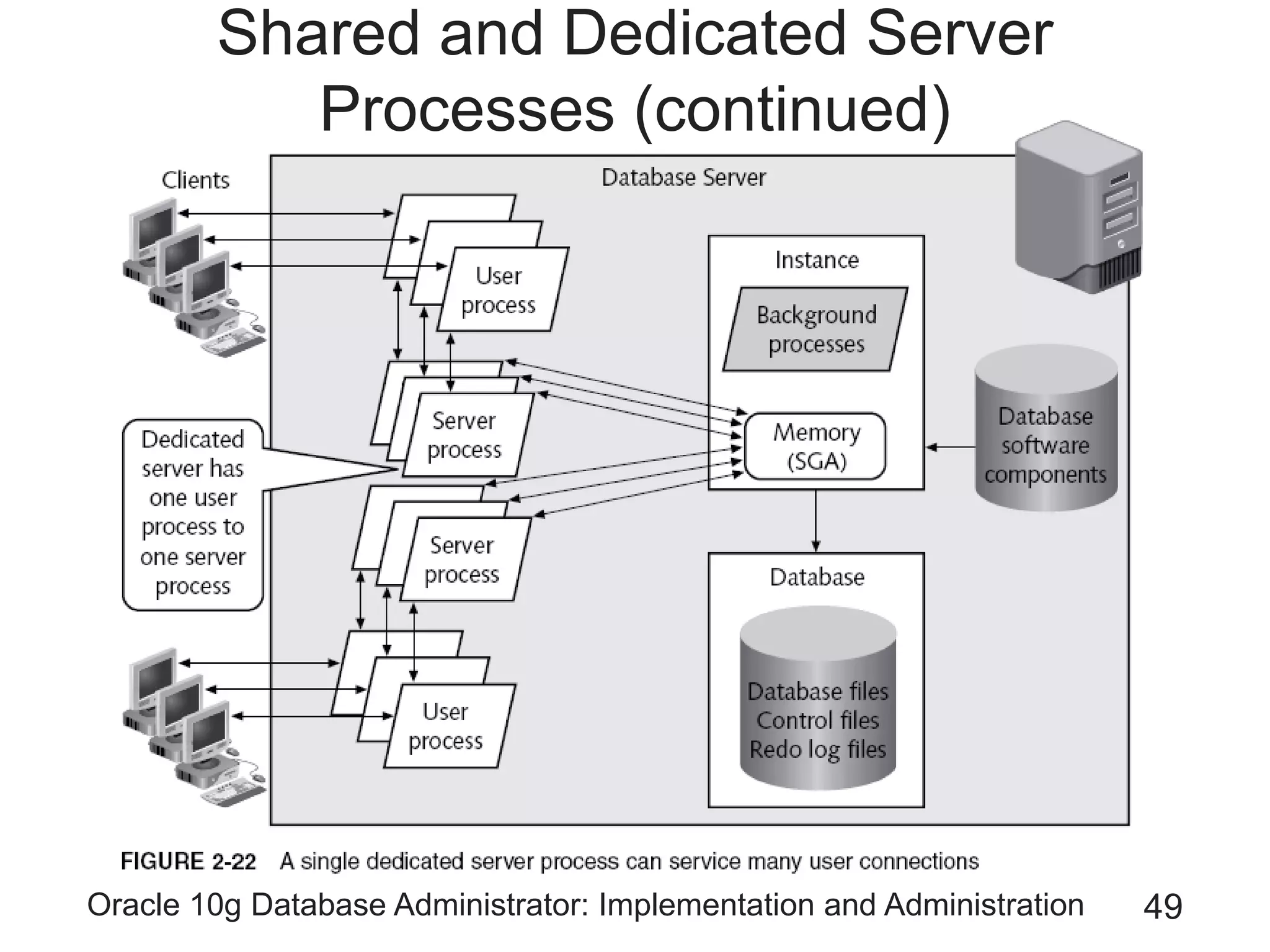
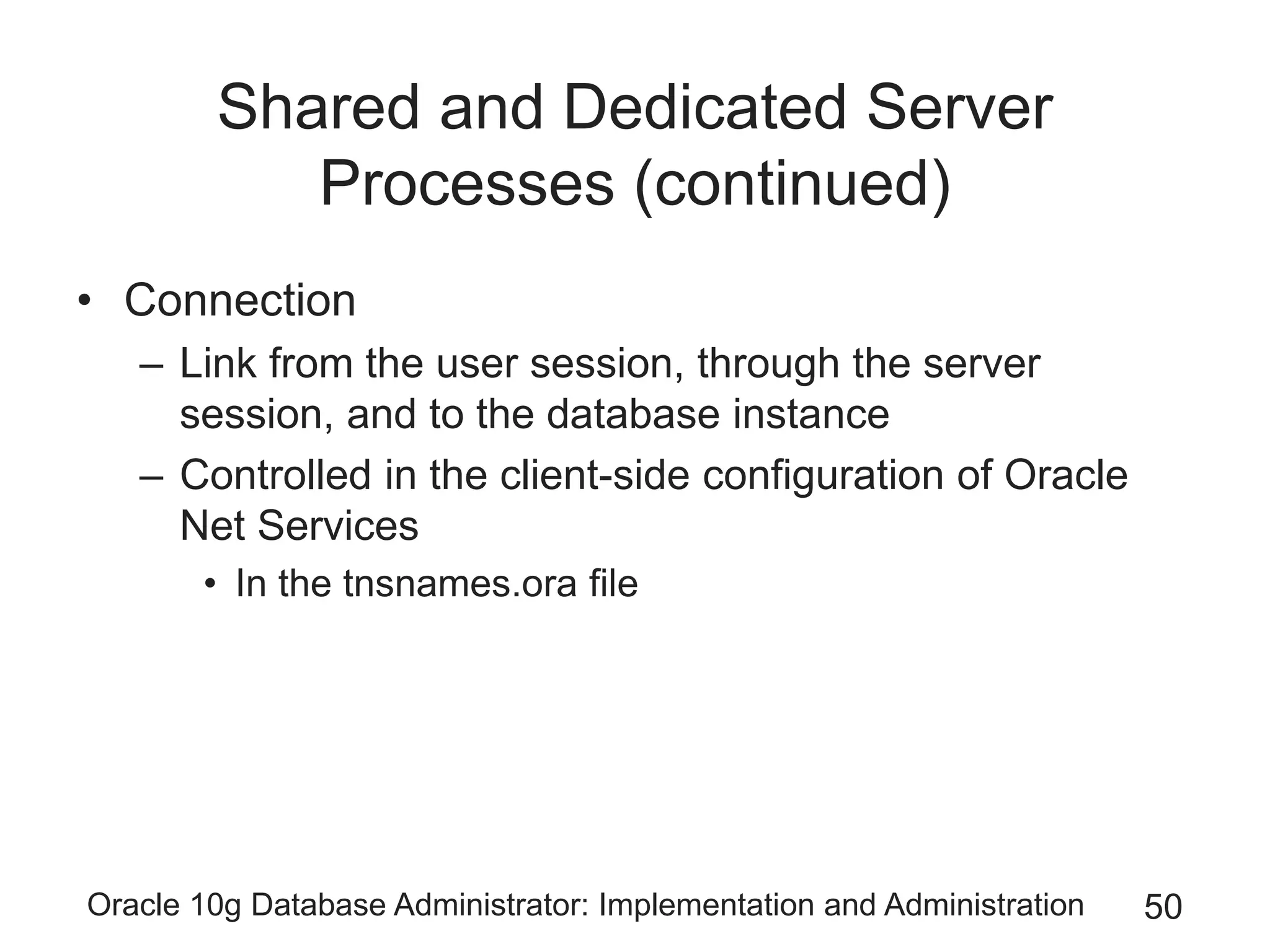
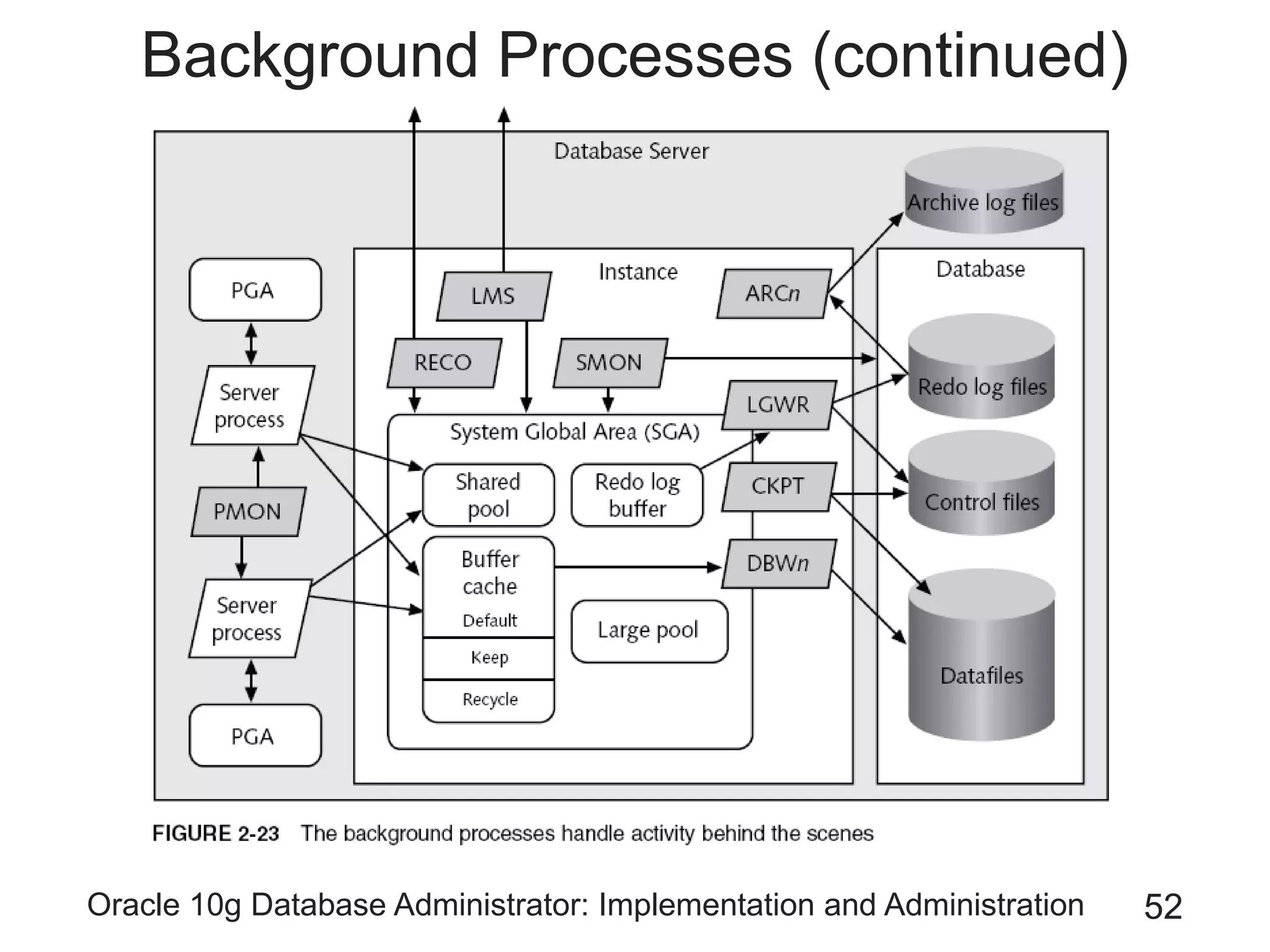
