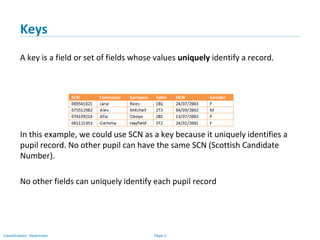
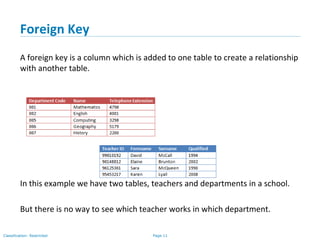
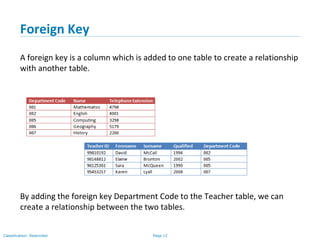
The document outlines various types of database keys, including candidate keys, primary keys, compound keys, surrogate keys, and foreign keys. It explains their definitions, characteristics, and uses, emphasizing how they uniquely identify records in database tables and establish relationships. Additionally, it includes notation guidelines for representing these keys visually in database schemas.