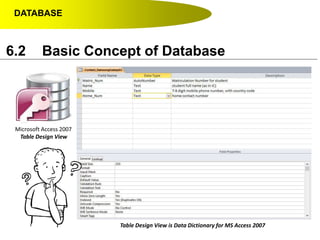
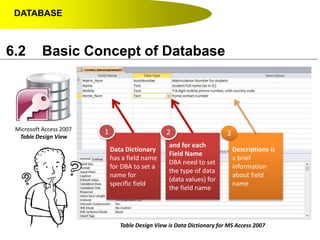
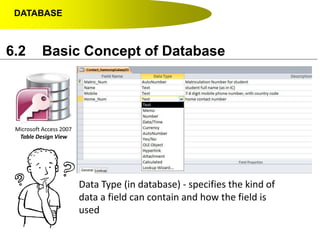
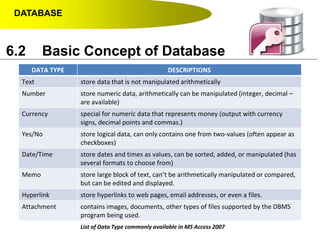
This document discusses key concepts related to databases including:
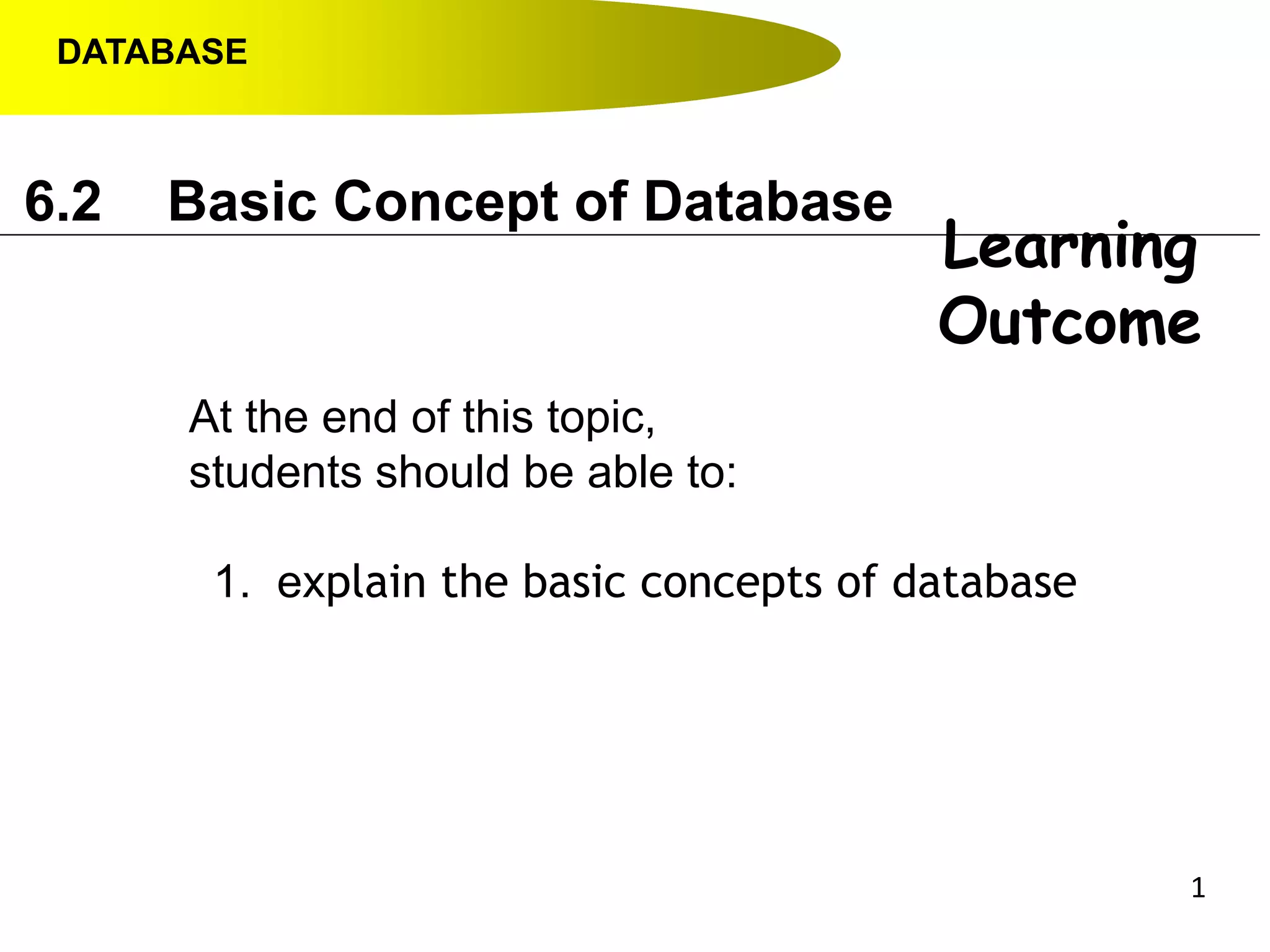
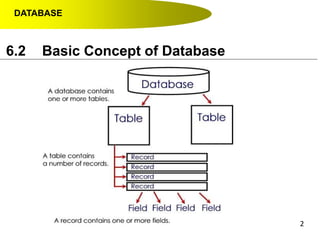
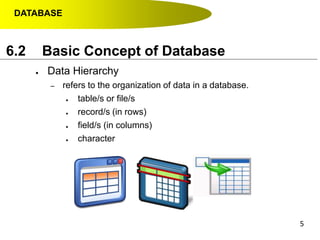
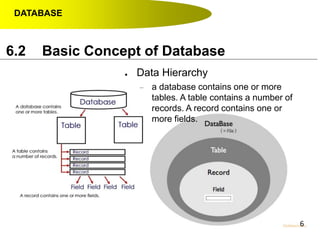
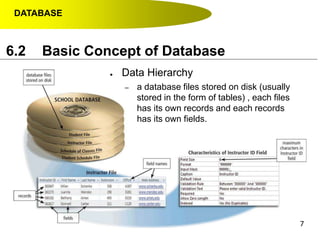
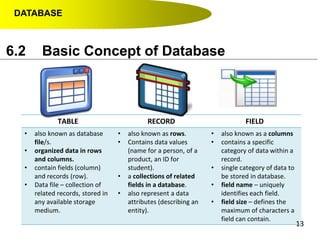
