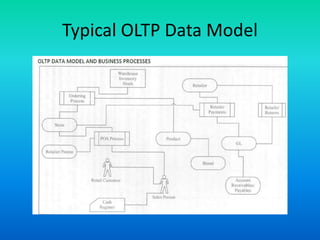
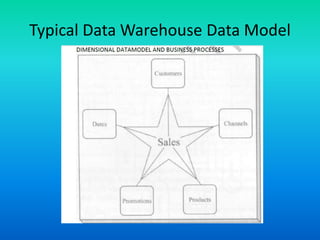
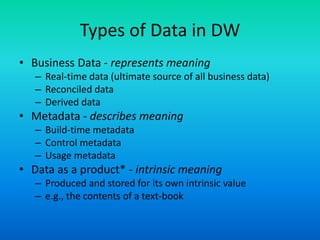
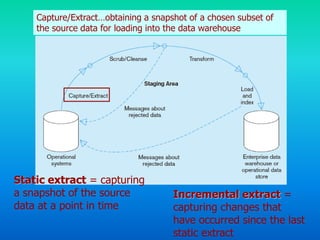
This document discusses data transformation in data warehousing. It explains that data warehouses contain large, historical datasets used for analysis rather than transactional data. The data undergoes ETL processing to reconcile inconsistencies and make it comprehensive, historical, and of high quality. This includes extracting data from operational databases, transforming it through cleansing and deriving new attributes, and loading it into the data warehouse where it can be analyzed.