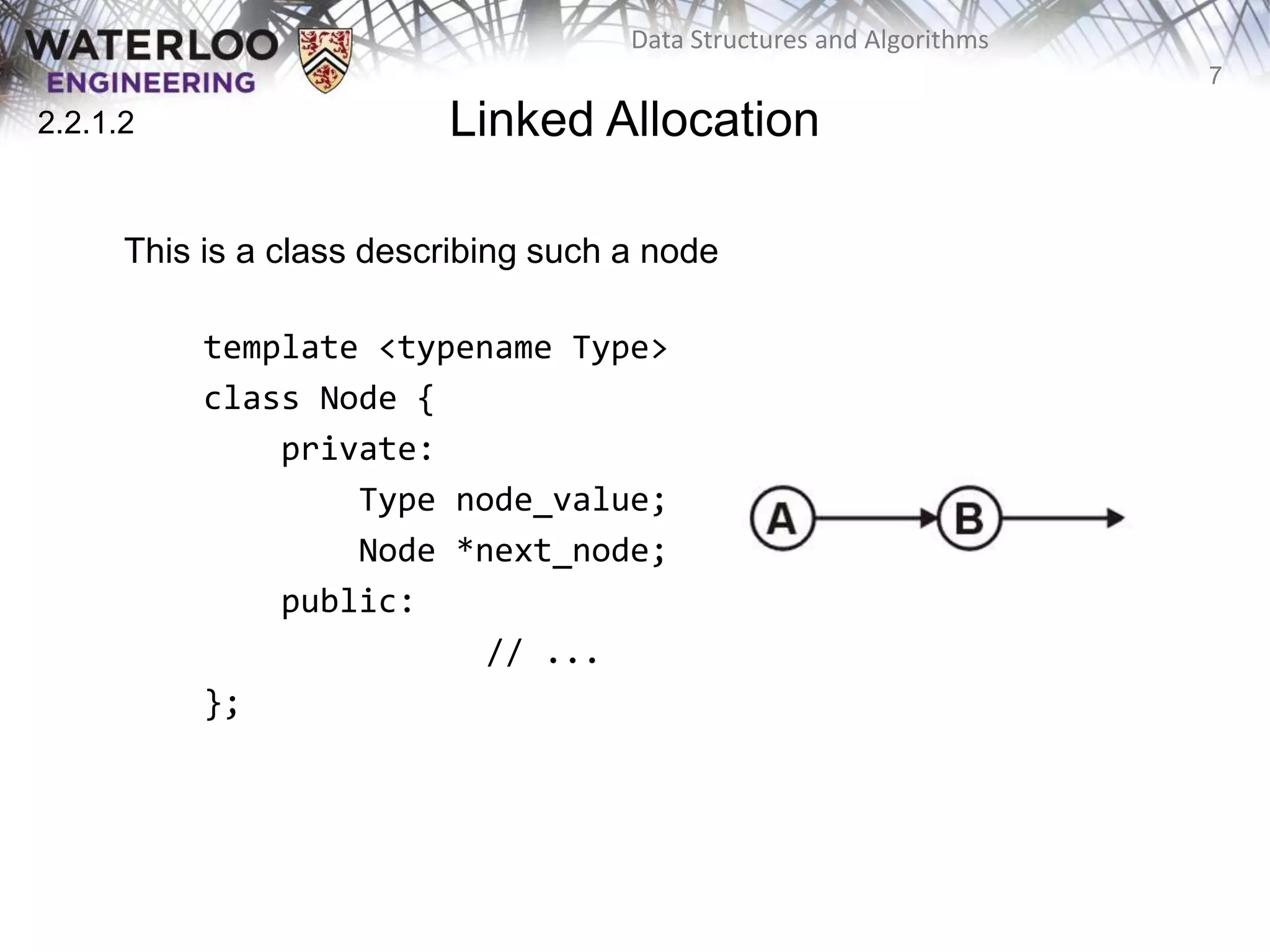
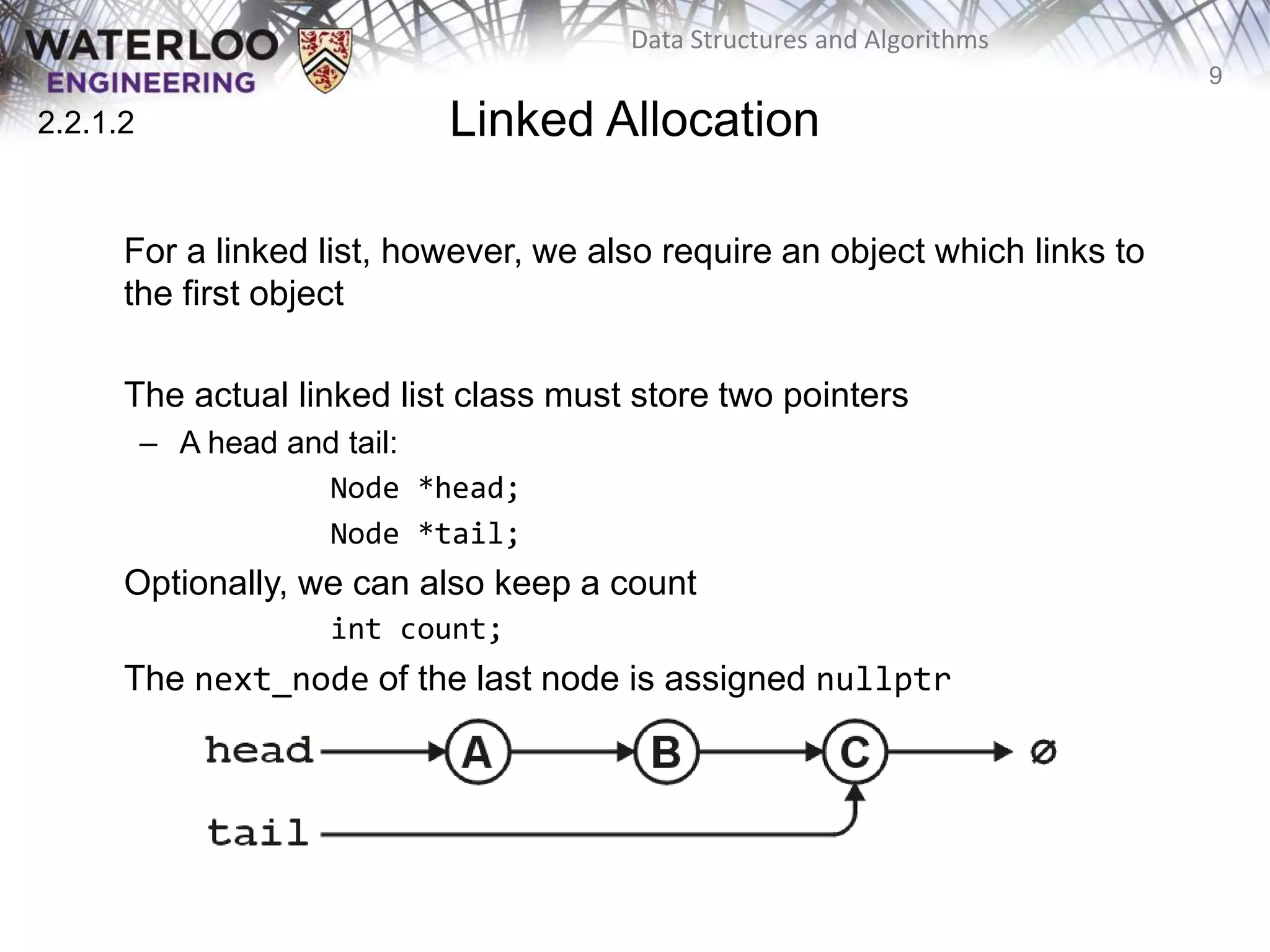
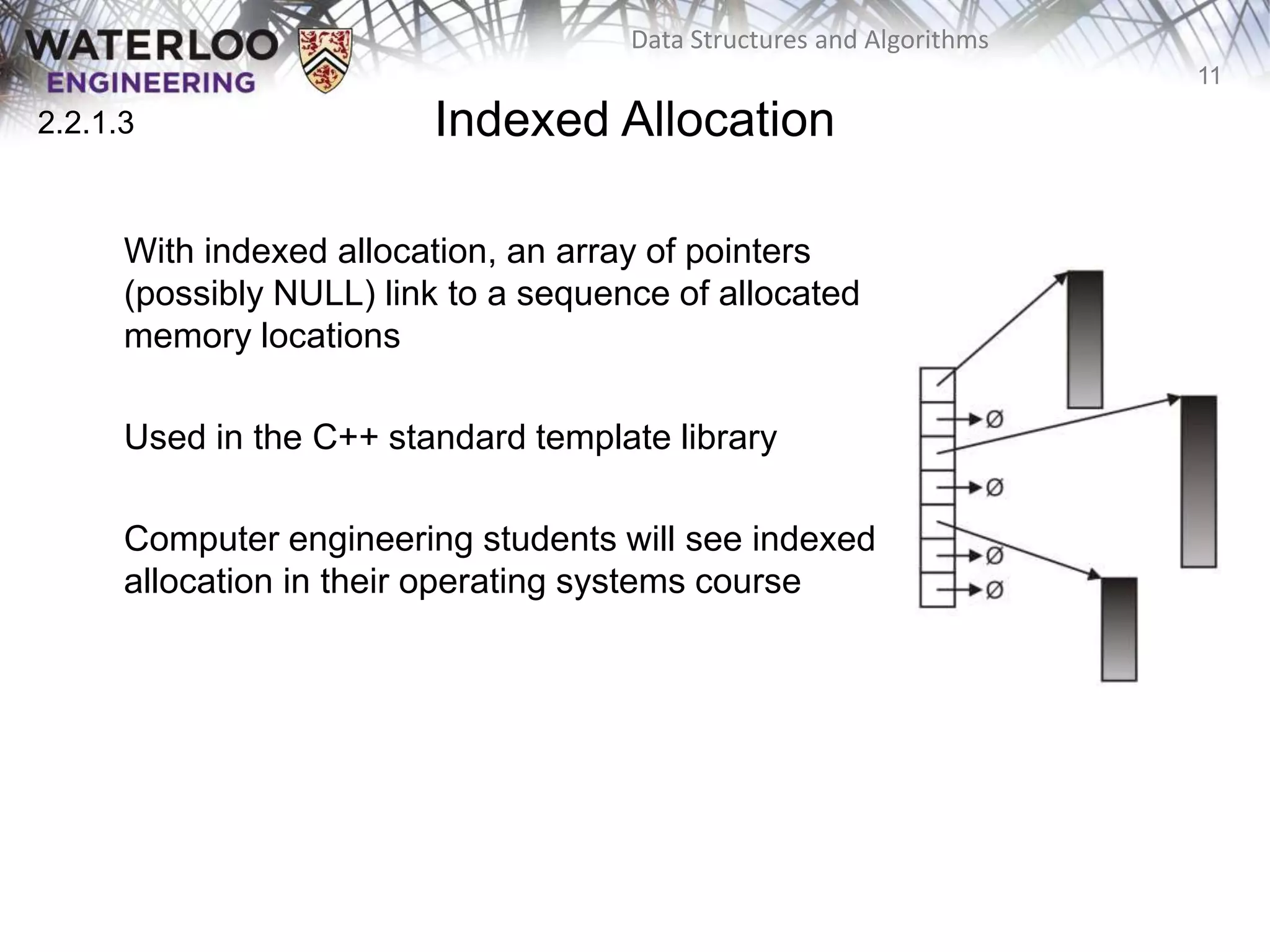
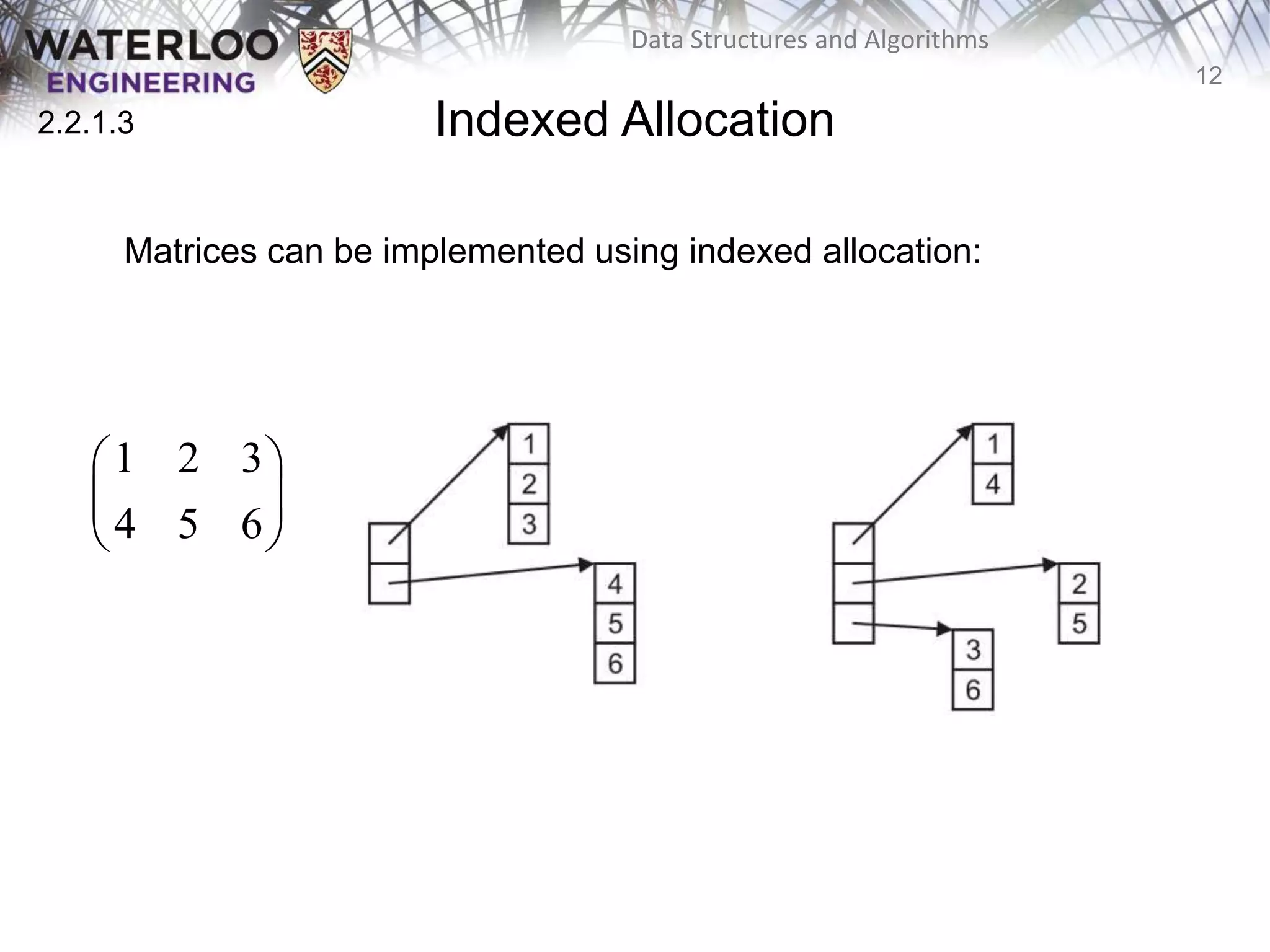
