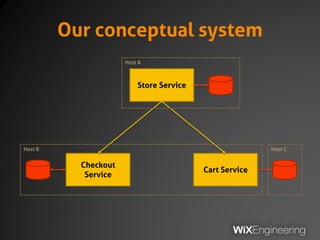
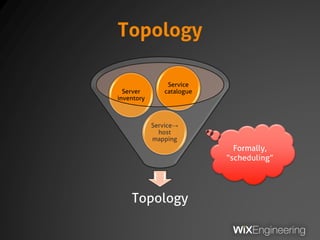
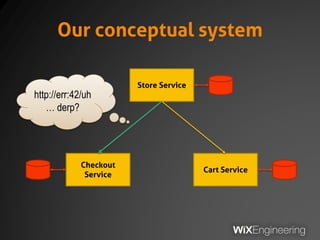
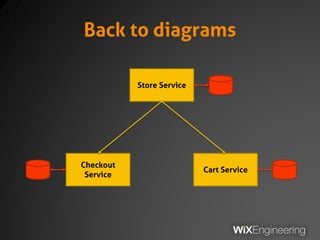
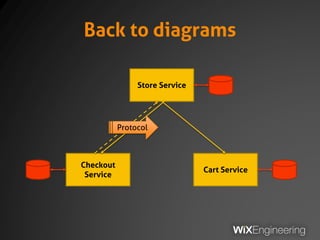
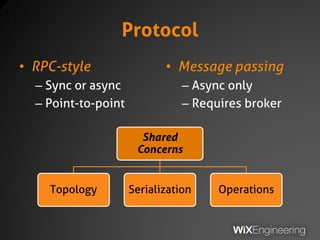
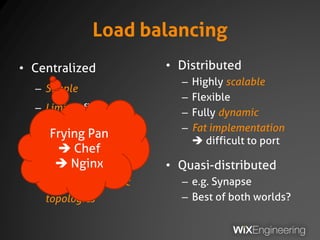
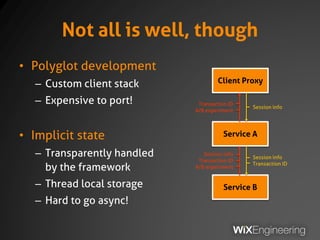
The document outlines the architecture and operations of Wix's microservice stack, including topology, networking, and service scheduling challenges. It discusses various protocols, load balancing strategies, and the structure of code repositories while emphasizing the importance of health monitoring and debugging practices. The presentation highlights the complexity of service management and operational metrics while inviting potential job candidates to consider employment opportunities at Wix.























![Version management
[INFO] QuickRelease
/home/builduser/agent01/work/d9922a1c87aee4bb
bf1bc8bcfb2eccebc4268651c5f19faa689be6e4
[08:10:55][INFO] Adding tag RC;.;1.20.0
[08:10:56][INFO] Tag RC;.;1.20.0 added
successfully
[08:10:56][INFO] Working on onboarding-server-web
[08:10:56][INFO] onboarding-server-web-1.19.0-
SNAPSHOT jar deployable copied
[08:10:56][INFO] onboarding-server-web-1.19.0-
SNAPSHOT jar sources copied
[08:10:56][INFO] onboarding-server-web-1.19.0-
SNAPSHOT jar copied
[08:10:56][INFO] onboarding-server-web-1.19.0-
SNAPSHOT jar tests copied
[08:10:56][INFO] onboarding-server-web pom
deployed
[08:10:57][INFO] Deploying artifacts to release
artifacts repository
[08:10:57][INFO] Deploying onboarding-server-web
to RELEASE
[08:10:57][INFO] pushing new pom
[08:10:59]2016-02-22 08:10:39 [INFO ] /usr/bin/git
push --tag origin master exitValue = 0
• All artifacts share a
common parent
– Master list of versions
• Manually-triggered
release builds
– Custom release plugin
– Increments version
– Updates master
– Pushes changes to git](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/javail-thewixmicroservicestack-160222220252/85/The-Wix-Microservice-Stack-36-320.jpg)