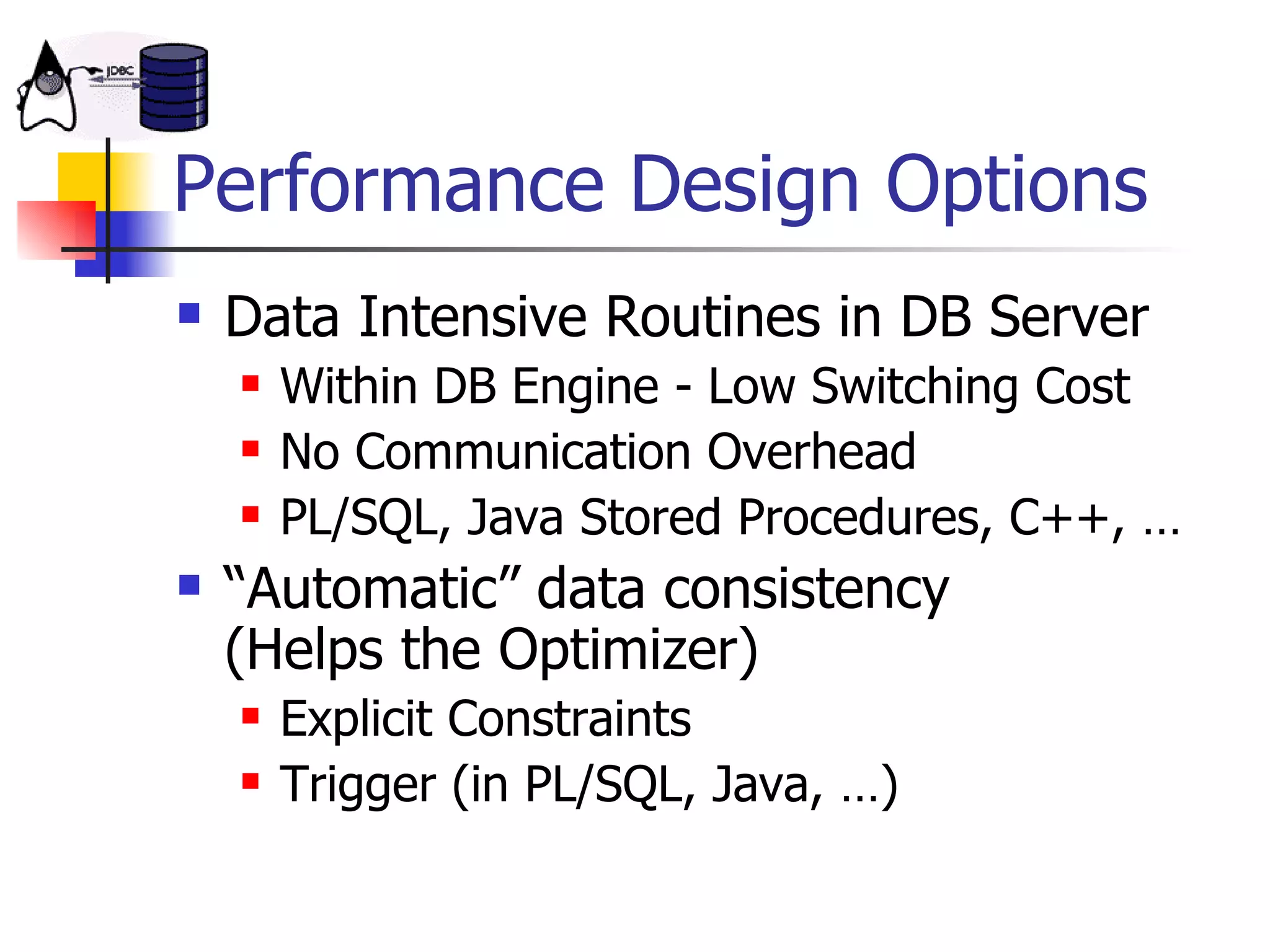
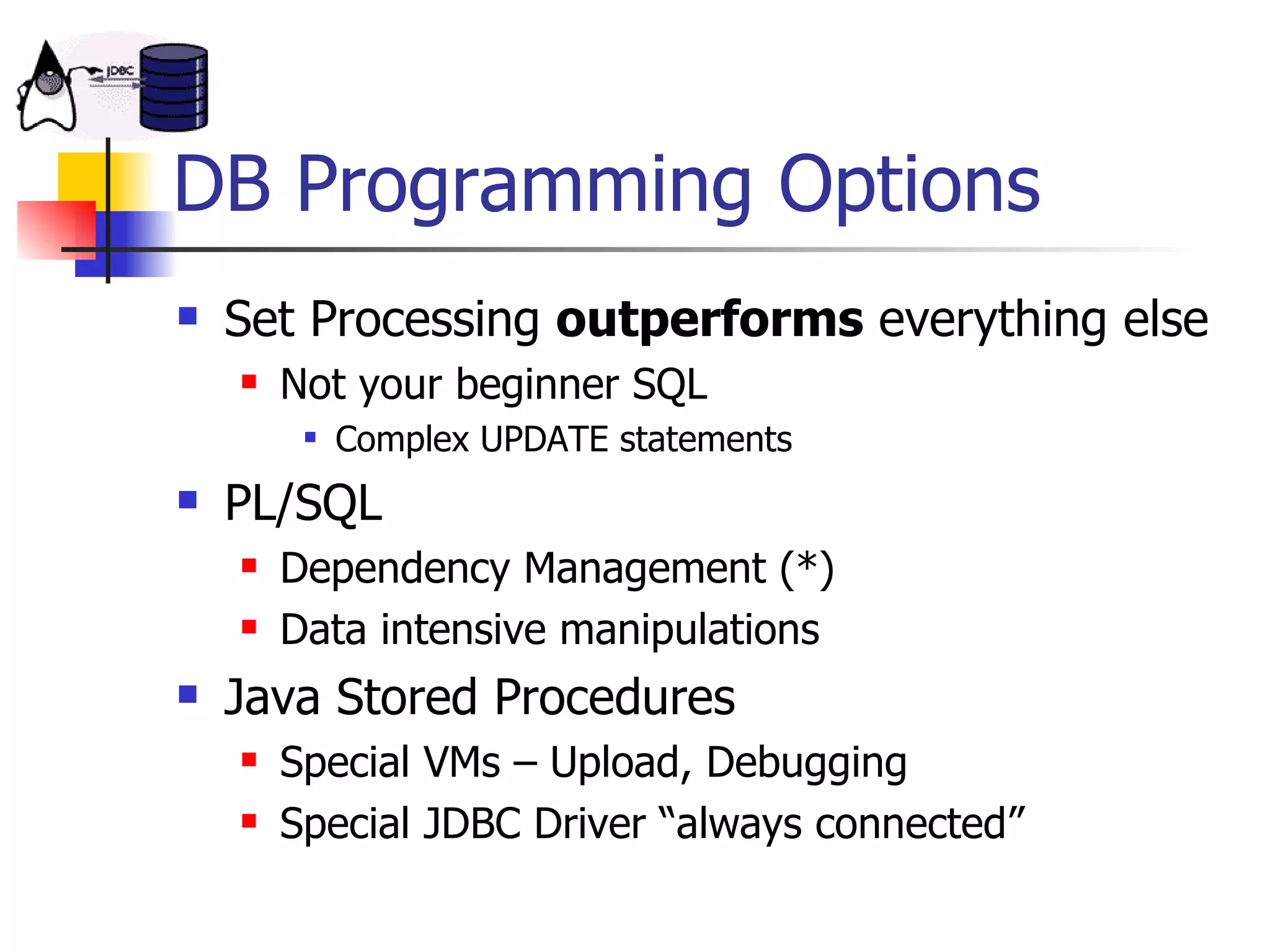
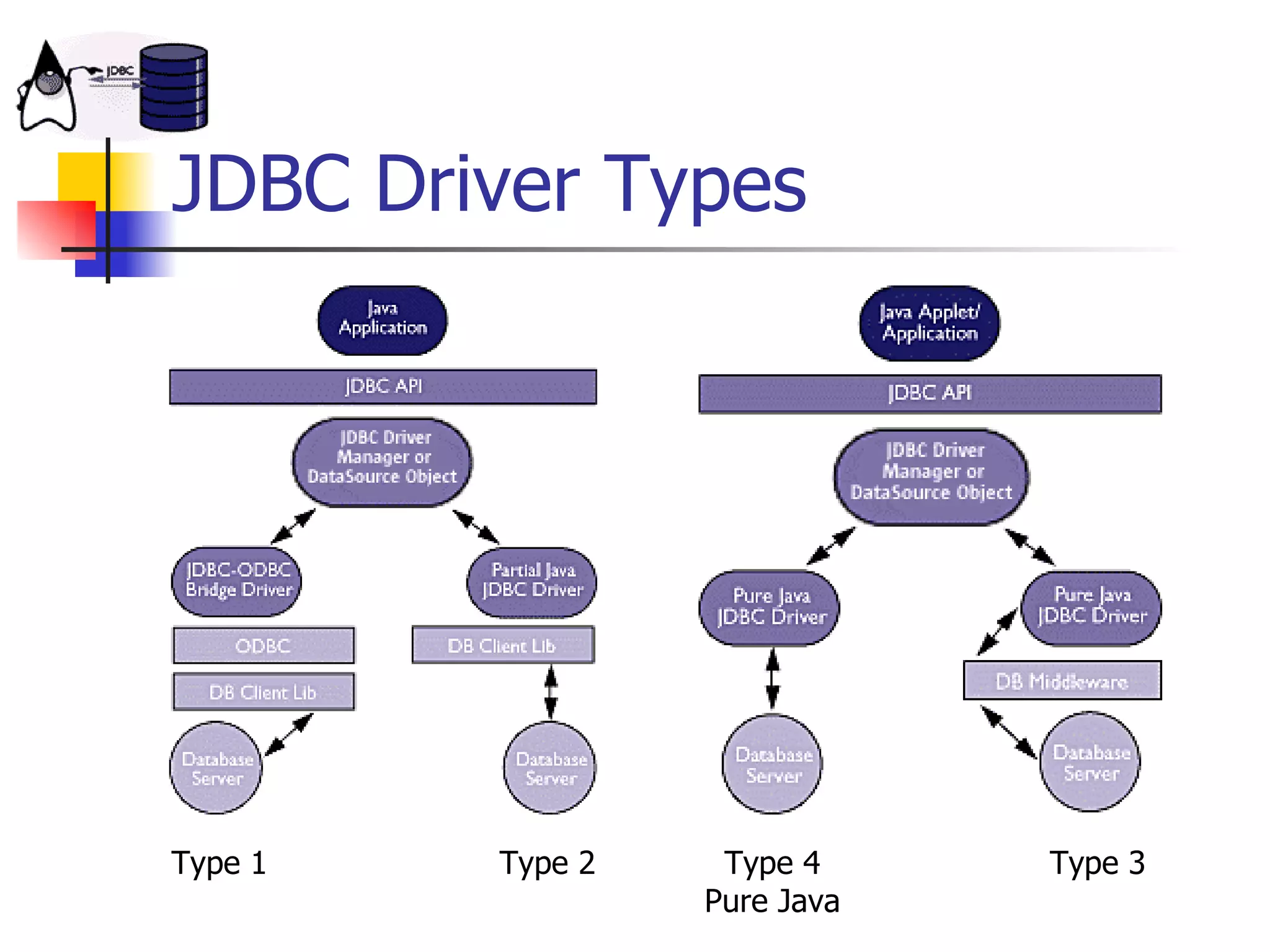
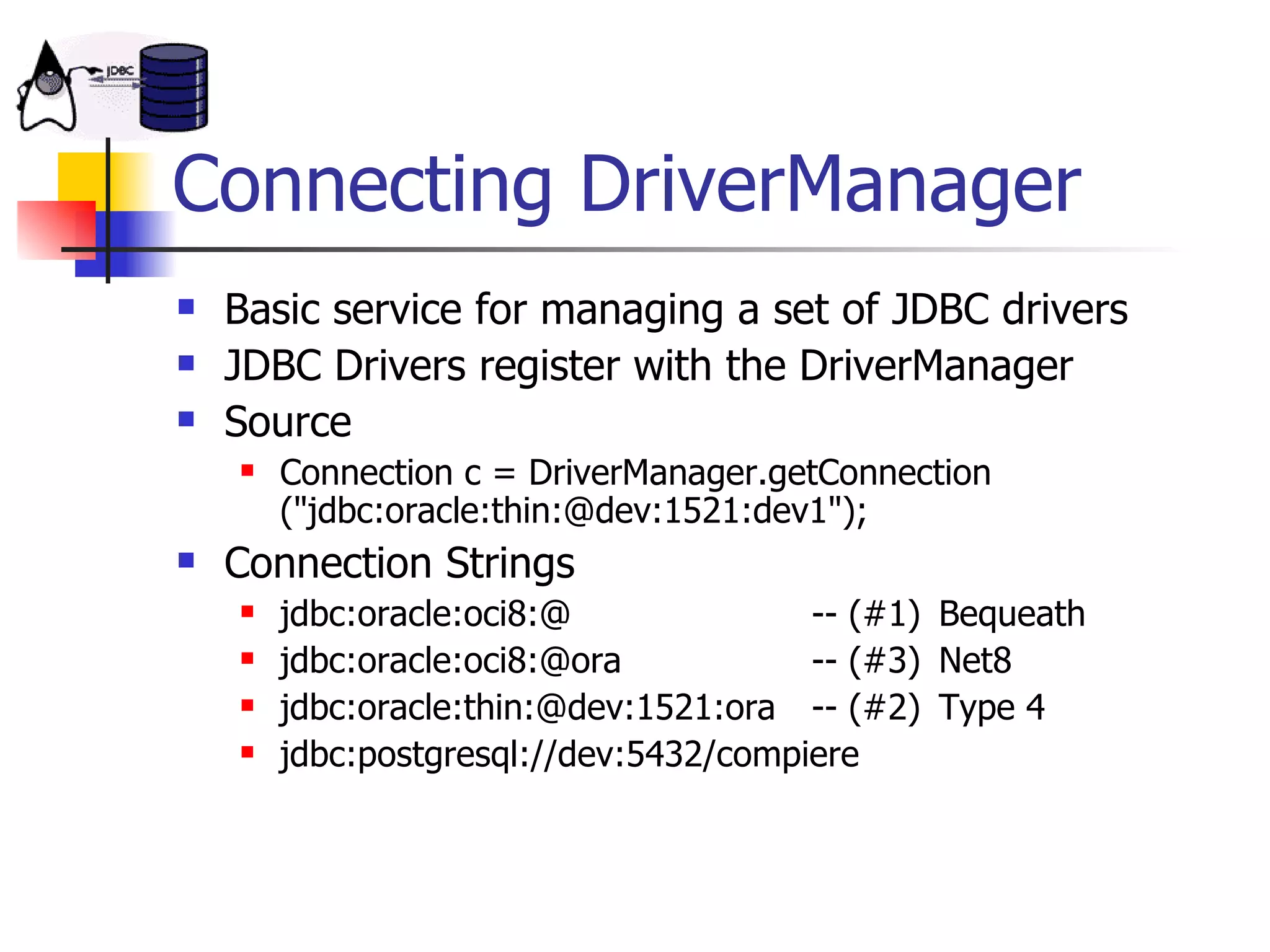
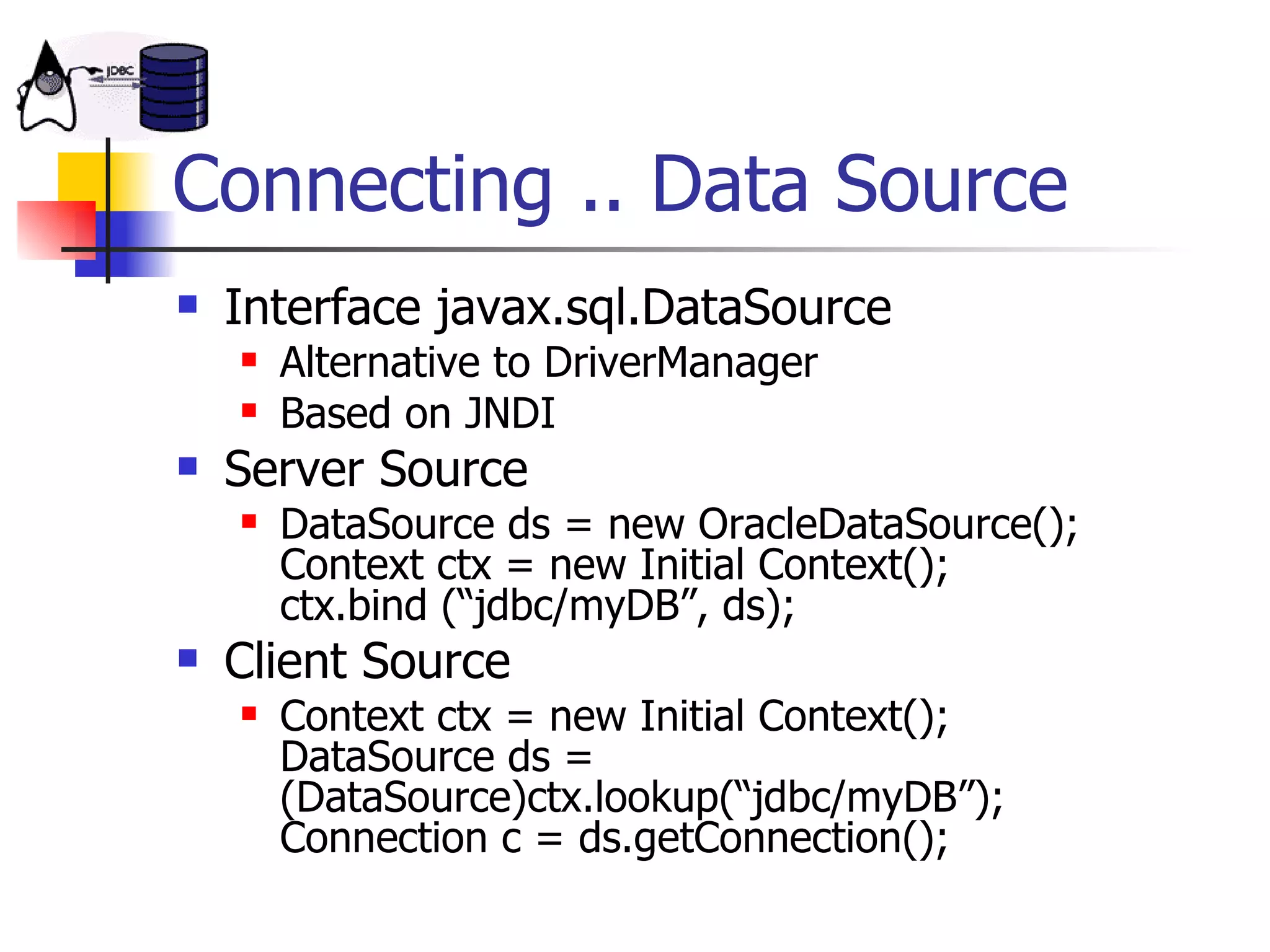
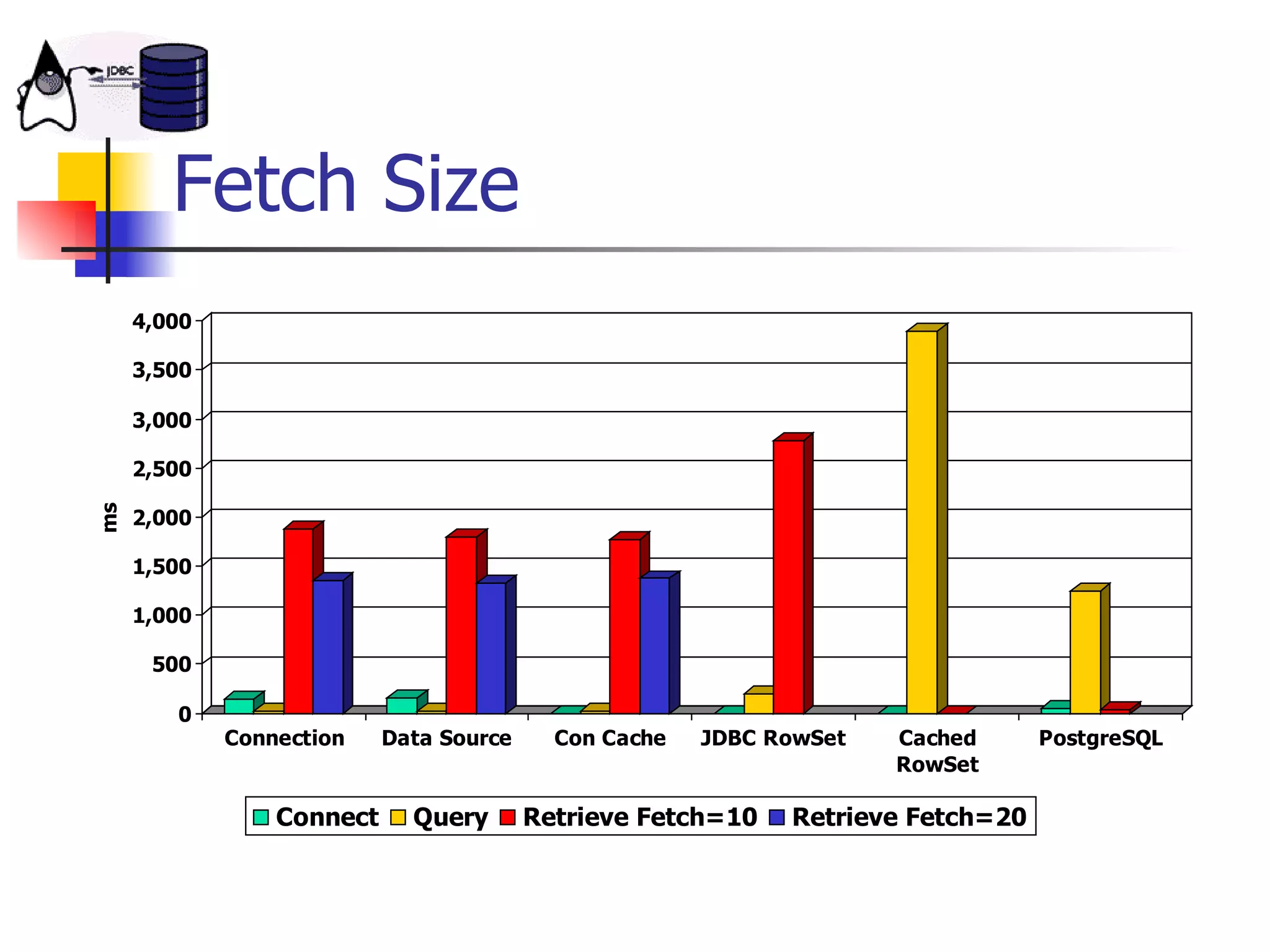