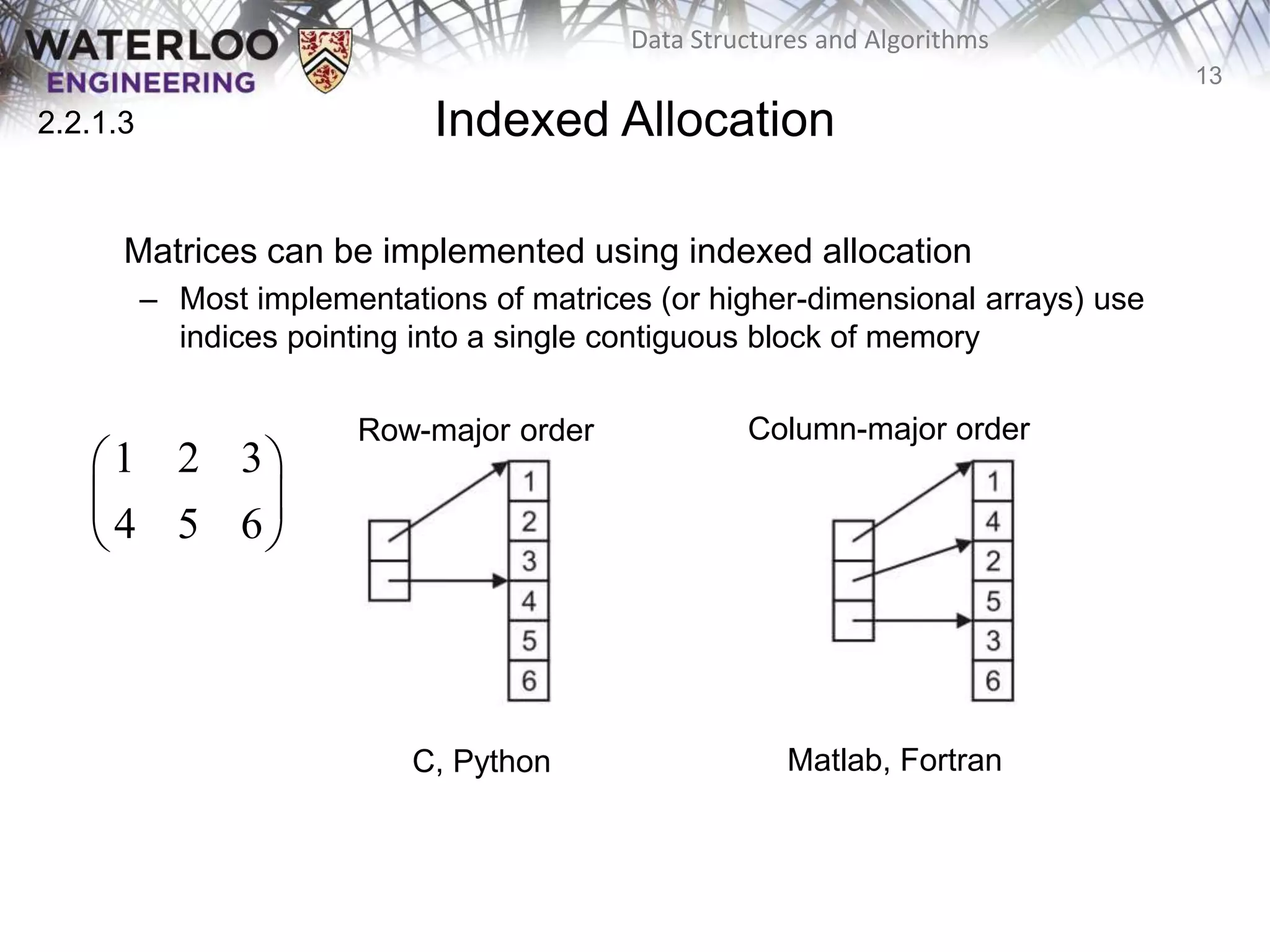
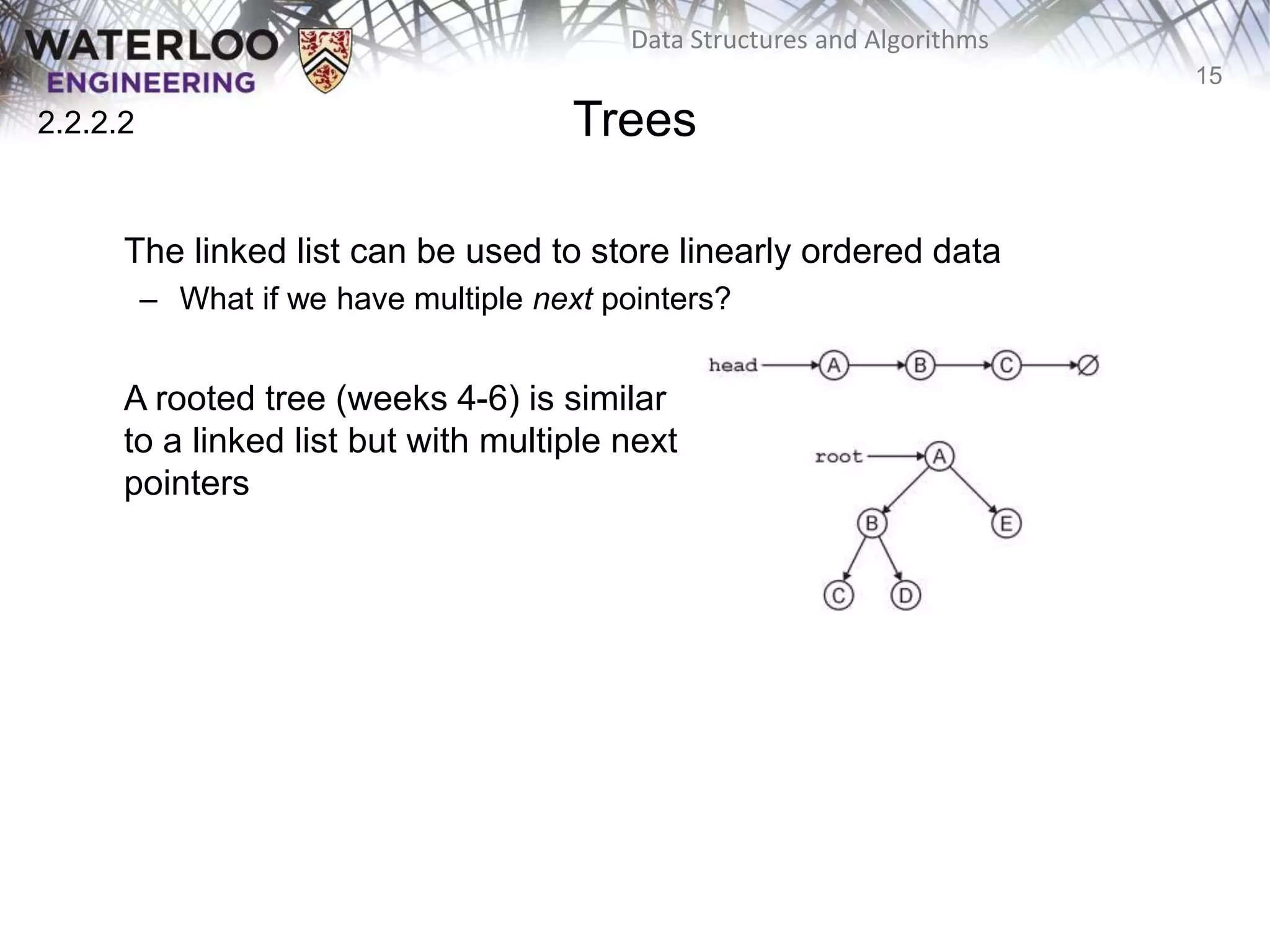
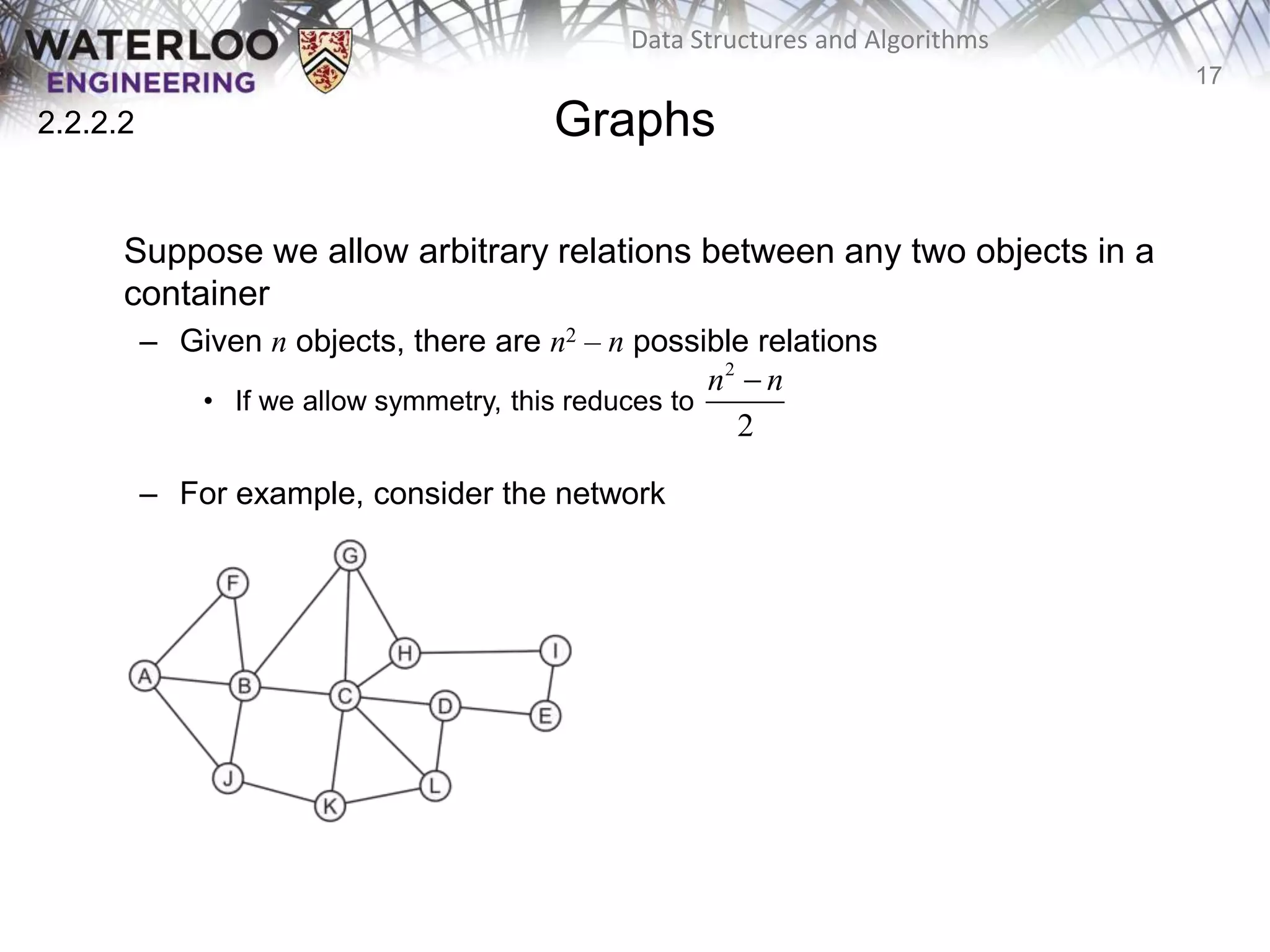
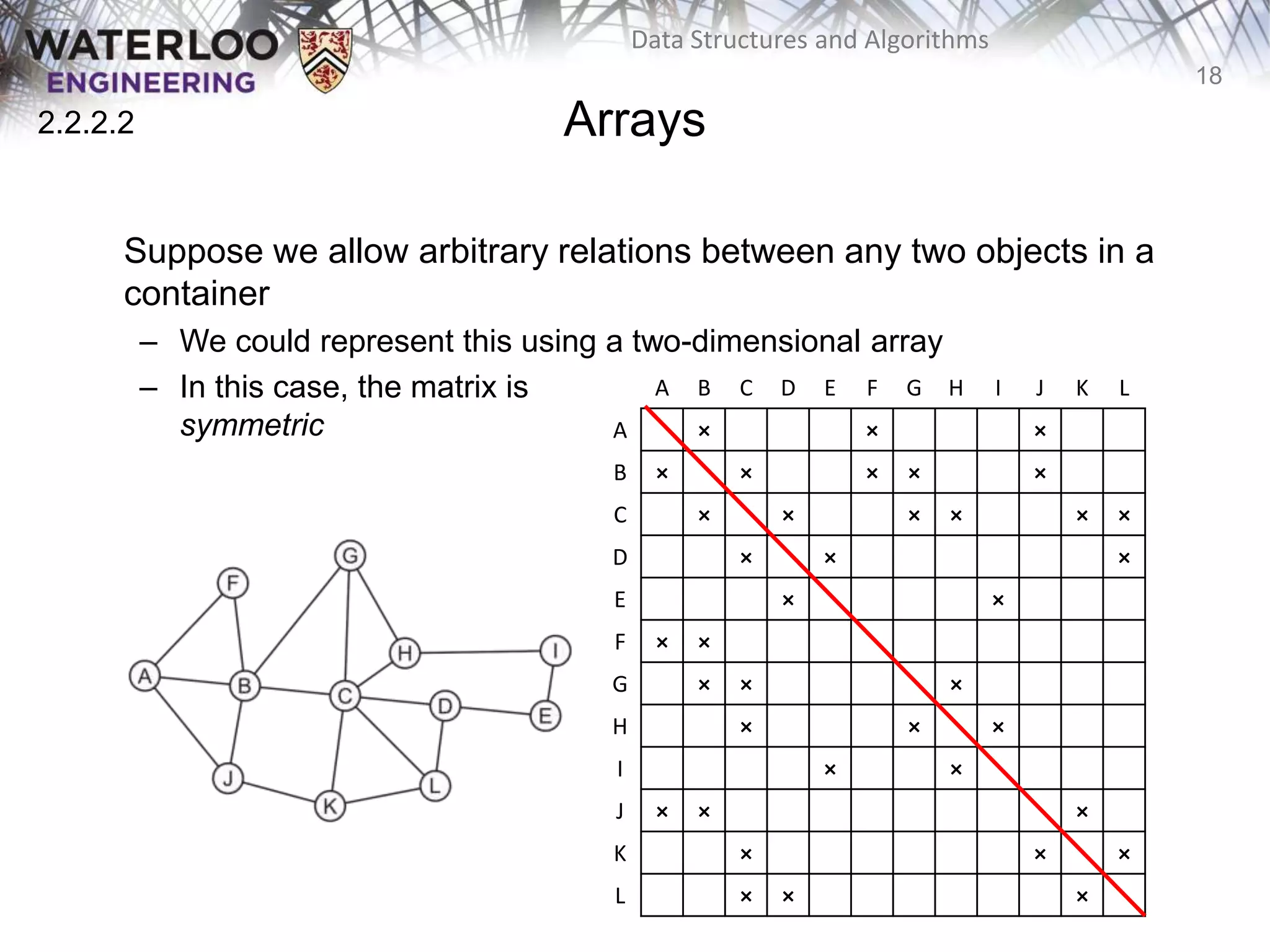
