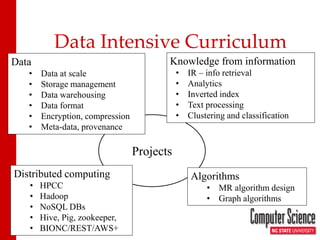
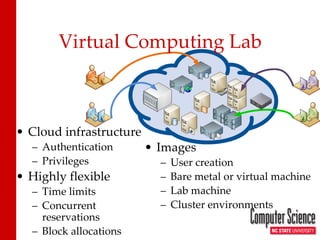
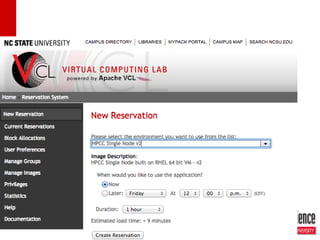
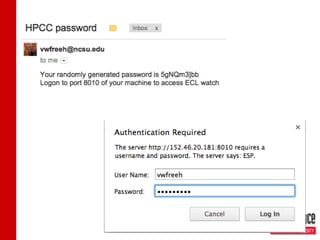
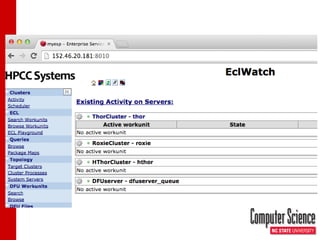
The document discusses leveraging HPCC systems within a Virtual Computing Lab (VCL) at North Carolina State University, focusing on data-intensive projects, distributed computing, and the creation of a standalone HPCC image for educational purposes. It outlines the laboratory's history, operational stats, configuration issues, and the potential for teaching various computing concepts using HPCC. Additionally, it touches upon research extending ECL with natural language processing and the transition to elastic HPCC systems for more efficient resource management.