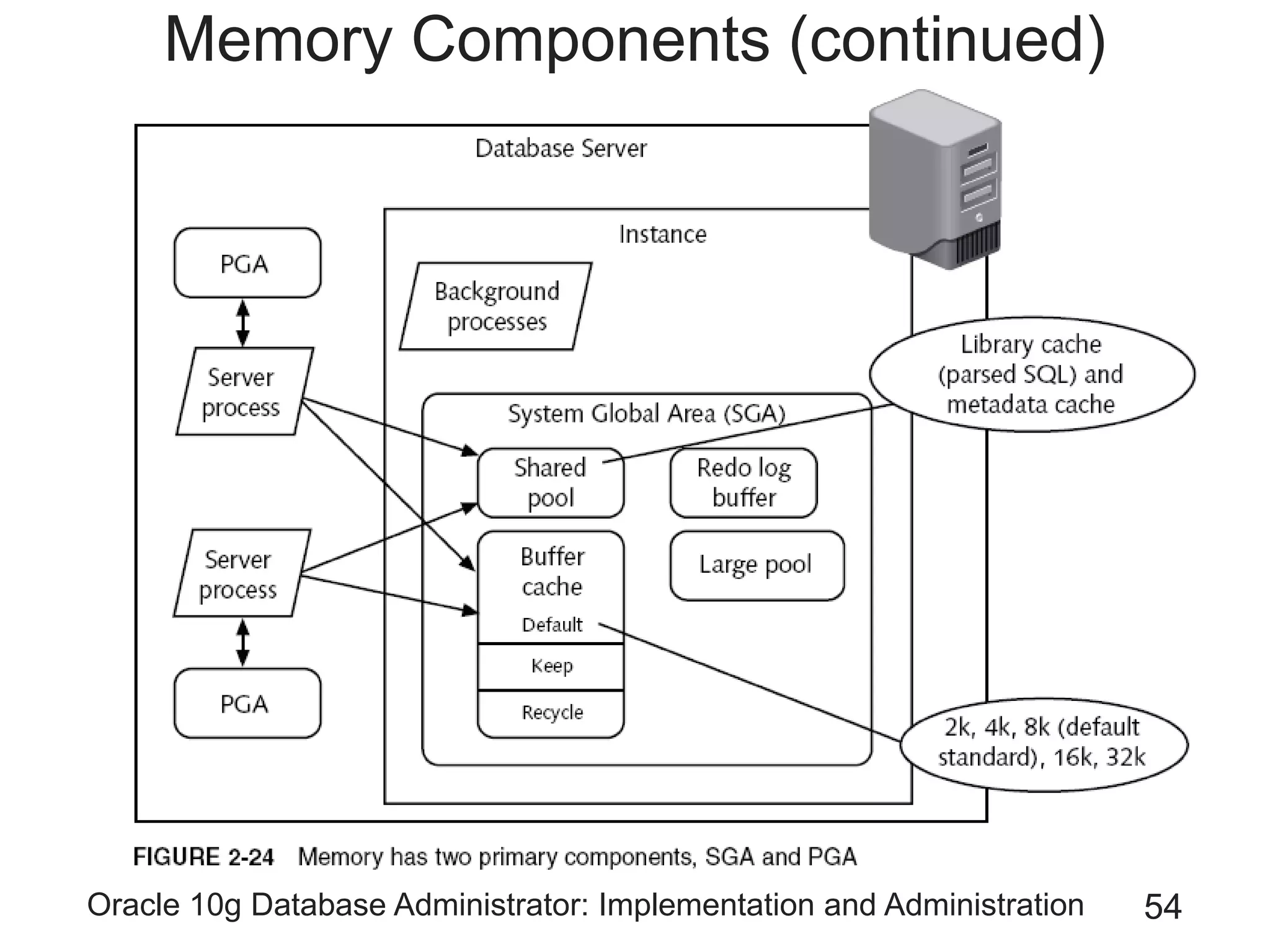
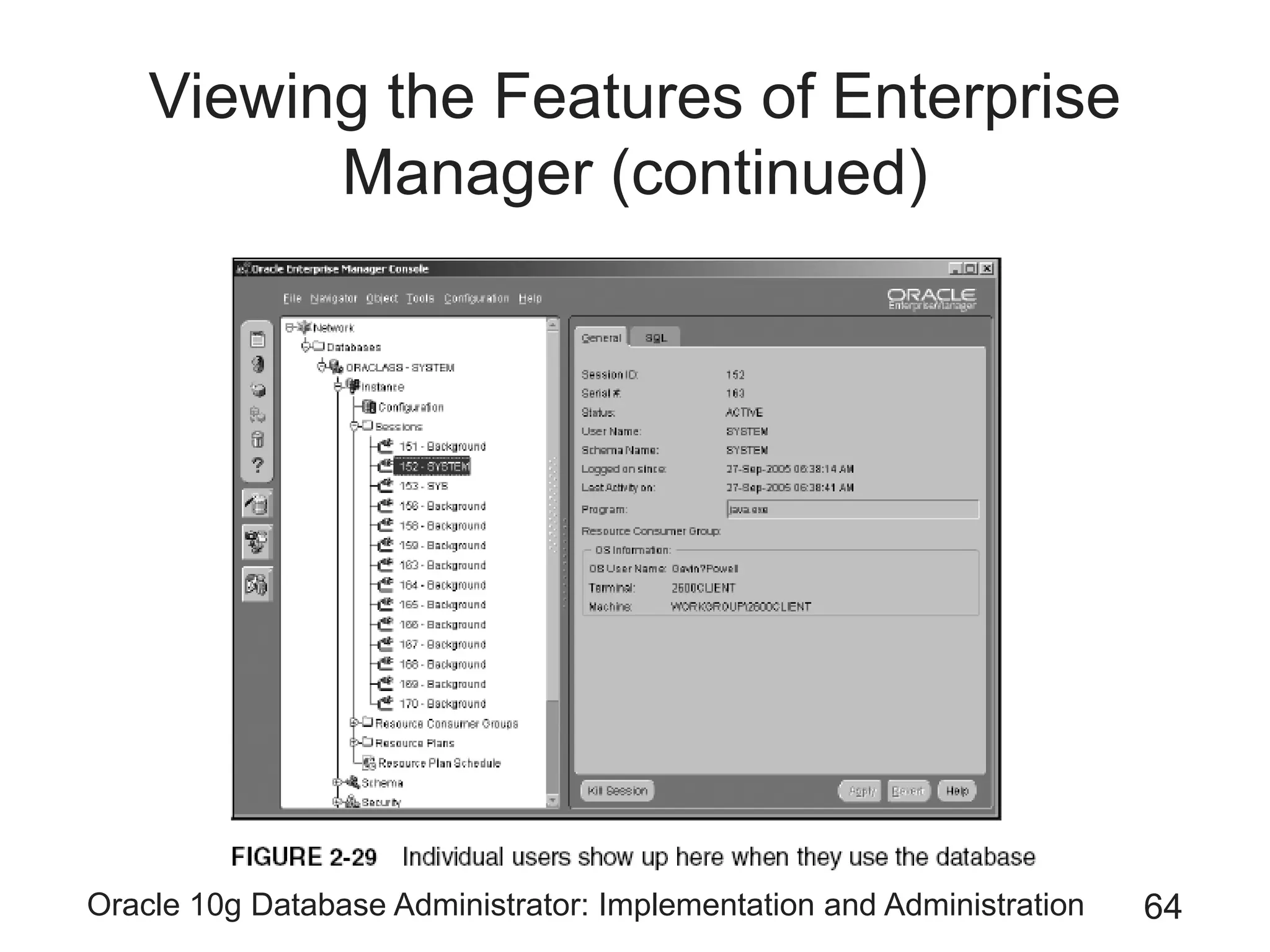
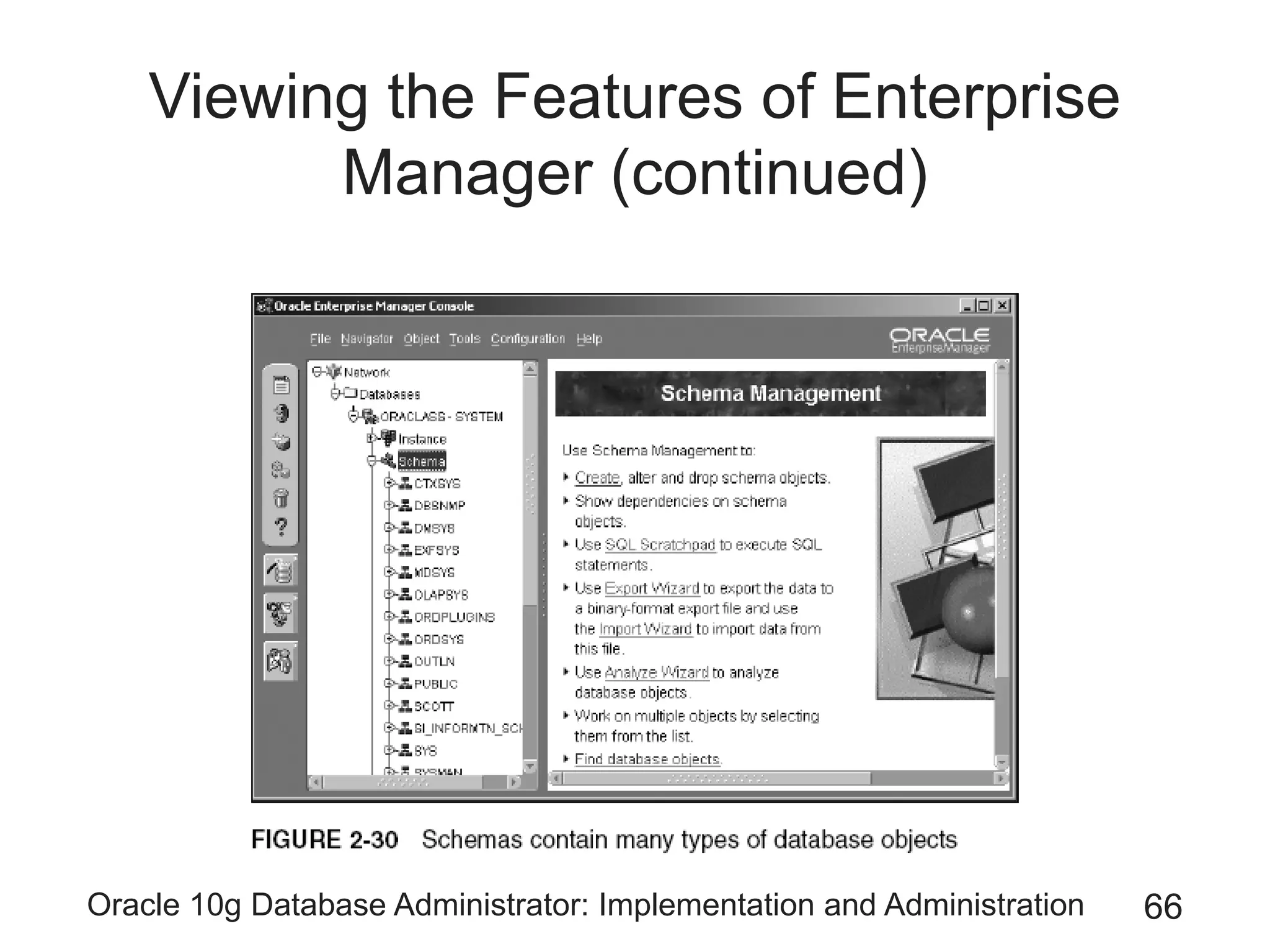