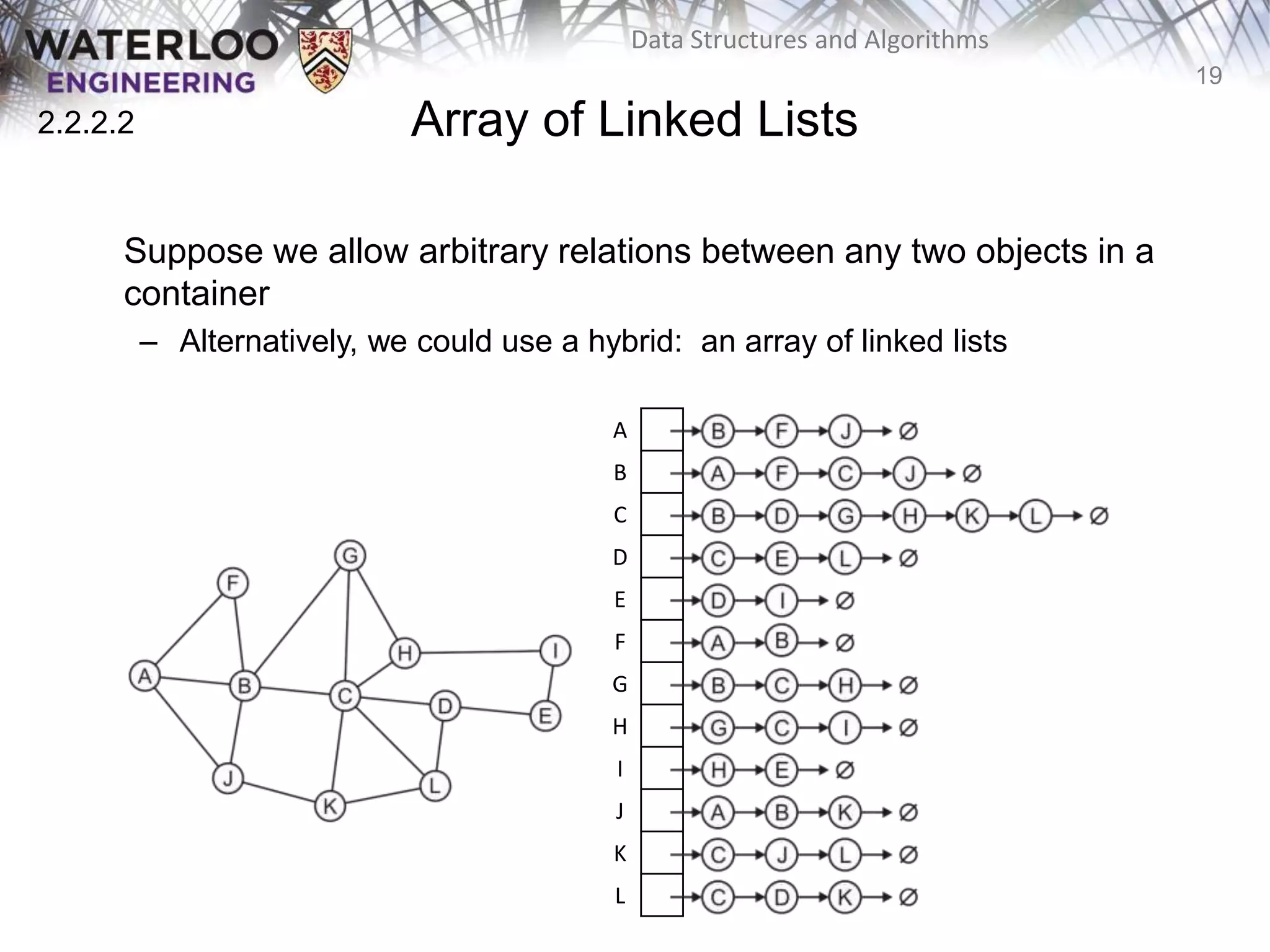
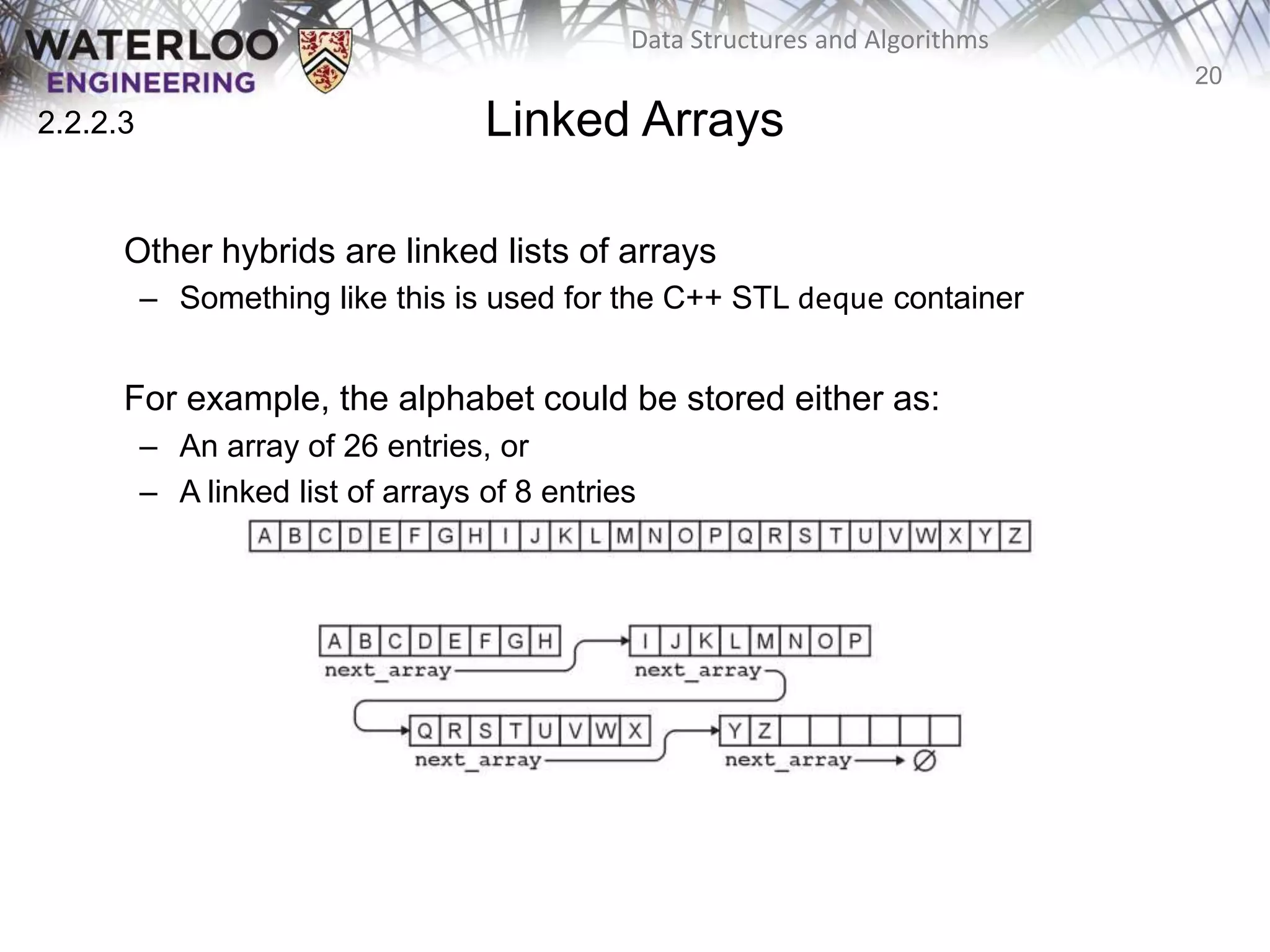
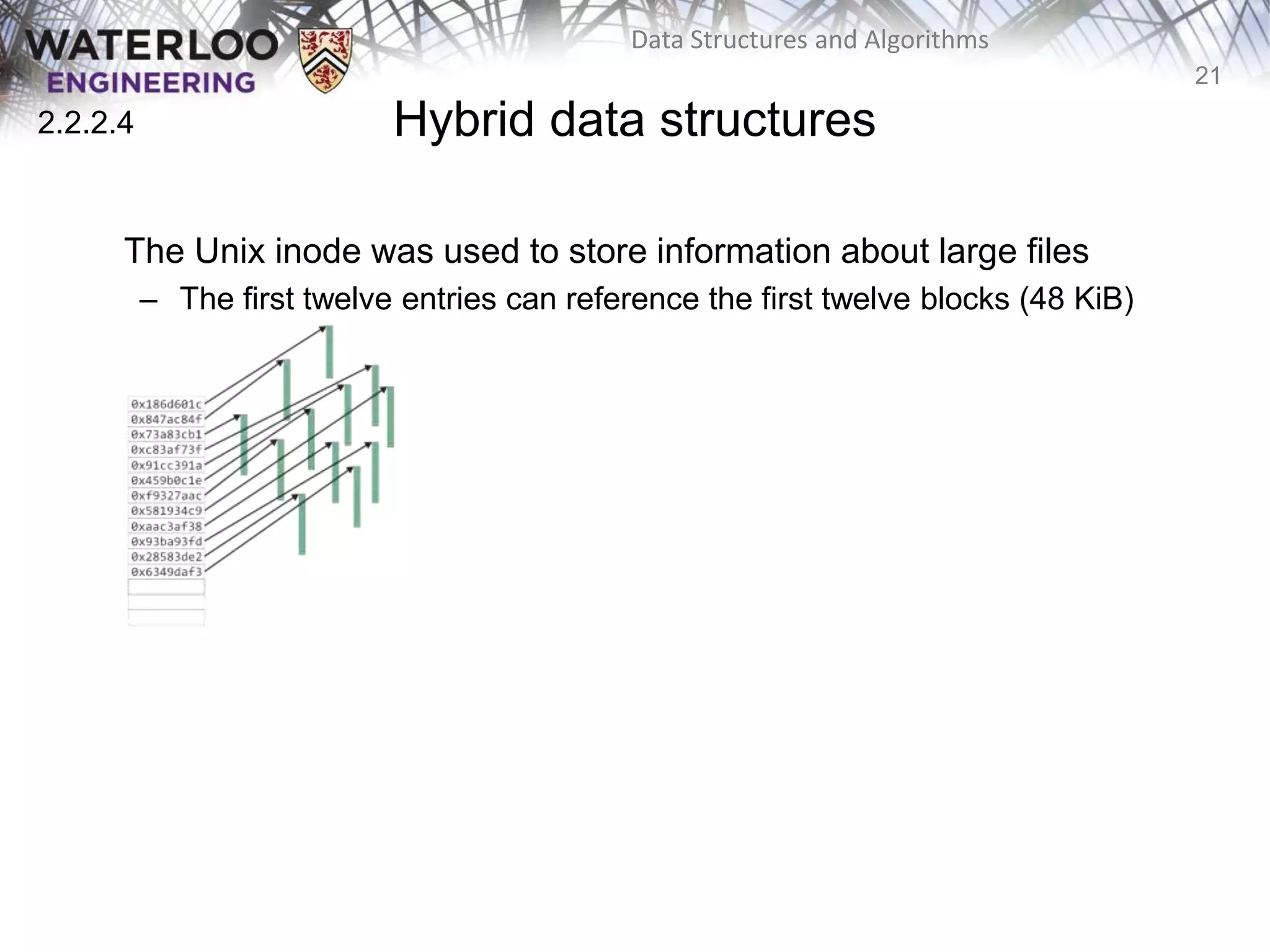
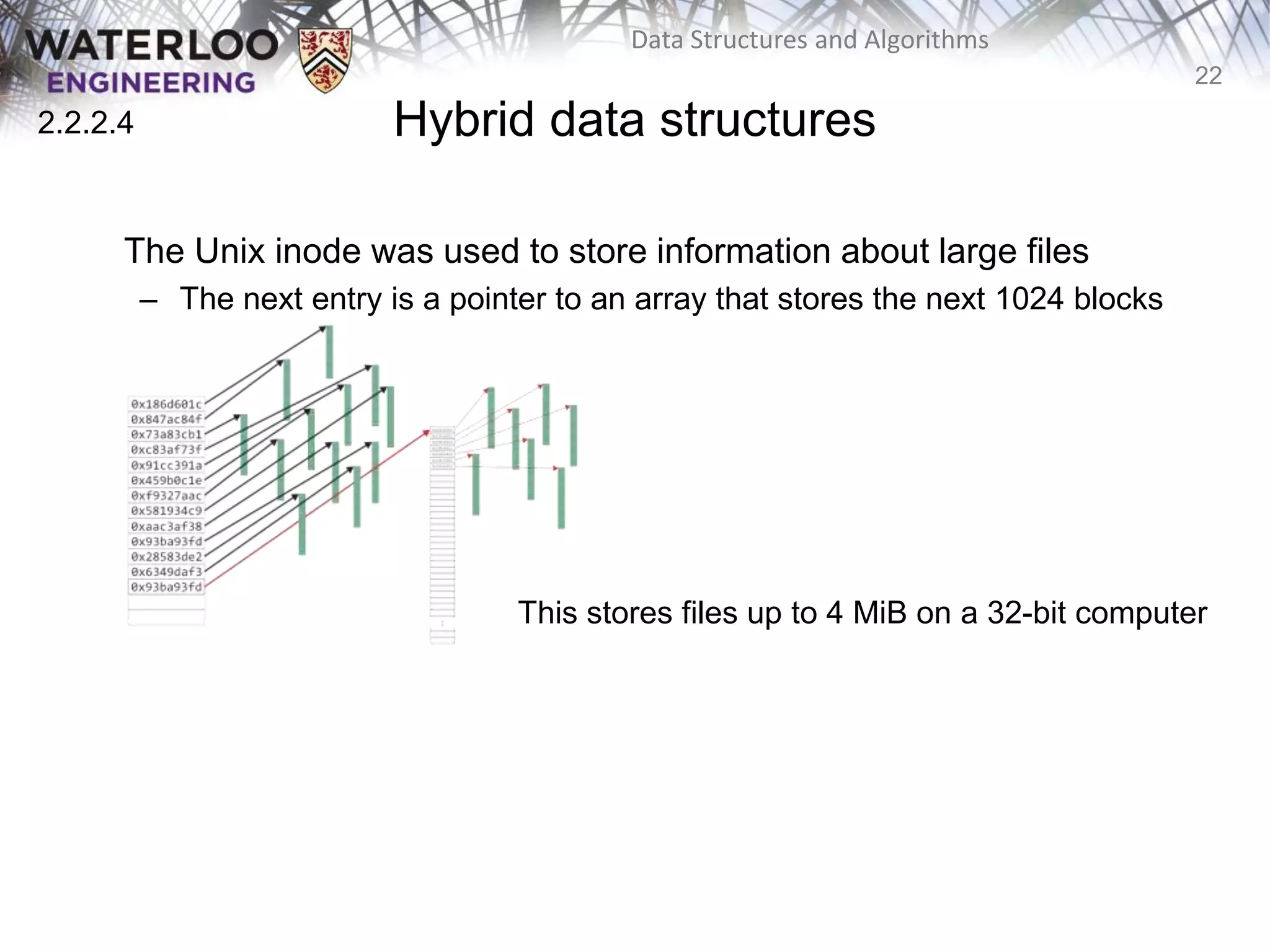
