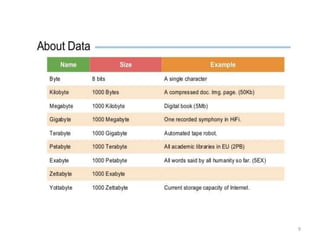
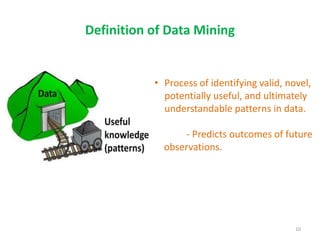
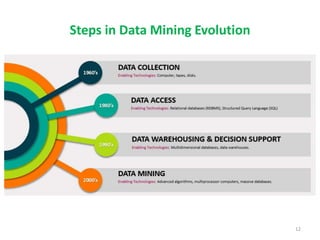
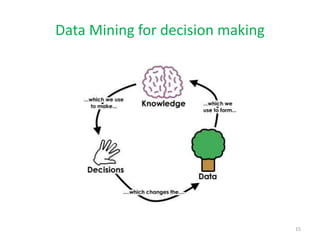
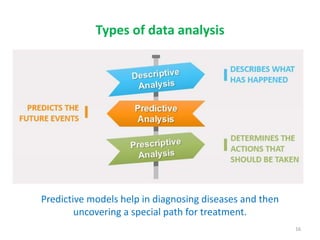
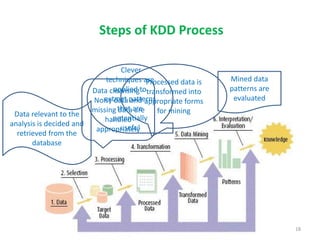
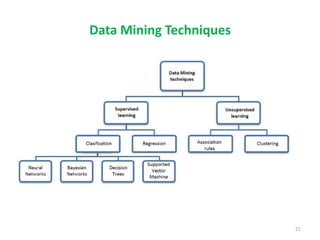
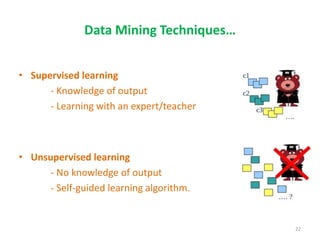
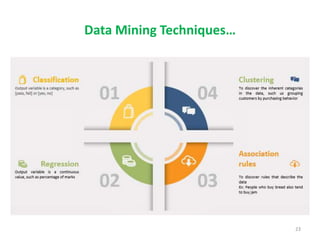
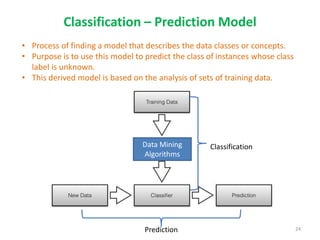
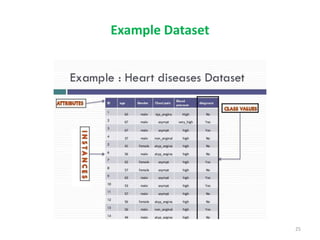
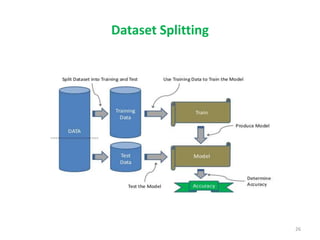
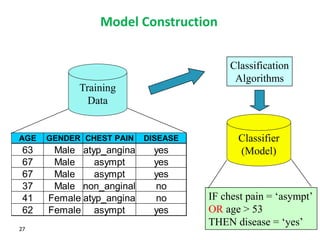
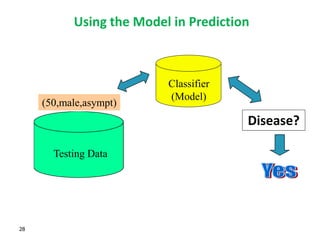
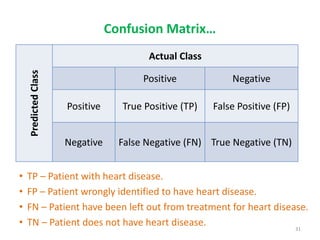
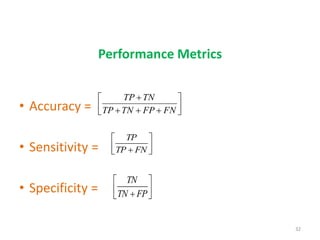
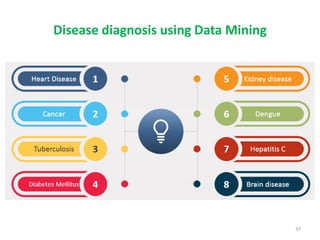
This document discusses data mining techniques and their applications in healthcare. It begins with an introduction to data mining, describing it as the process of identifying patterns in data. Several data mining techniques are covered, including classification models for prediction. The document then focuses on how these techniques can be used in healthcare for applications like disease diagnosis and treatment recommendations. Examples of data mining aiding healthcare include predicting patient health outcomes and uncovering specialized treatment paths for diseases.