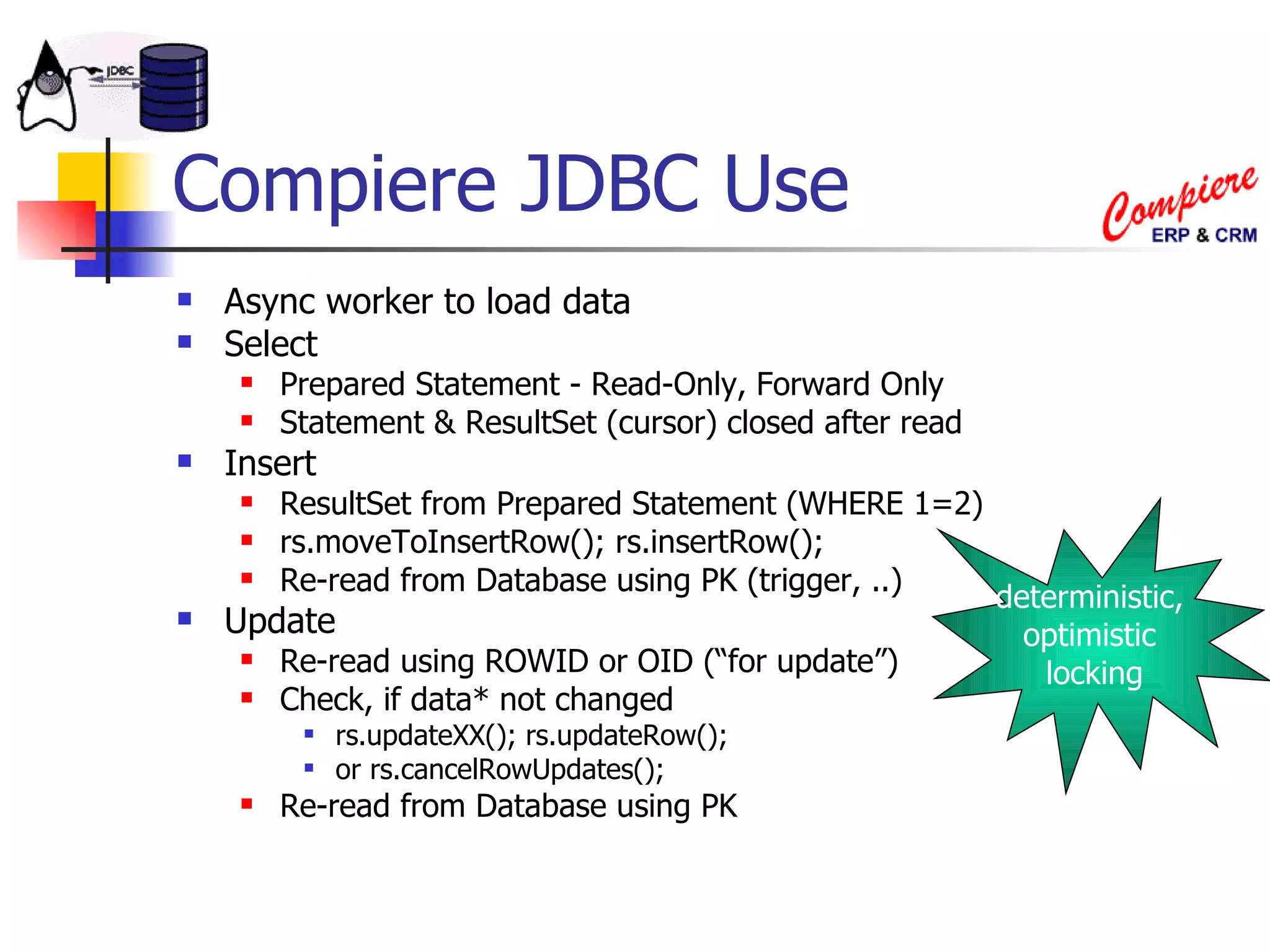
The document discusses high performance JDBC and database optimization. It covers topics like persistence frameworks, JDBC drivers and connections, query performance, and tuning database and application design. Specific tips