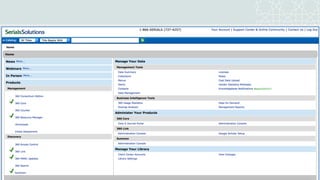
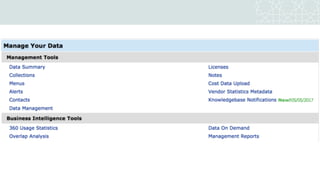
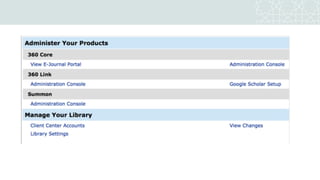
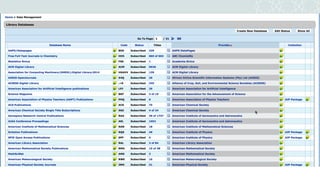
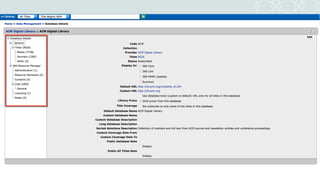
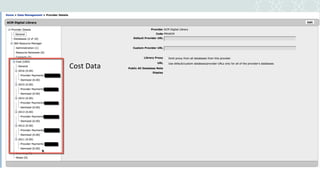
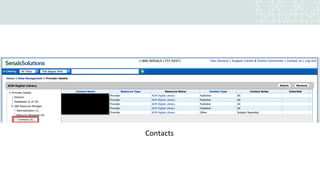
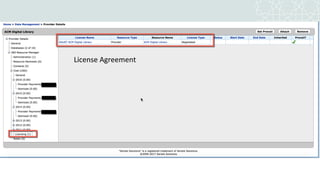
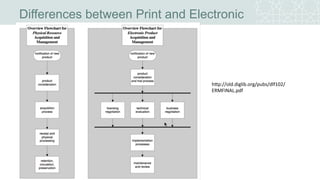
The document outlines a project to migrate data from an outdated electronic resources management system (ERMS) to a new platform, focusing on reviewing market options and implementing a suitable ERMS for the King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) library. It details the project's three phases: data migration, recommending a new ERMS, and its implementation, highlighting key deliverables and team responsibilities. An evaluation of existing ERMS options led to the recommendation of ProQuest 360 Resource Manager, which aligns with the library's needs and existing products.





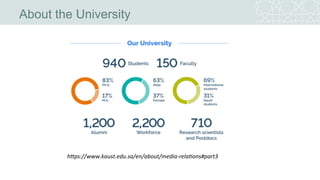
![• King Abdullah University of Science and Technology was inaugurated on Sept 23,
2009
• International Graduate Research University
• “Located on the Red Sea at Thuwal,[8] is sited on more than 36 square kilometres
(14 sq mi), encompassing a marine sanctuary, museum, and research facility.”
• Close to 700 students from 63 nations enrolled for 2010
• KAUST aspires to be a destination for scientific and technological education and
research
• KAUST advances science and technology through distinctive and collaborative
research integrated with graduate education
https://www.kaust.edu.sa/en/about/vision
About the University](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ermsimplementation2017-170517122712/85/From-Millennium-ERMS-to-Proquest-360-Resource-Manager-8-320.jpg)