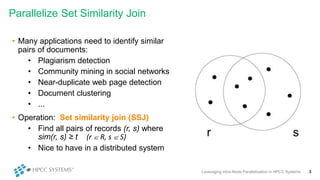
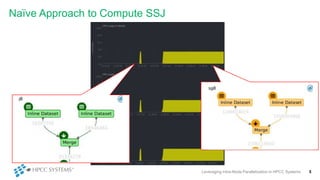
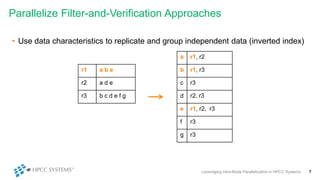
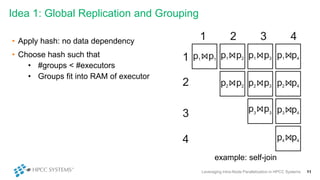
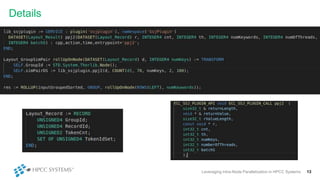
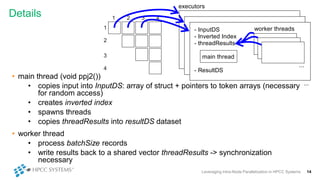
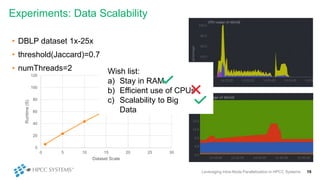
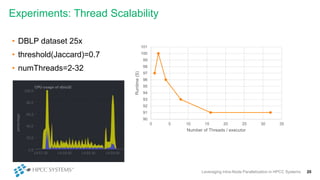
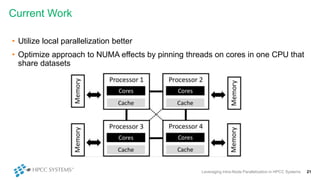
This document discusses leveraging intra-node parallelization in HPCC Systems to improve the performance of set similarity joins (SSJ). It describes a naïve approach to computing SSJ that suffers from memory exhaustion and straggling executors. The presented approach replicates and groups independent data using hashing to address these issues while enabling efficient use of multiple CPU cores through multithreading. Experiments show the approach scales to larger datasets and achieves better performance by increasing the number of threads per executor. Lessons learned include that less complex optimizations are more robust in distributed environments.