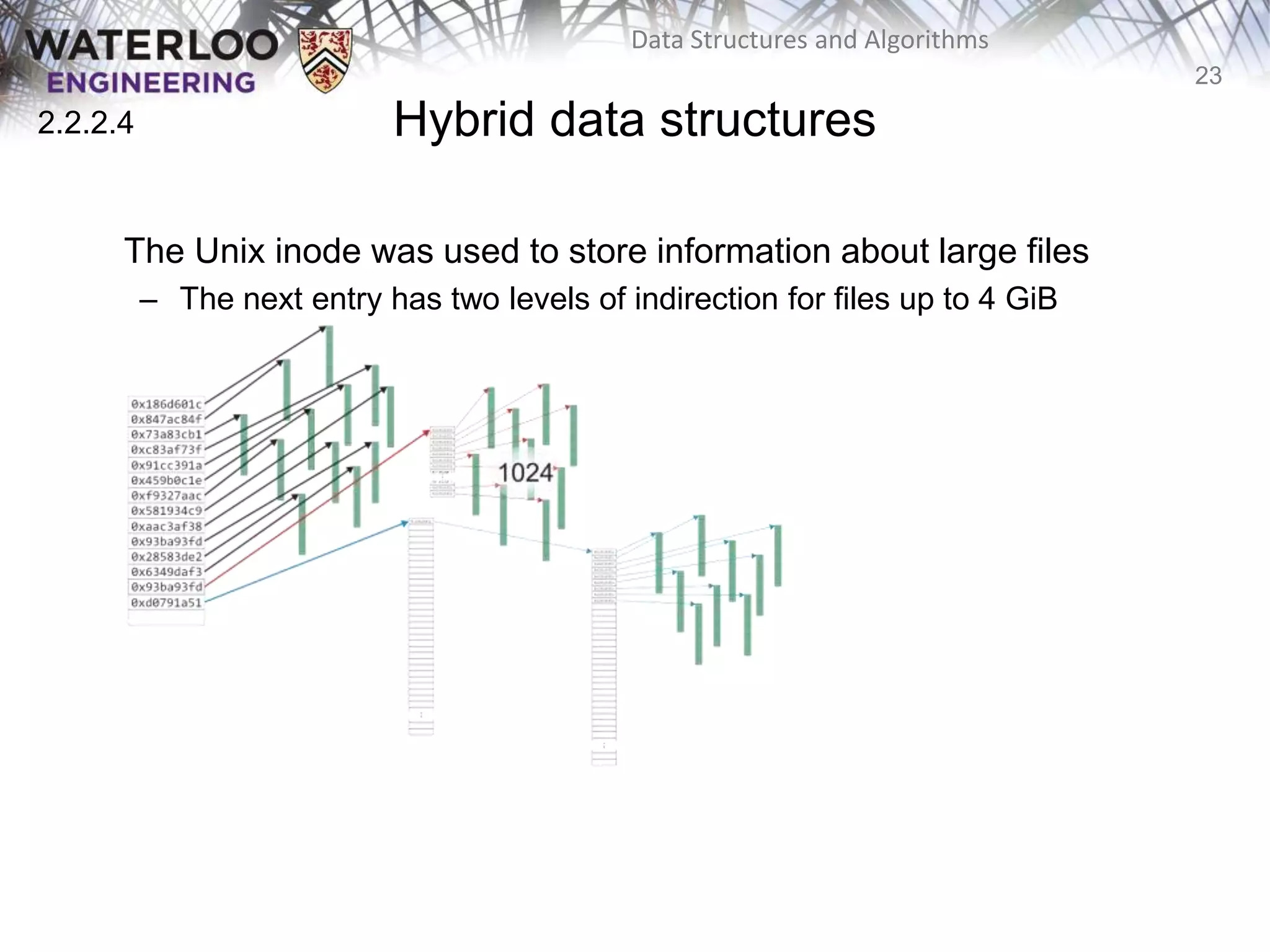
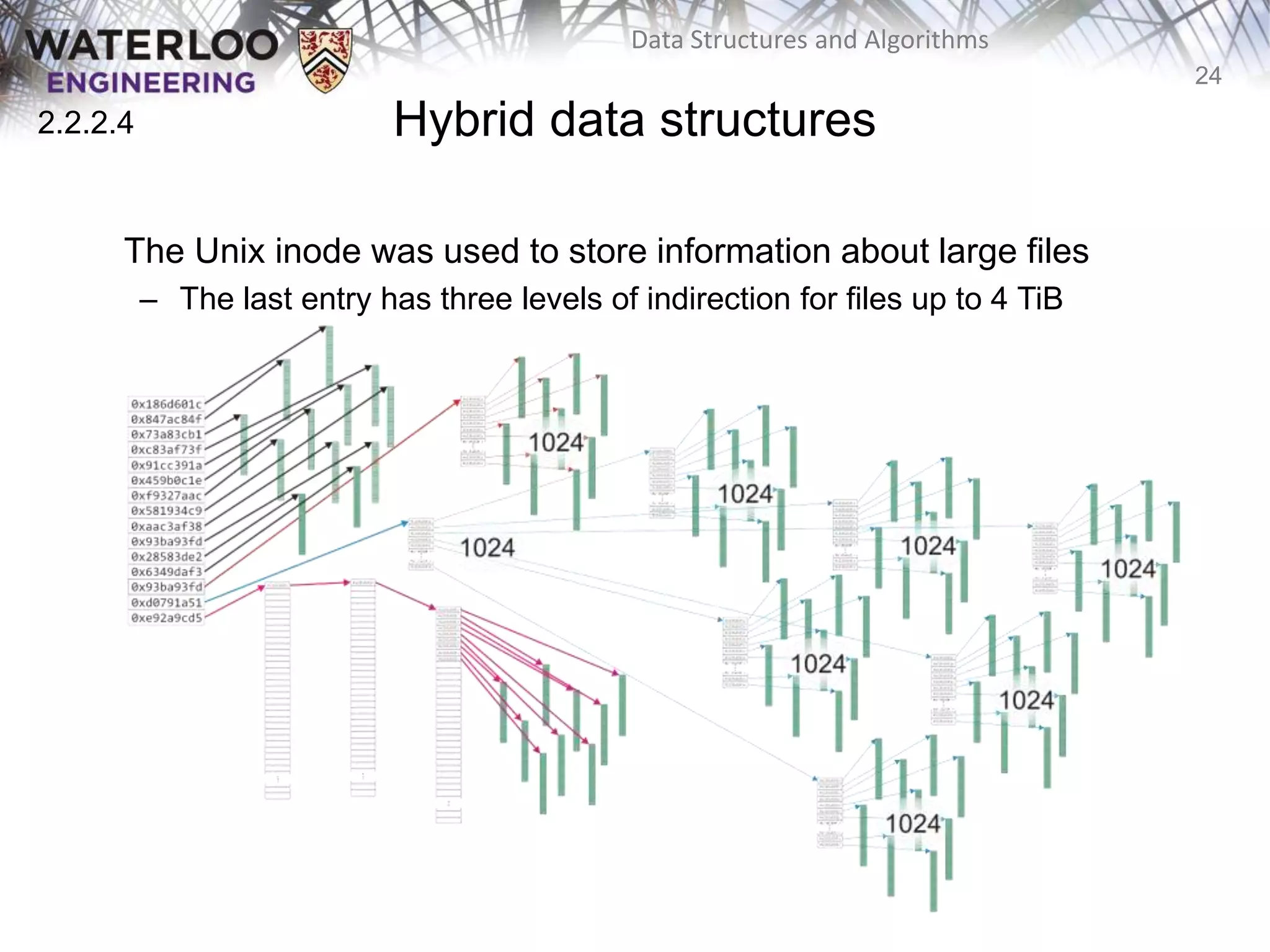
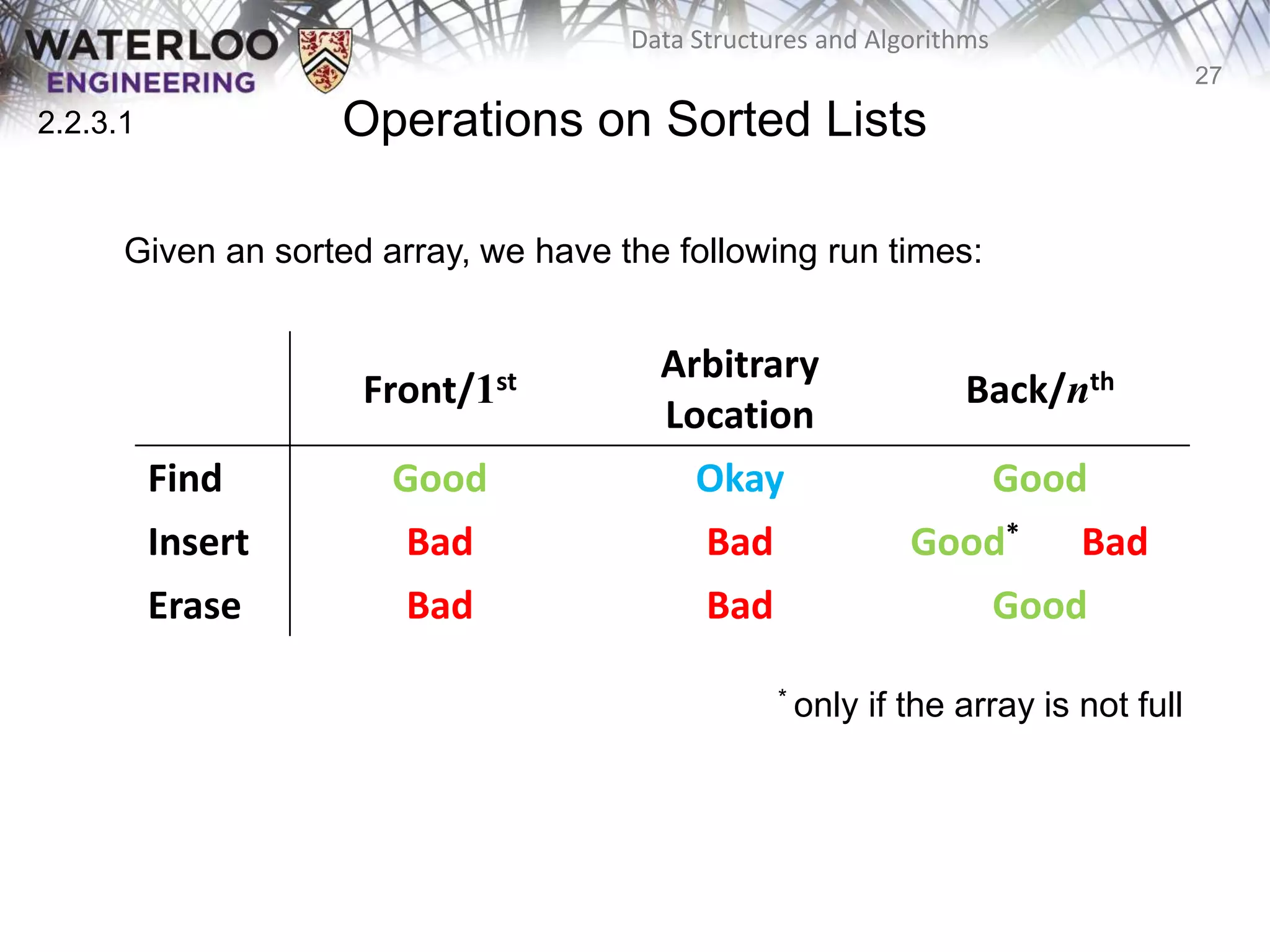
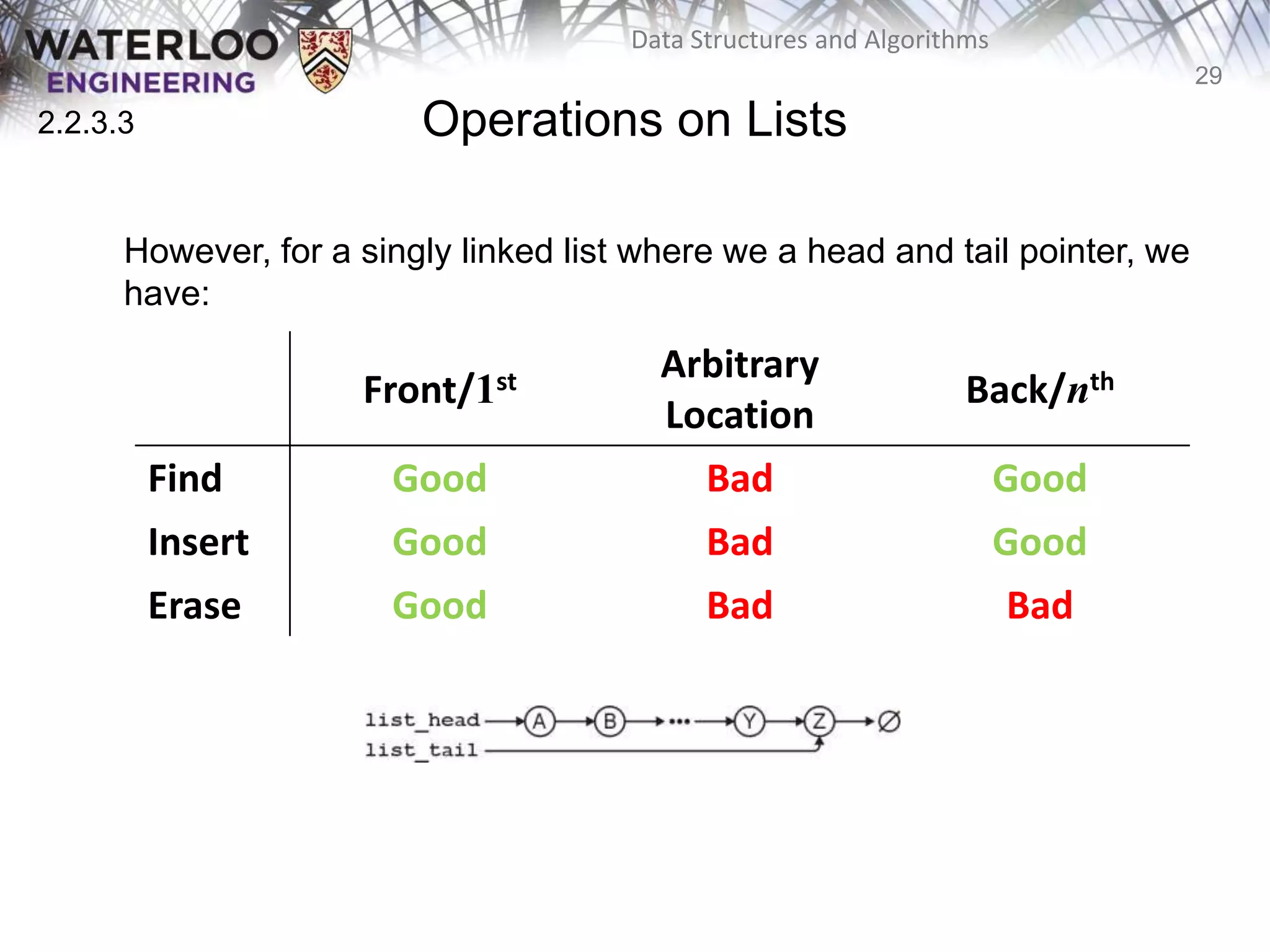
