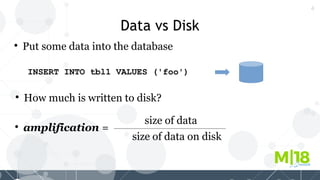
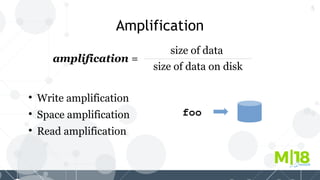
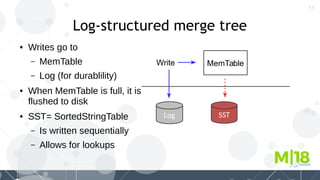
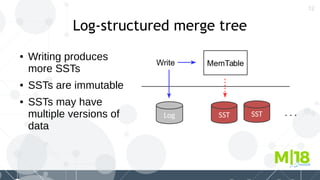
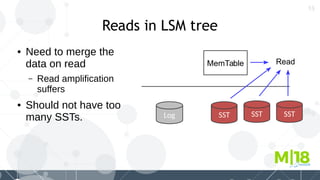
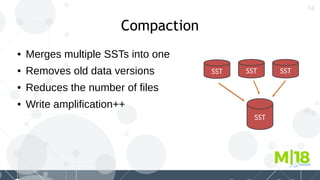
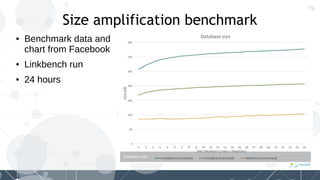
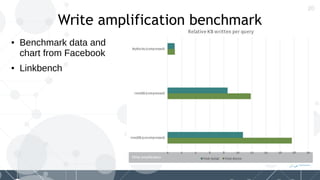
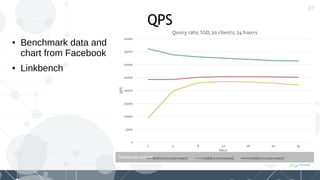
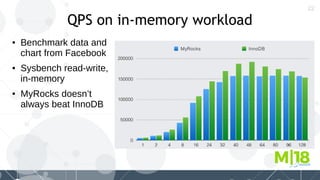
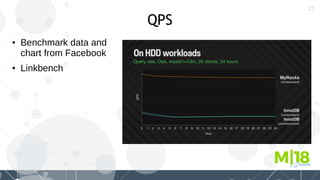
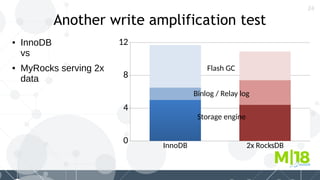
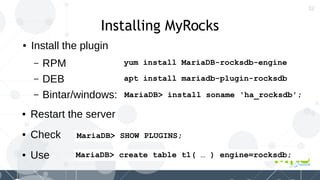
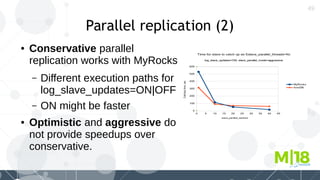
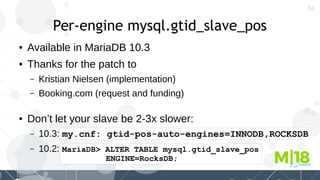
MyRocks in MariaDB summarizes MyRocks, a storage engine for MariaDB that is based on RocksDB. It discusses how MyRocks addresses some of the limitations of InnoDB such as high write and space amplification. It provides details on installing and using MyRocks, including data loading techniques, tuning considerations, and replication support. Parallel replication is supported, but the highest isolation level is repeatable-read and row-based replication must be used.