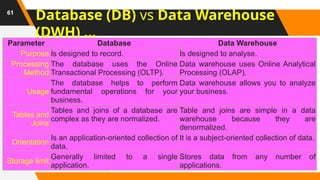
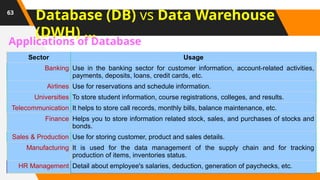
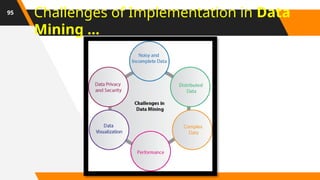
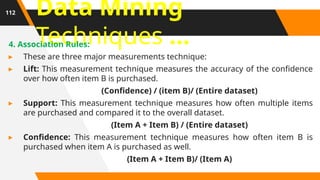
A Database Administrator (DBA) is a professional responsible for managing and maintaining computer databases. Their duties include ensuring data is stored securely and retrieved efficiently, as well as designing, implementing, and troubleshooting databases. They also handle tasks like capacity planning, performance monitoring, and data recovery.