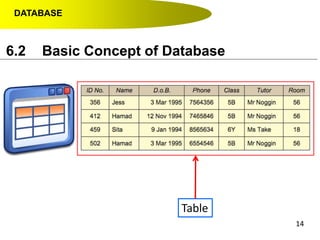
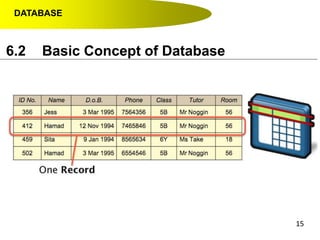
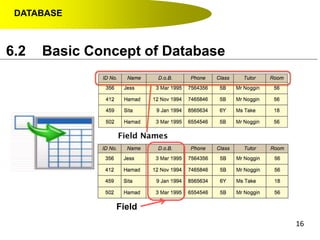
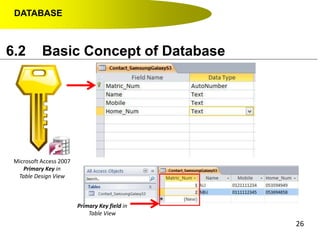
- Data hierarchy refers to the organization of data in a database with tables containing records made up of individual fields.
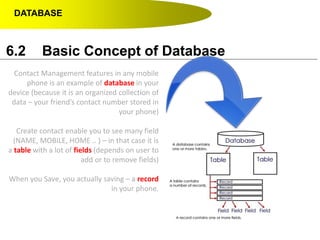
- A contact list on a mobile phone is an example of a simple database with tables (contacts), records (individual contacts) and fields (name, phone number, etc.).
