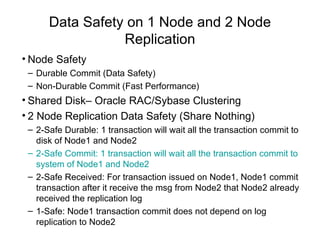
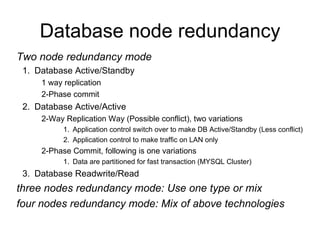
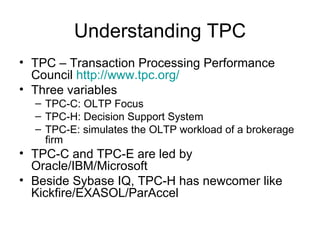
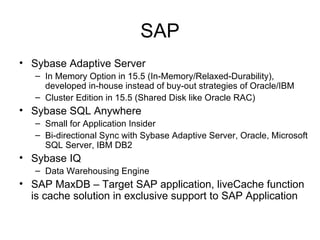
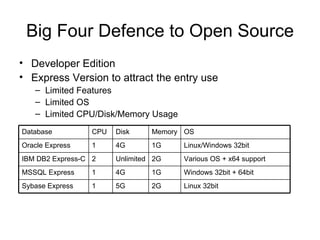
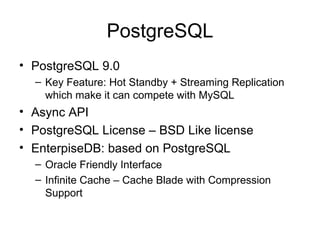
The document discusses various database technologies and concepts. It covers database fundamentals like transactions, isolation levels, and data replication. It also summarizes major commercial database vendors like Oracle, IBM, Microsoft, and SAP and their product offerings. Open source databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, and databases embedded in Java are also briefly covered. The document concludes with a short overview of NoSQL databases.