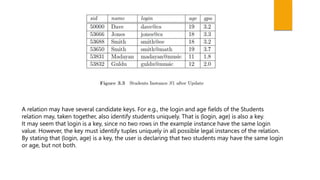
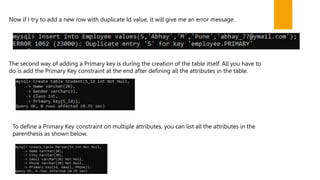
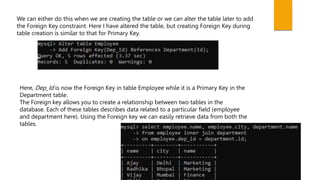
This document provides an introduction to keys in relational databases. It defines key terminology including candidate keys, primary keys, alternate keys, foreign keys, and superkeys. It explains that candidate keys uniquely identify tuples, the primary key is the selected candidate key, alternate keys are other candidate keys, foreign keys link tables based on matching primary keys, and superkeys may contain but not uniquely identify tuples. Examples are given of each key type using tables with employee and department data.