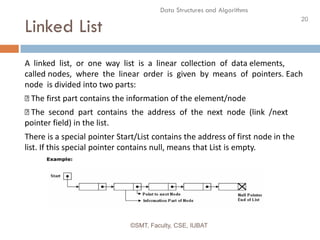
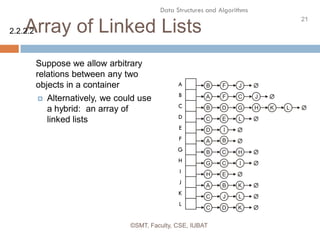
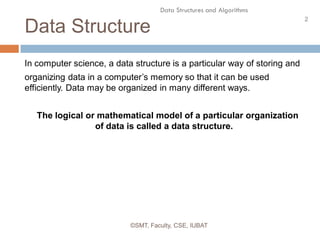
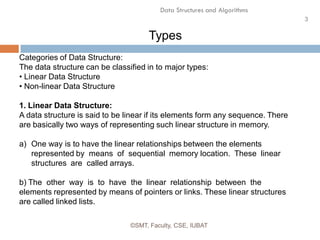
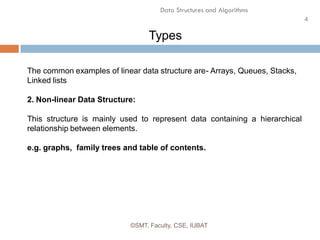
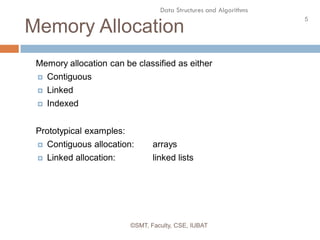
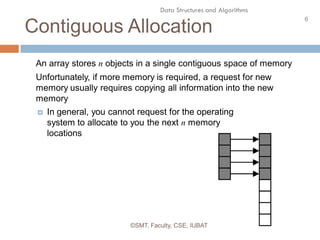
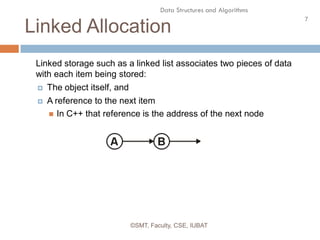
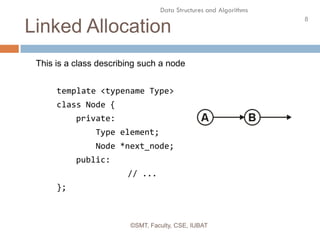
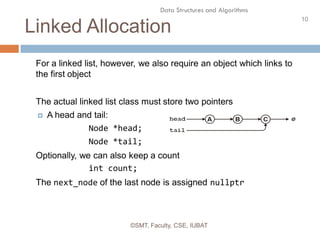
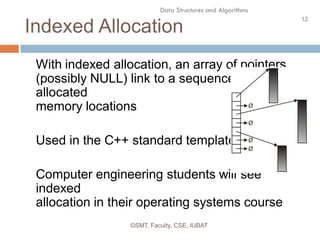
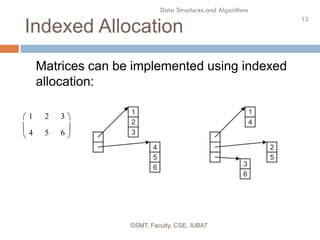
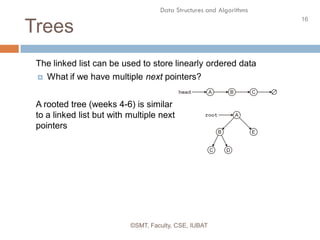
This document discusses data structures and their organization in computer memory. It defines a data structure as a way of storing and organizing data in memory for efficient use. There are two main types of data structures - linear and non-linear. Linear data structures like arrays and linked lists represent sequential relationships, while non-linear structures like trees and graphs represent hierarchical relationships. Memory can be allocated contiguously, linked, or indexed to implement different data structure formats. Common examples discussed are arrays, linked lists, stacks, queues, trees and graphs.




![19
Data Structures and Algorithms
Arrays
©SMT, Faculty, CSE, IUBAT
2.2.2.2
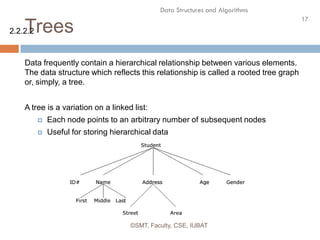
The simplest type of data structure is a linear (or one dimensional)
array. A list of a finite number n of similar data referenced respectively
by a set of n consecutive numbers, usually 1, 2, 3 . . . . . . . n. if we choose
the name A for the array, then the elements of A are denoted by subscript
notation A 1 , A 2 , A 3 . . . . A n
or by the parenthesis notation A (1), A (2), A (3) . . . . . . A (n)
or by the bracket notation A [1], A [2], A [3] . . . . . . A [n]
Example:
A linear array A[8] consisting of numbers is pictured in following figure](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/datastructures1-140521041431-phpapp02/85/Data-Structure-Basics-19-320.jpg)