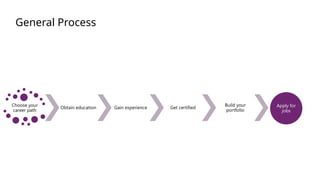
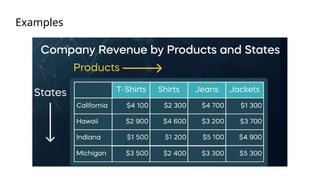
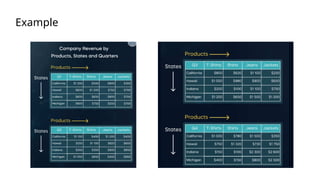
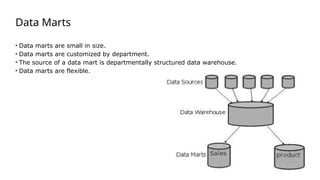
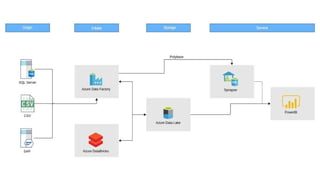
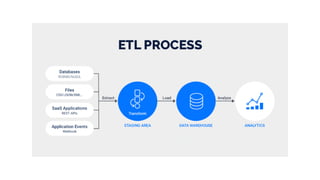
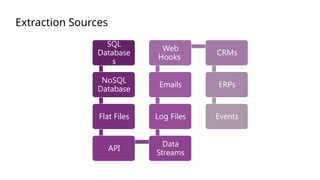
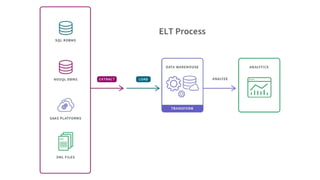
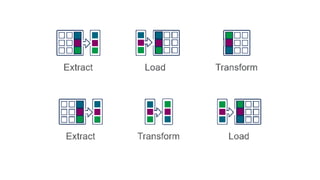
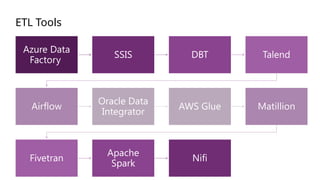
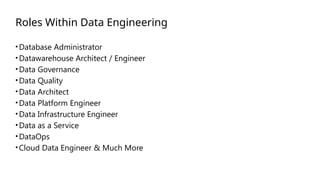
The document is a data engineering guide presented by Usman Khan, outlining the objectives of the session, which include implementing end-to-end analytics solutions using Microsoft Fabric and understanding data warehousing concepts. It covers important topics such as operational databases, data warehouse features, ETL processes, data modeling, and necessary skills for a career in data engineering. The guide also provides resources for learning and emphasizes the importance of hands-on experience and networking.