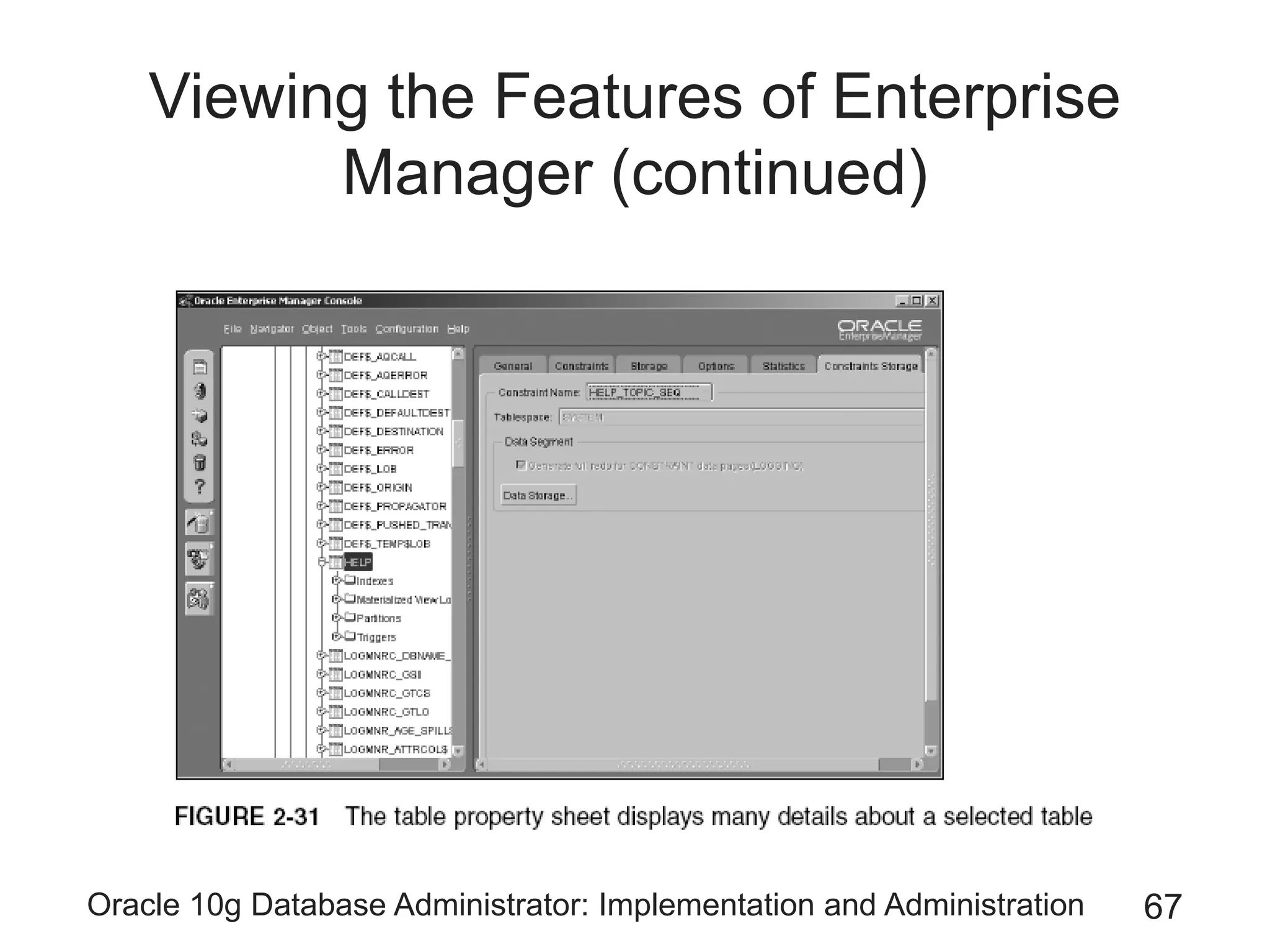
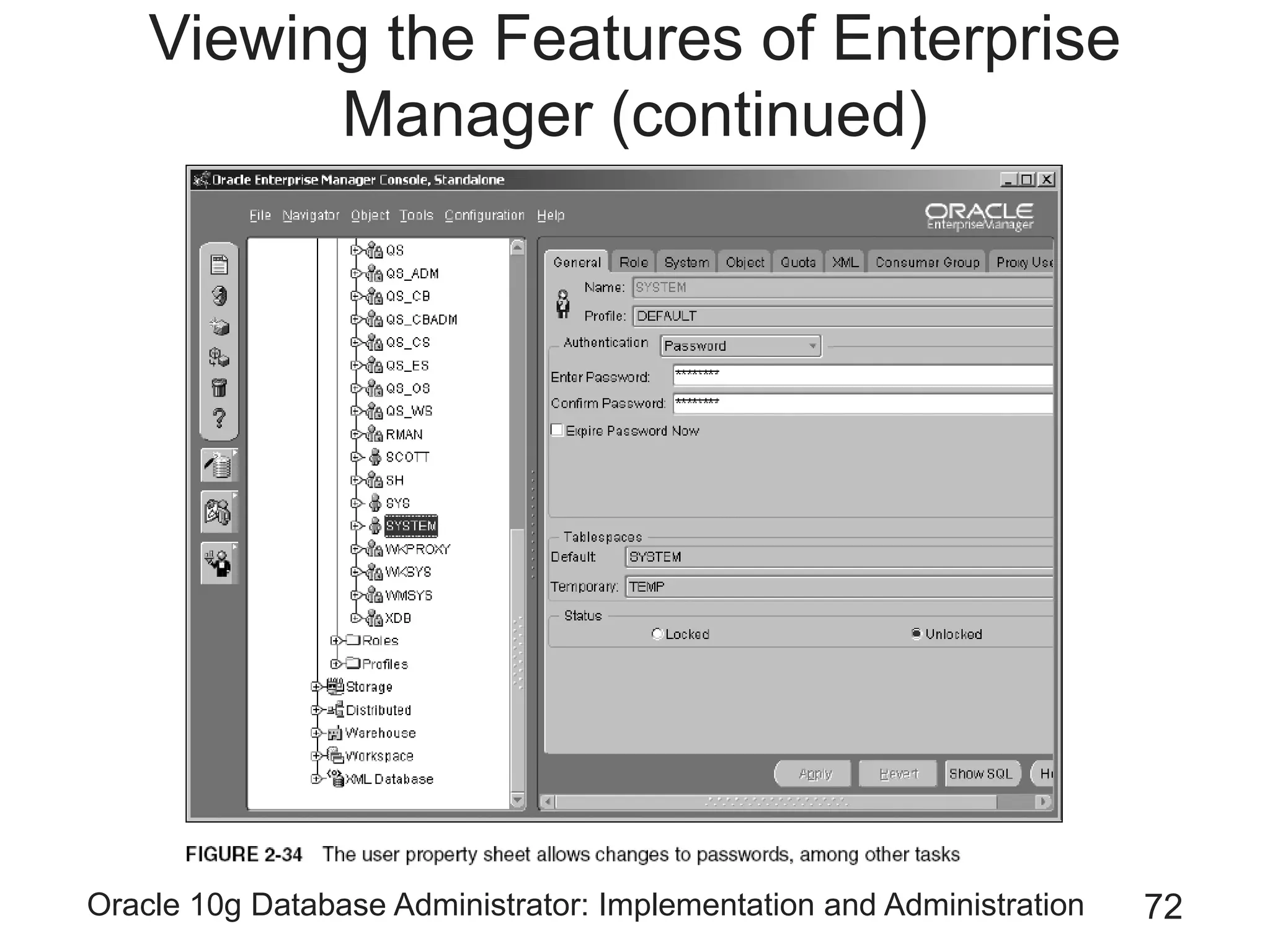
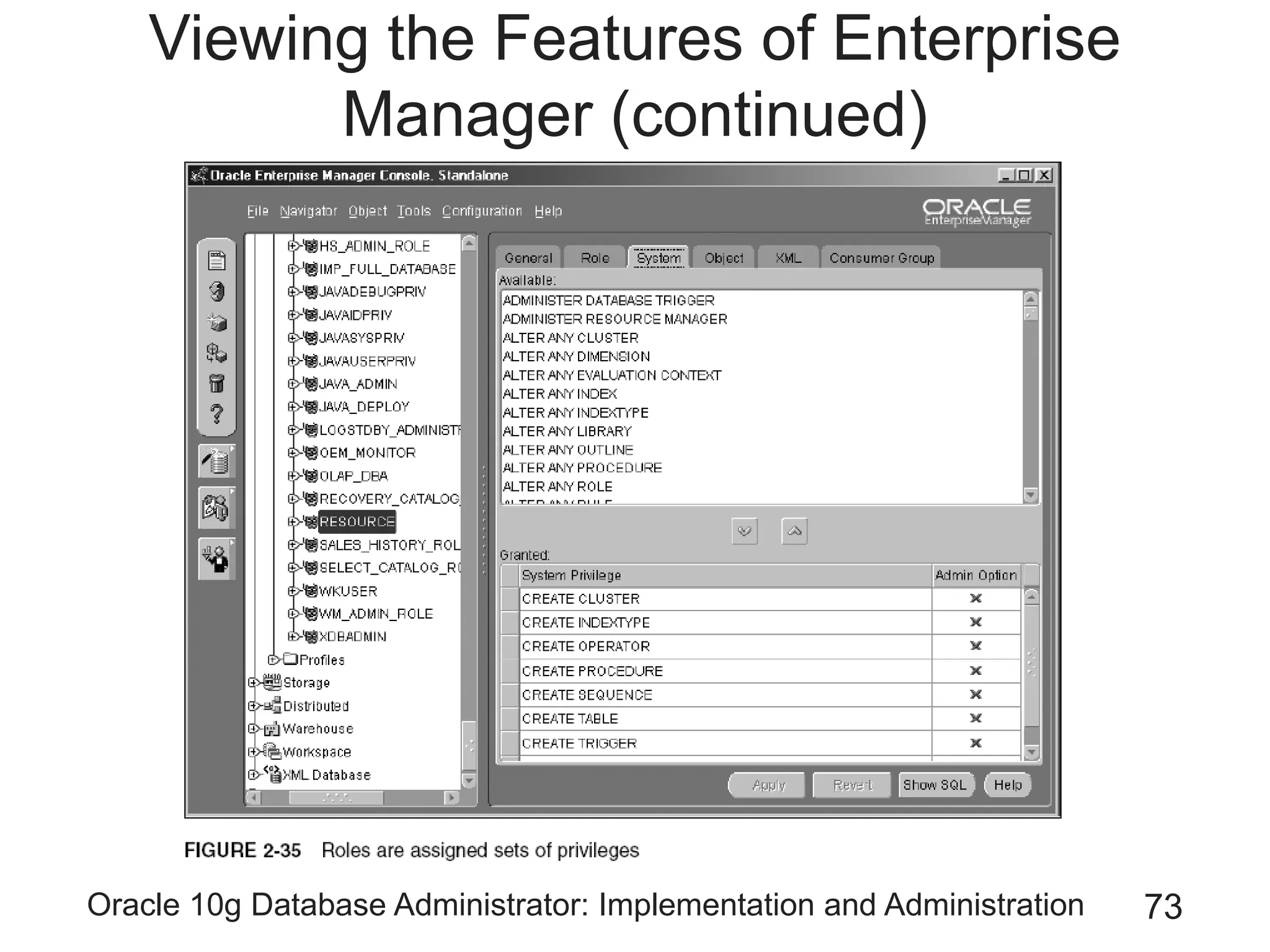
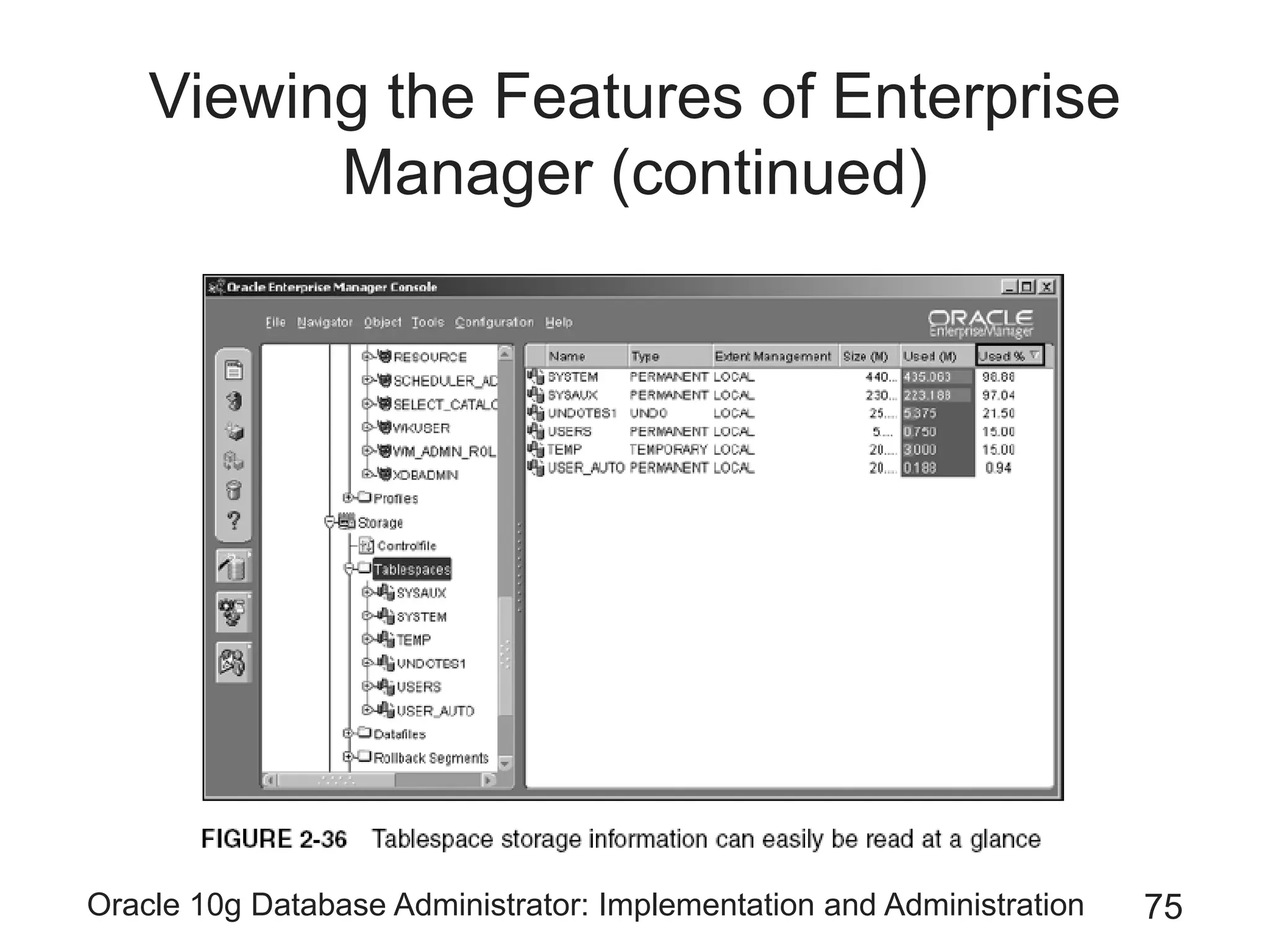