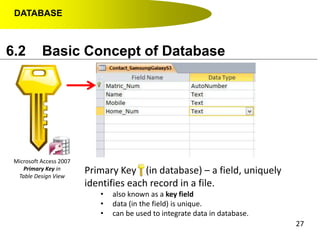
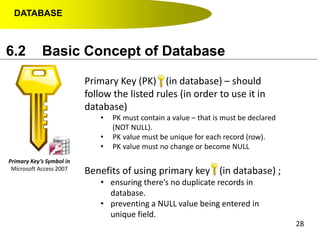
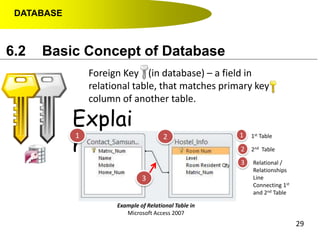
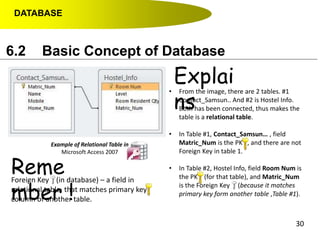
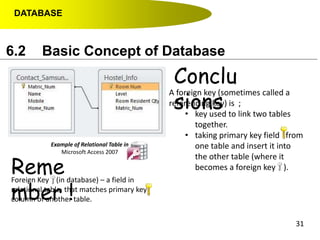
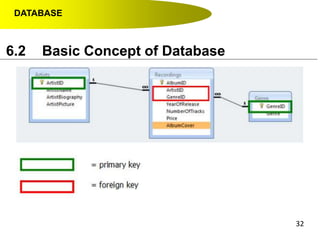
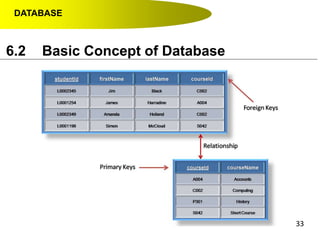
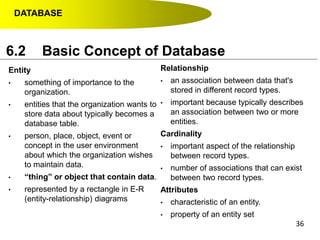
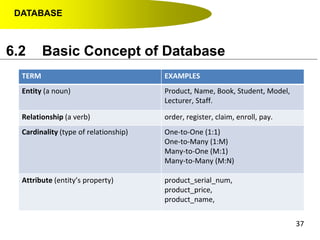
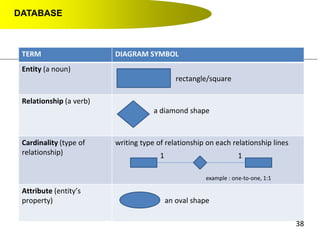
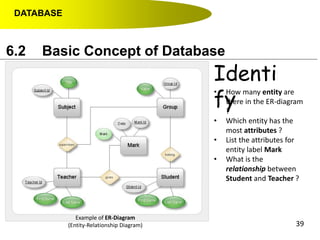
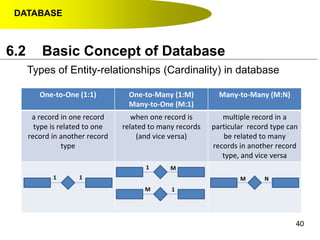
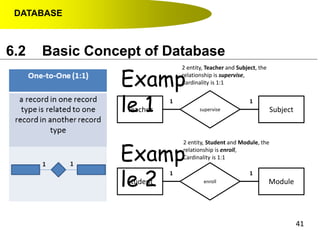
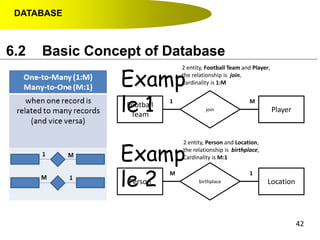
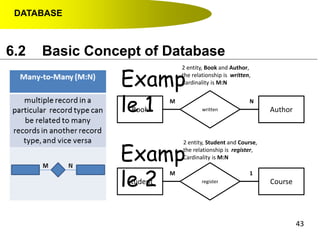
- Primary keys uniquely identify each record in a table while foreign keys in one table match the primary key of another table to link the tables together in a relational database.