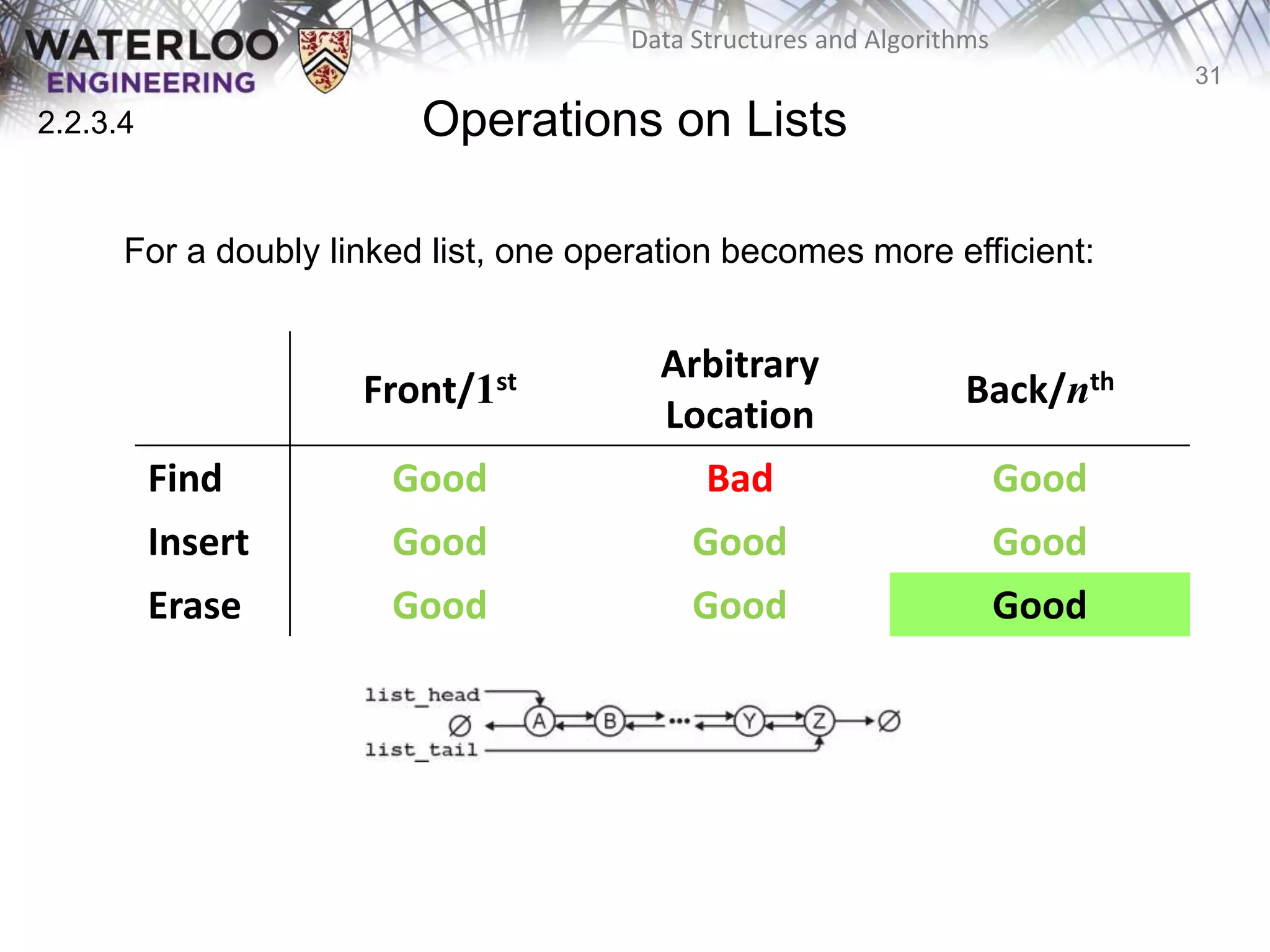
This document provides an outline and overview of key topics related to data structures and algorithms that will be covered in an ECE 250 course, including different types of memory allocation (contiguous, linked, indexed), examples of basic data structures (arrays, linked lists, trees), analysis of algorithm runtimes for different operations (find, insert, erase) on various data structures, and a brief overview of subsequent topics to be addressed in the course like asymptotic analysis, specific linearly ordered and relation-free data structures, sorting algorithms, and algorithm design techniques.