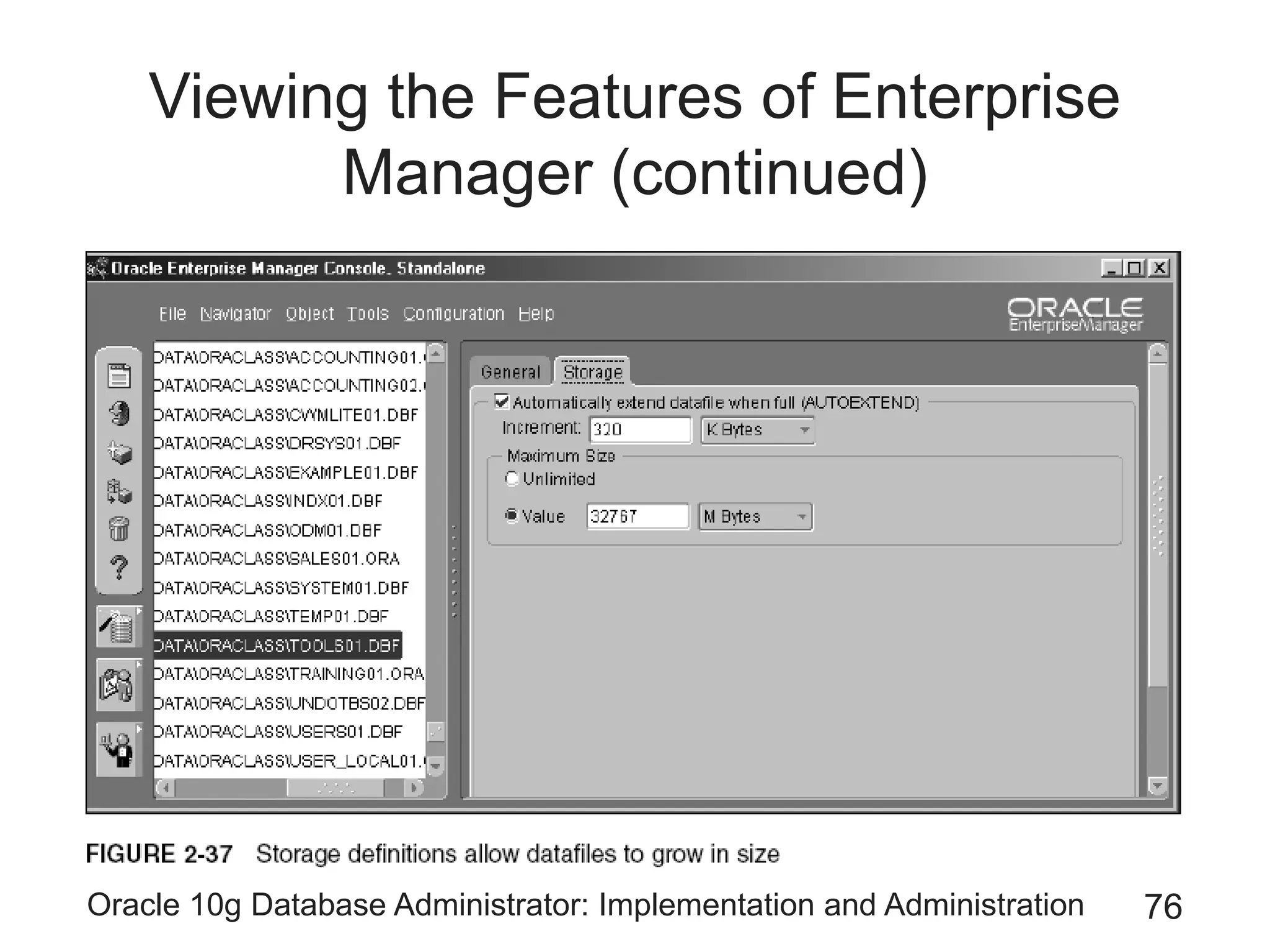
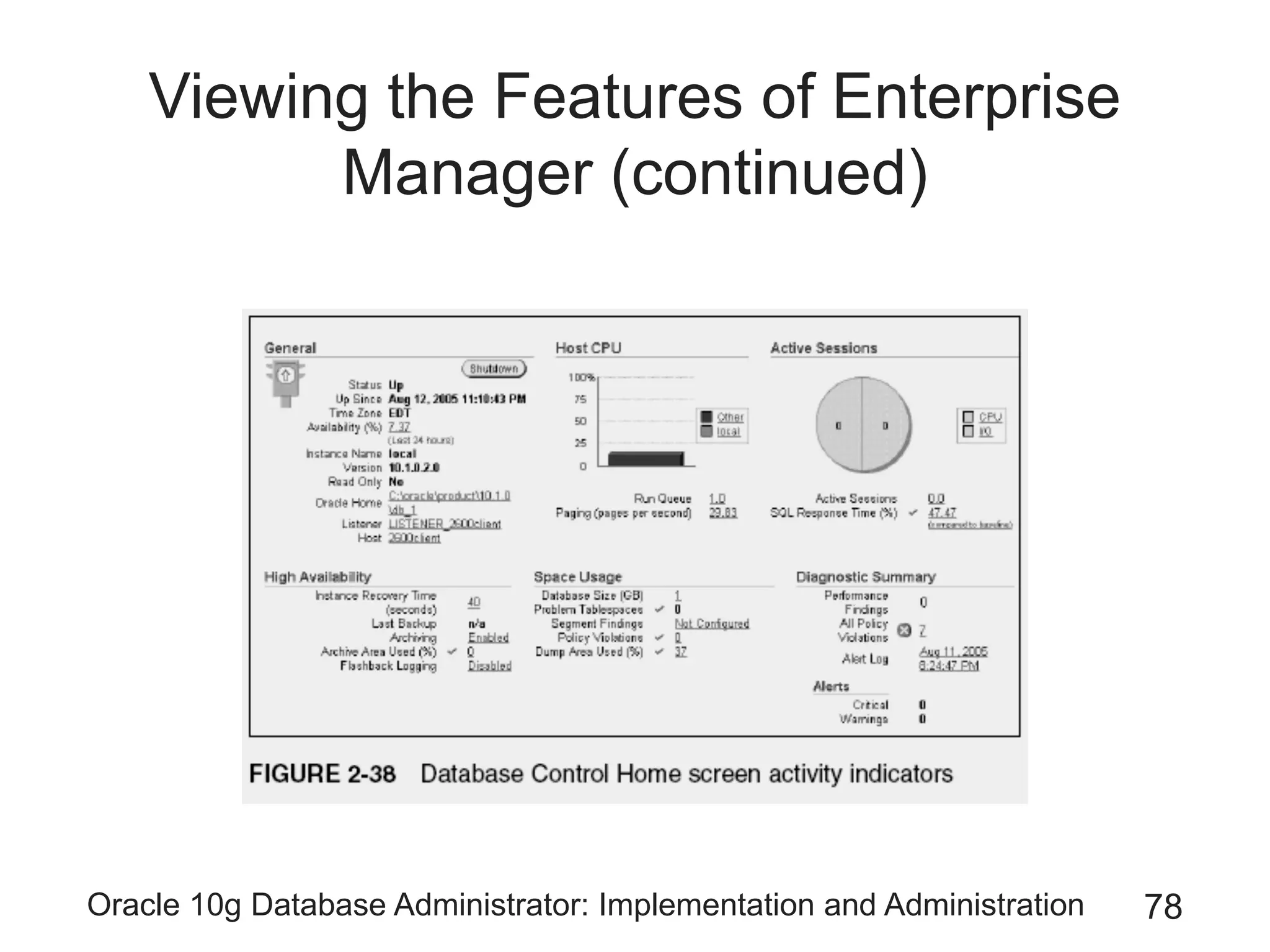
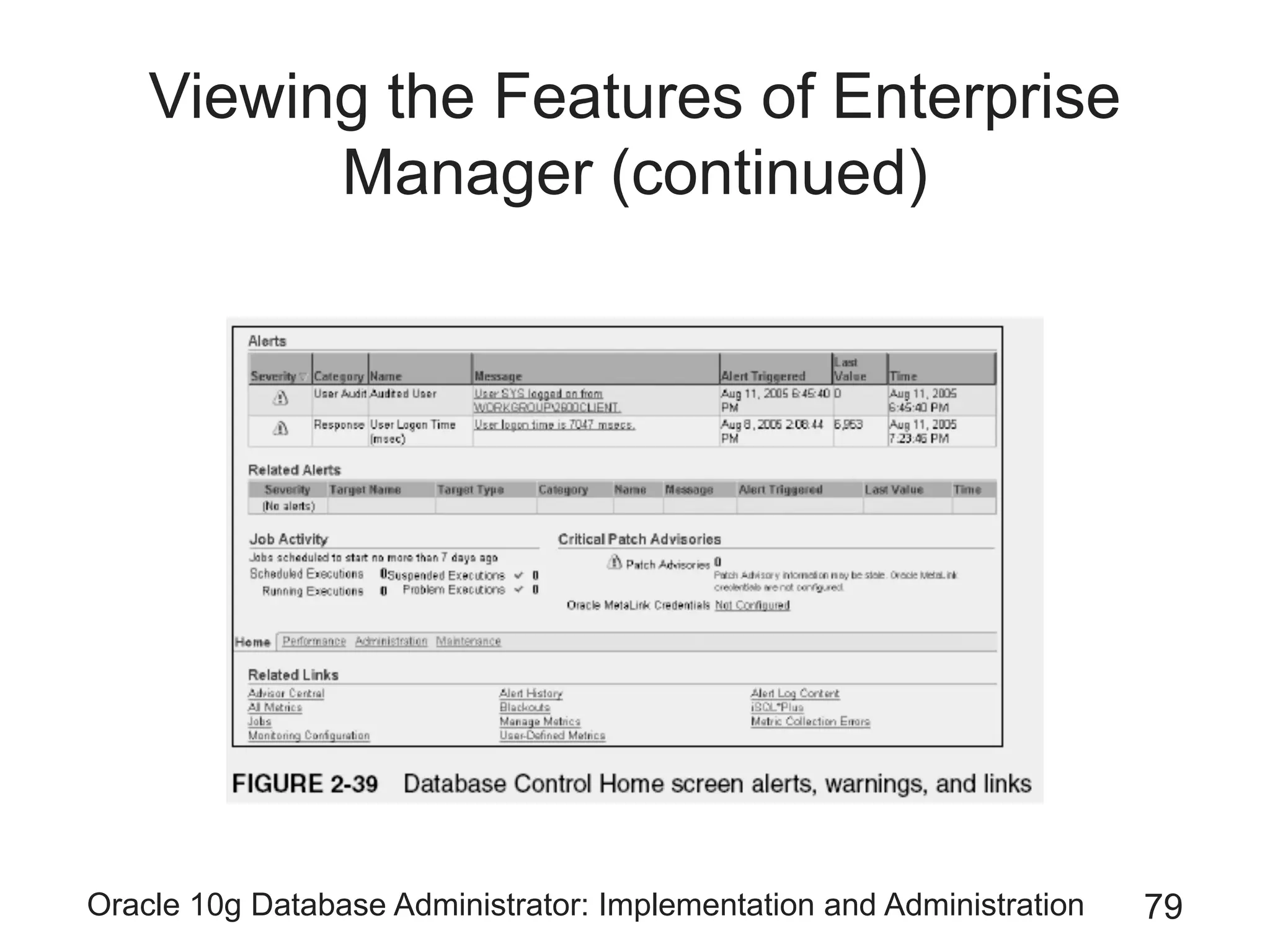
