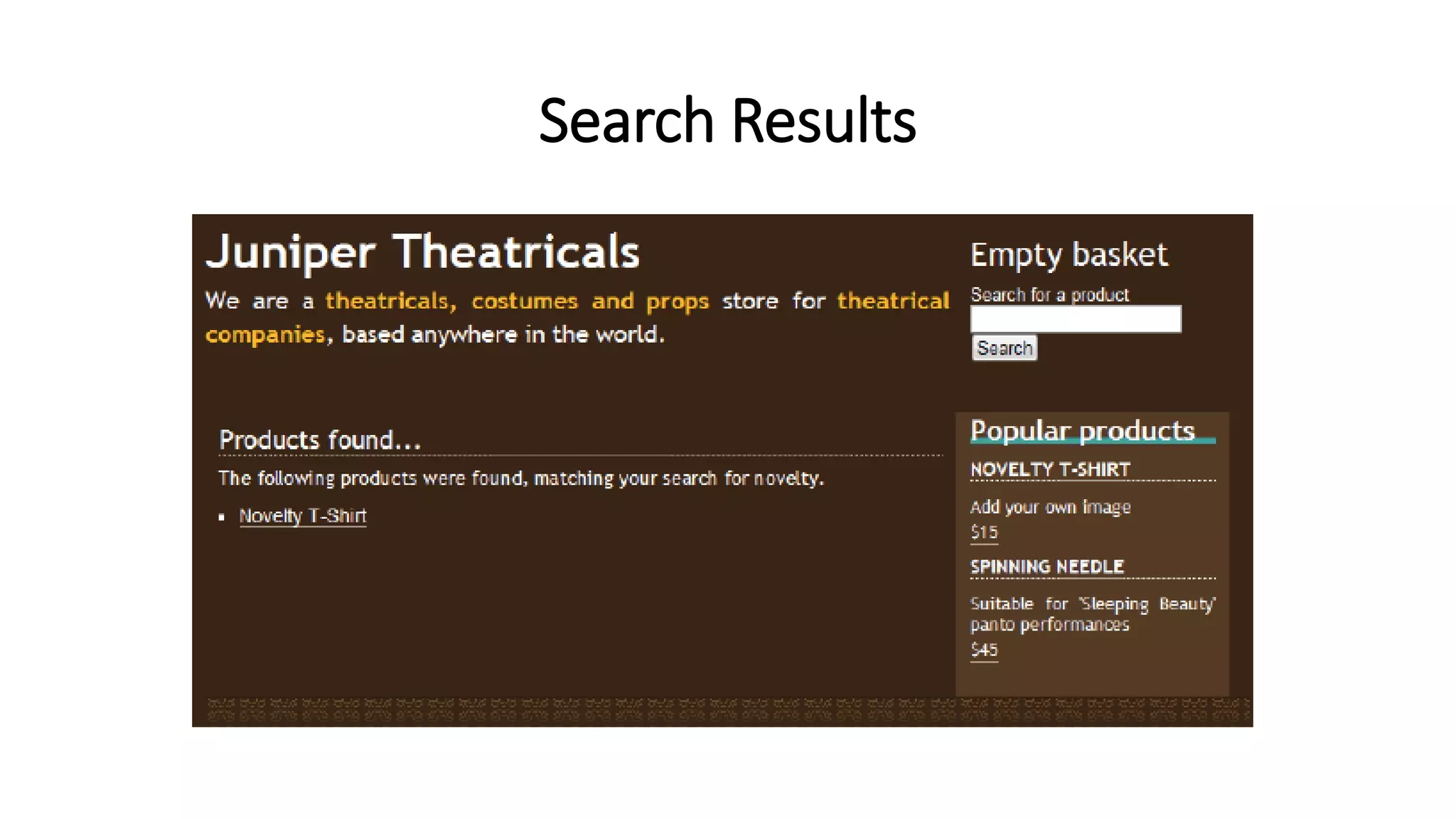
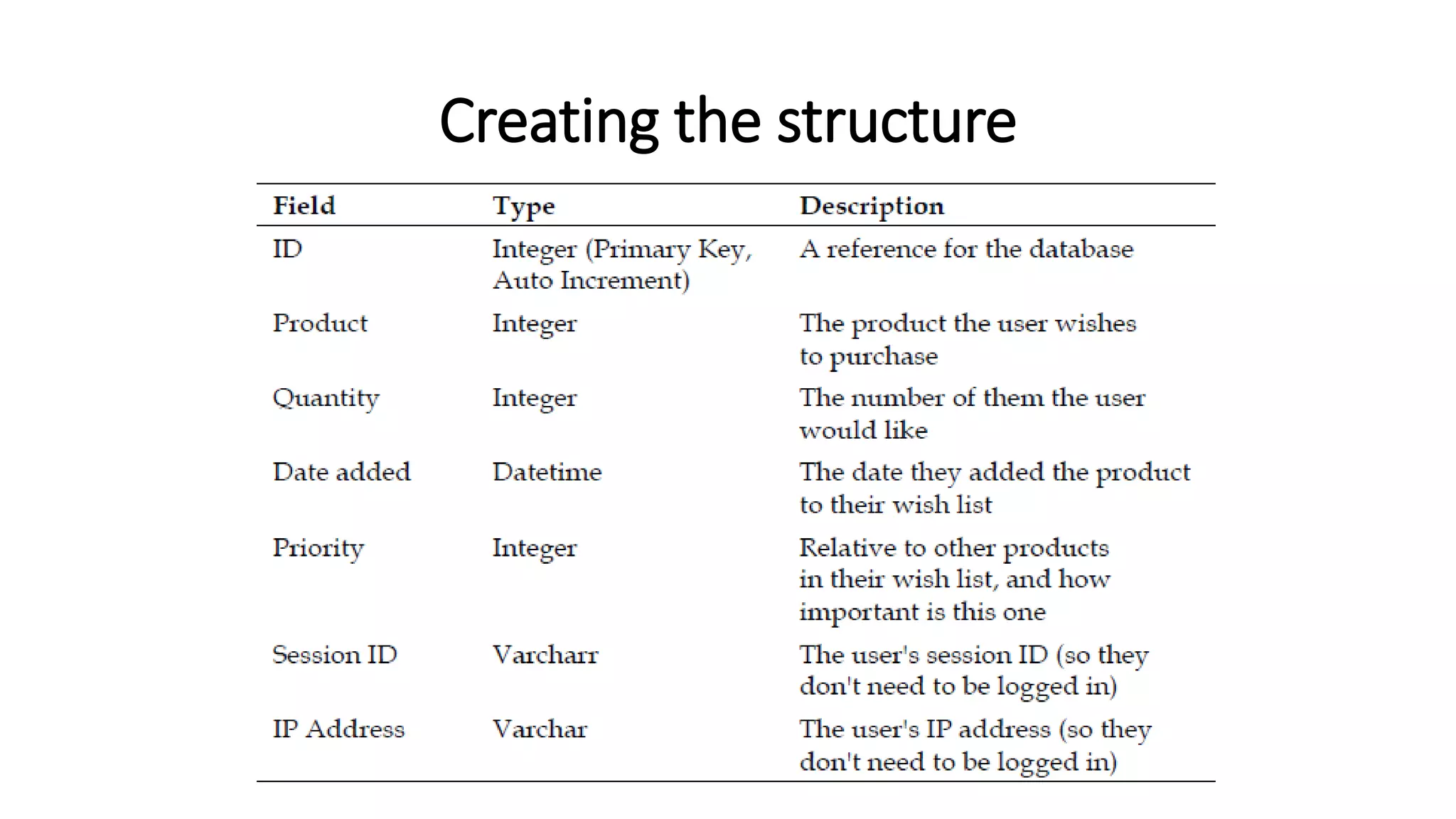
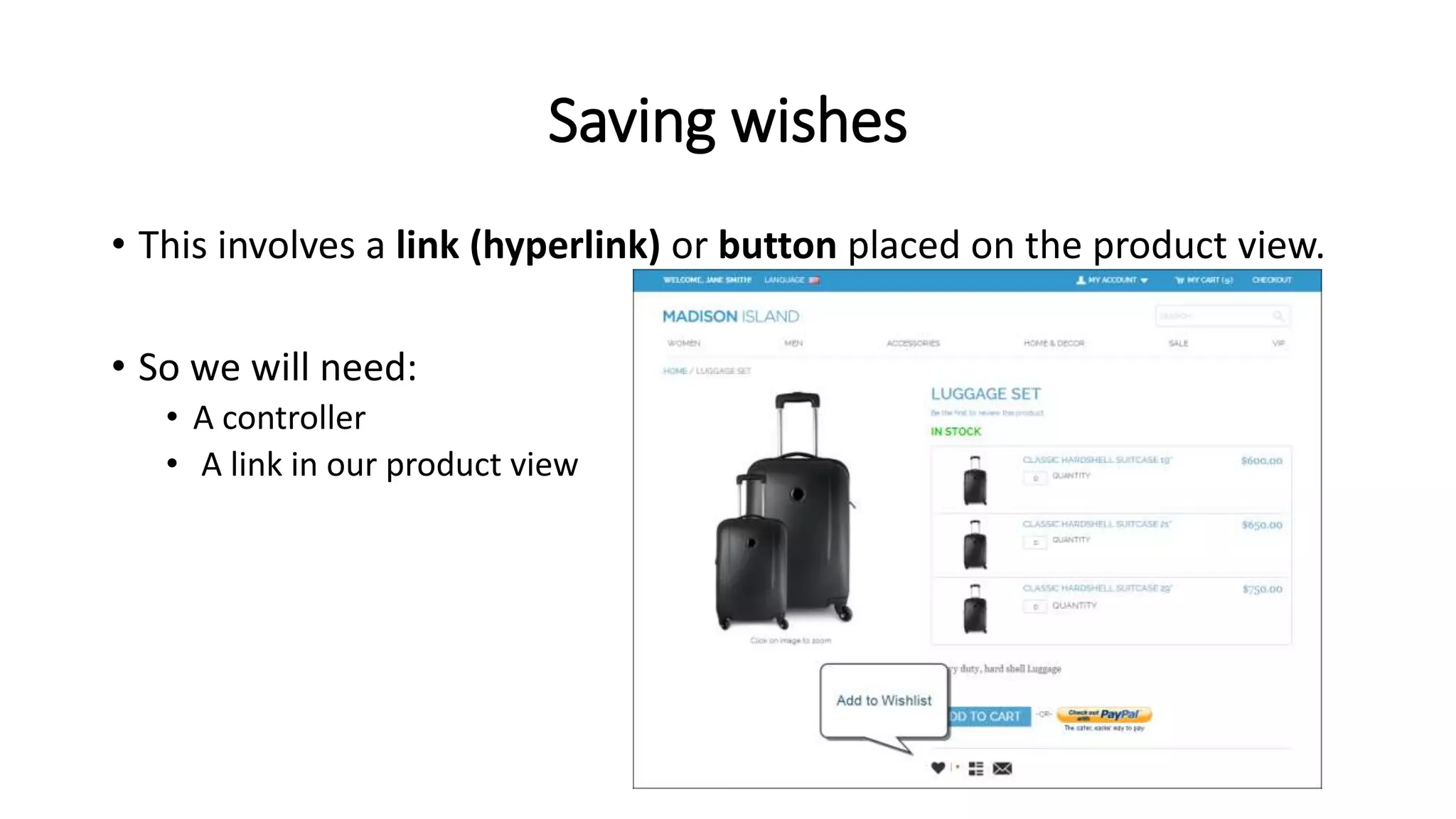
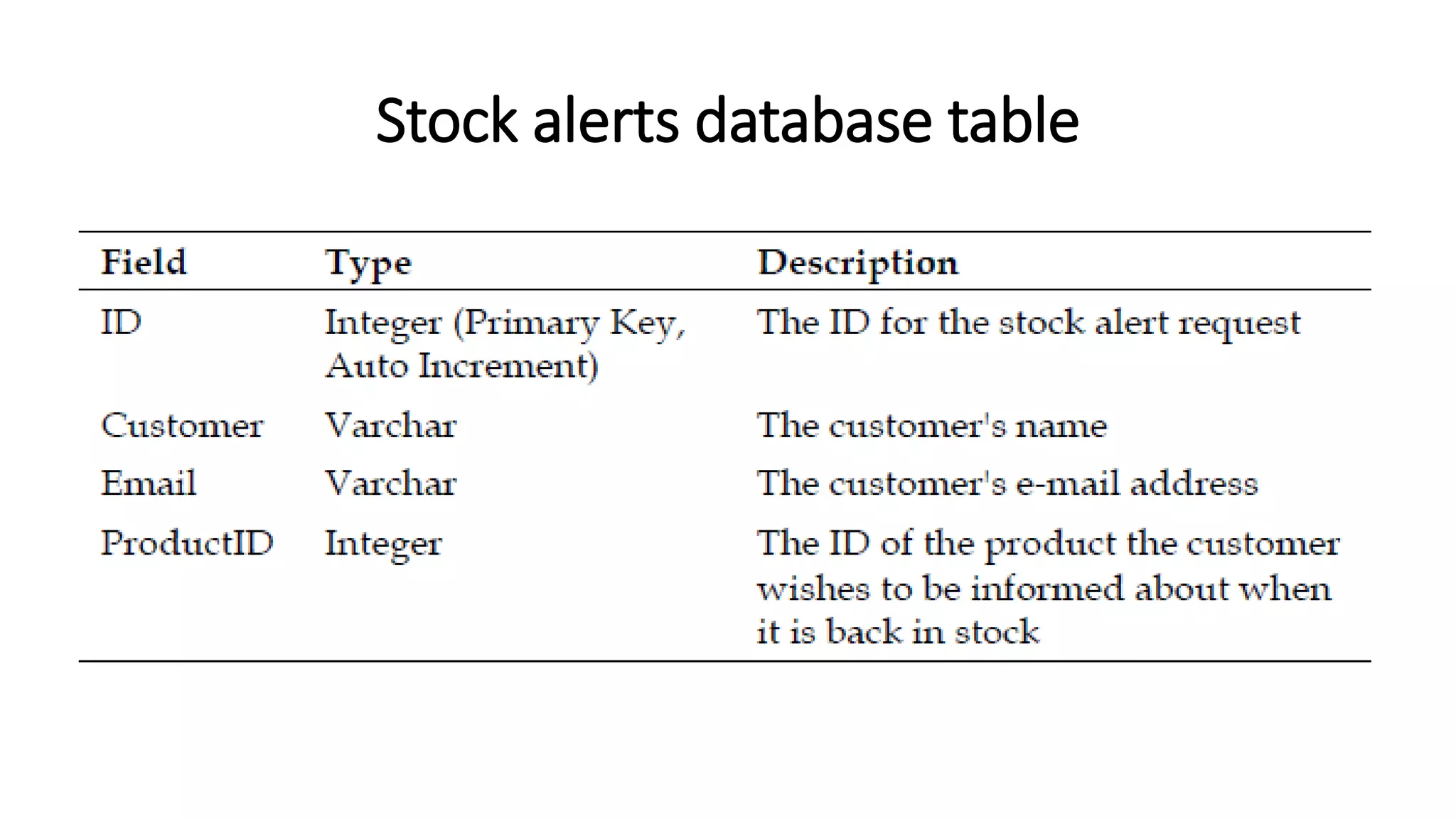
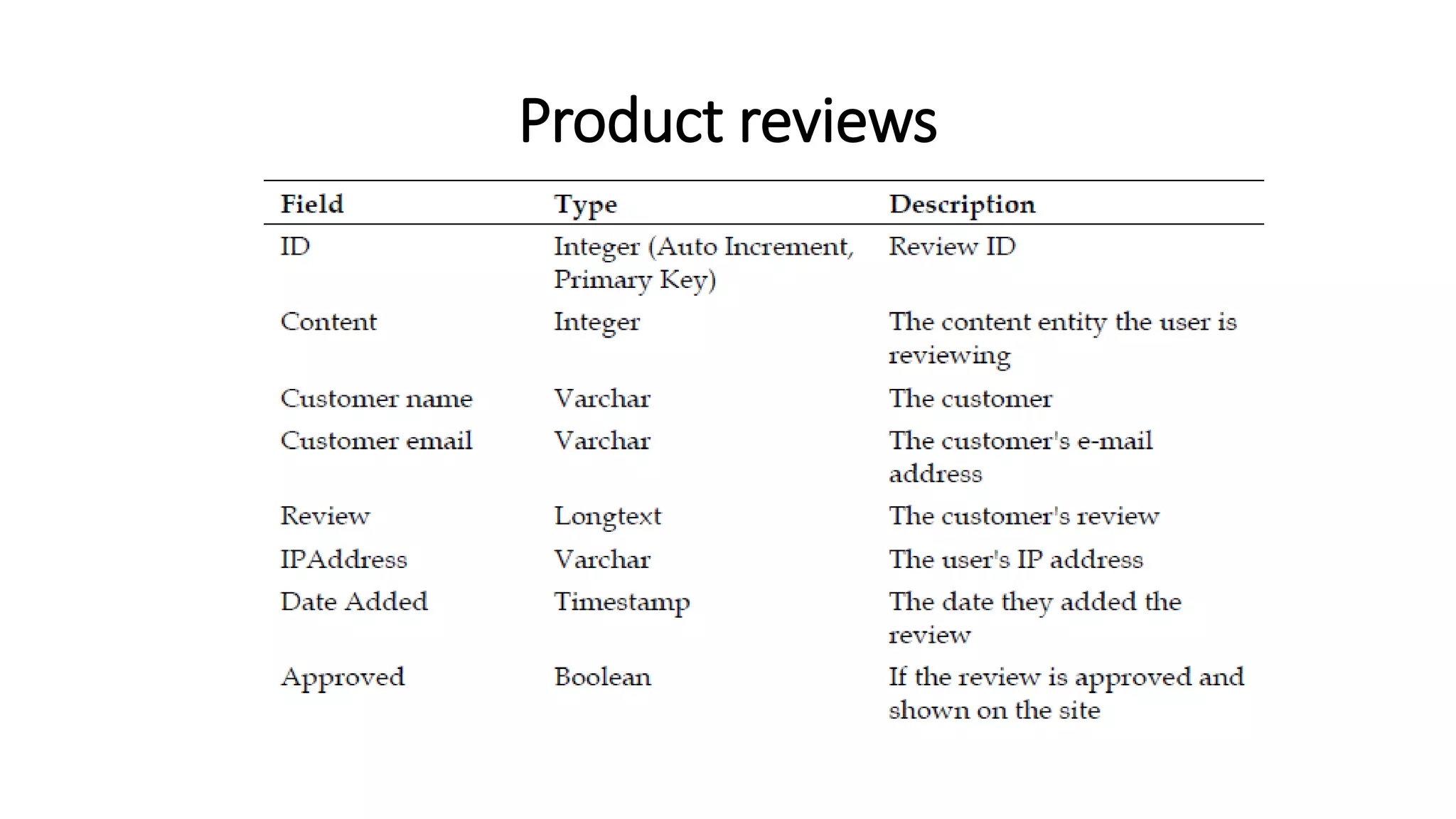
The document discusses various methods to enhance user experience in e-commerce applications, including effective product search functionality, wish list management, stock alerts, and product recommendations. It emphasizes the importance of features like filtering products, storing user preferences, and notifying customers about stock availability or related products. Additionally, it outlines technical implementations for these features, such as modifying database structures and creating user interfaces for interaction.






![Constructor changes
switch( $urlBits[1] )
case 'view’:
$this->viewProduct();
break;
case 'search’:
$this->searchProducts();
break;
default:
$this->listProducts();
break;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/05ecom-220509033848-ad332d2b/75/Enhancing-the-User-Experience-7-2048.jpg)
![Search function
private function searchProducts()
{
// check to see if the user has actually submitted the search form
if( isset( $_POST['product_search'] ) &&
$_POST['product_search'] != ‘’ )
…
…
…
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/05ecom-220509033848-ad332d2b/75/Enhancing-the-User-Experience-8-2048.jpg)