mentioned include using prepared statements, setting fetch sizes, closing resources, and leveraging database features like indexes and materialized views.
![High Performance JDBC Jorg Janke Consultant and Coach [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/highperformancejdbc-091104225649-phpapp02/75/High-Performance-Jdbc-1-2048.jpg)













![Querying Statement – conn.createStatement() ResultSet.TYPE_ FORWARD_ONLY, SCROLL_INSENSITIVE, SCROLL_SENSITIVE ResultSet.CONCUR_ READ_ONLY or _UPDATABLE Prepared Statement – conn.prepareStatement() Database dependent statement caching “ UPDATE EMPLOYEES SET SALARY = ? WHERE ID = ?” pstmt.setDataType (pos, value); Callable Statement – conn.prepareCall() “ {?= call myProcedure (?,?)}” Batch [implementation not mandatory] stmt.addBatch(“Insert ..”); stmt.executeBatch();](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/highperformancejdbc-091104225649-phpapp02/75/High-Performance-Jdbc-37-2048.jpg)



![Thanks You can download the presentation http://www.compiere.org/download/ If you have questions [email_address] (203) 445-8182 Have a look http://www.compiere.com/consulting.html](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/highperformancejdbc-091104225649-phpapp02/75/High-Performance-Jdbc-50-2048.jpg)