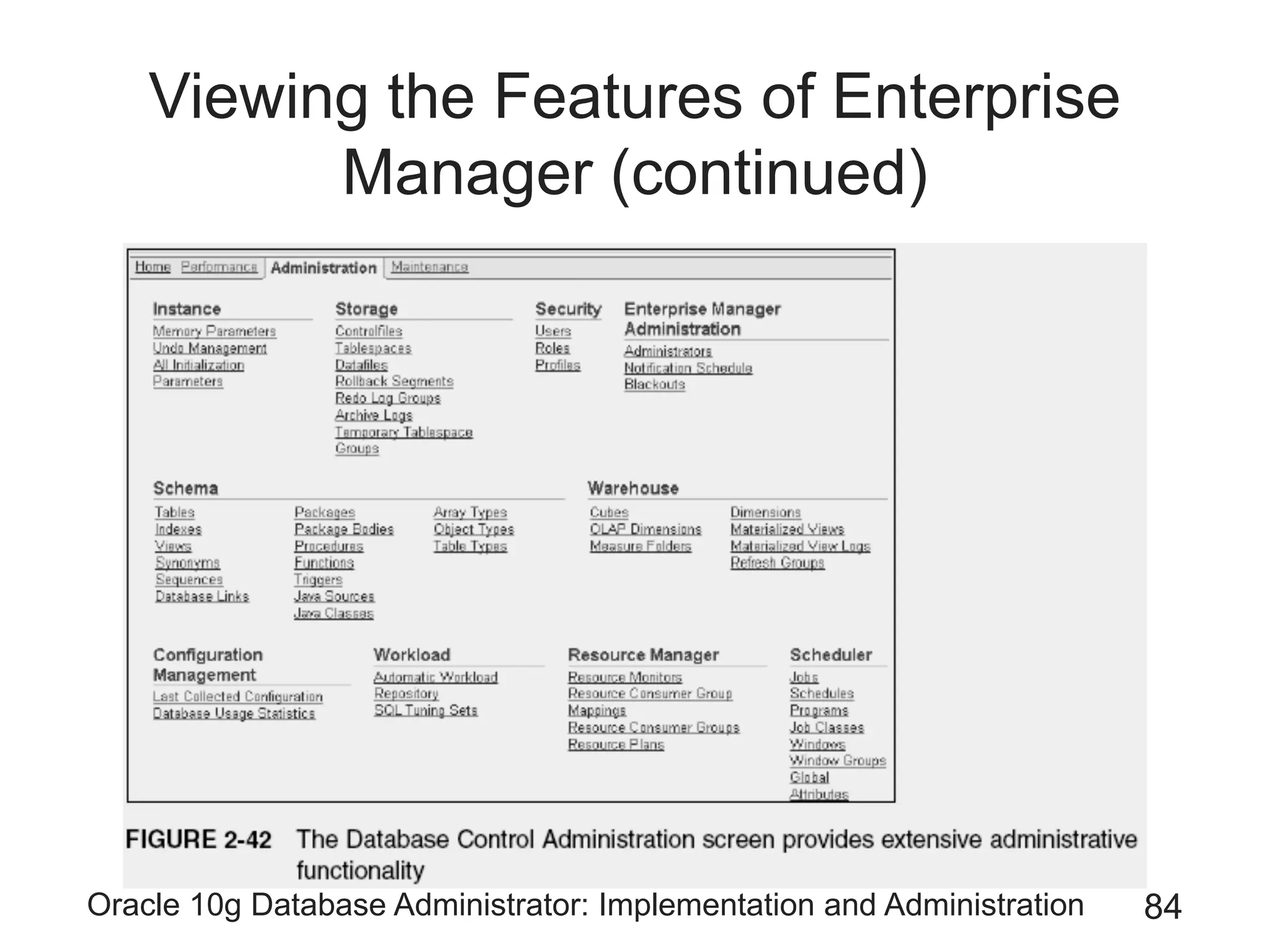
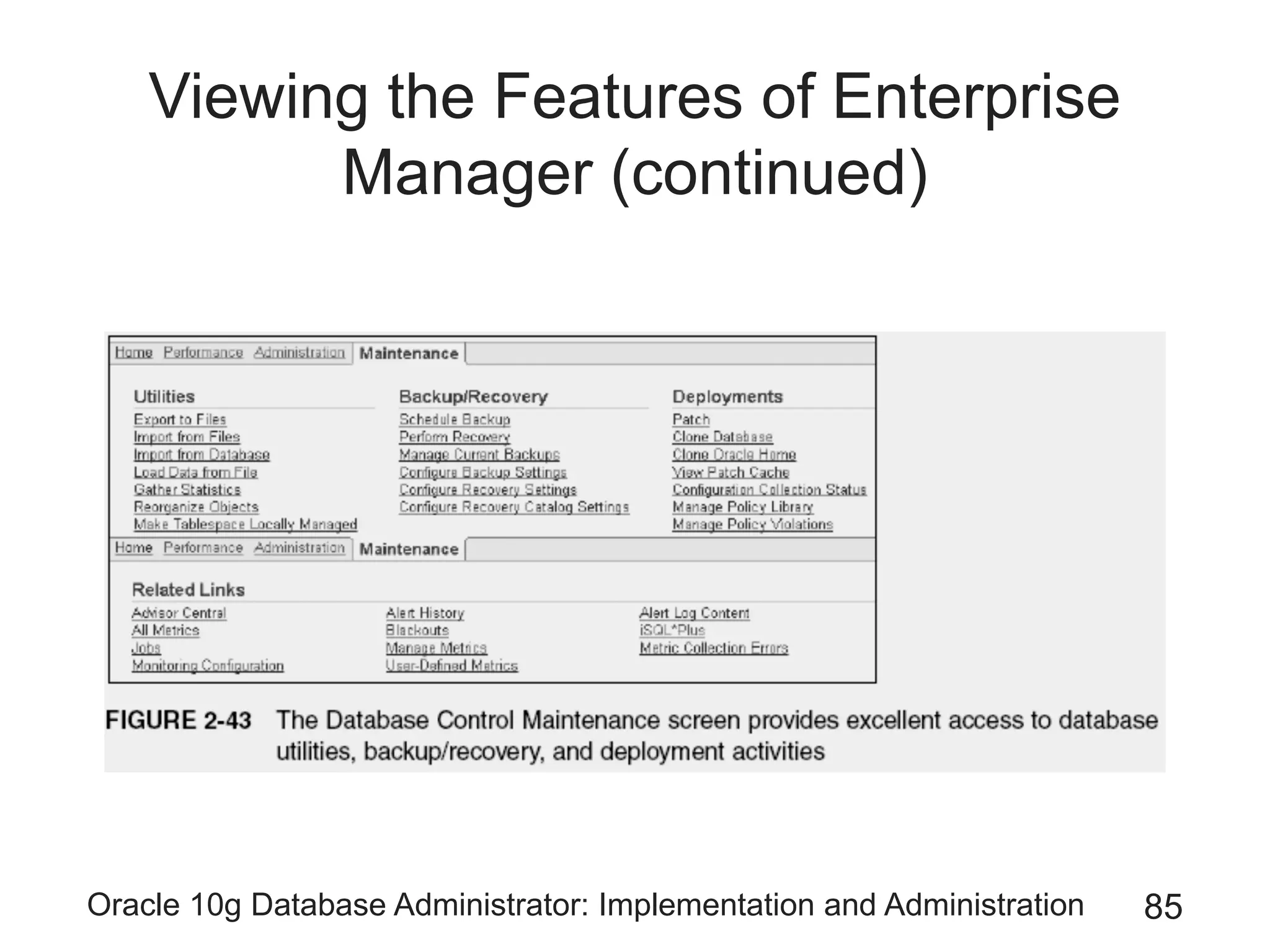
The document covers the implementation and administration of Oracle 10g Database, focusing on main DBA tools, Oracle net services configuration, and database architecture. It explains various components including the instance architecture, memory structure, and the use of Enterprise Manager for database management. Key processes for connecting users to the database, configuring settings, and managing user access and security are also detailed.