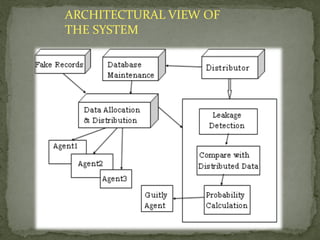
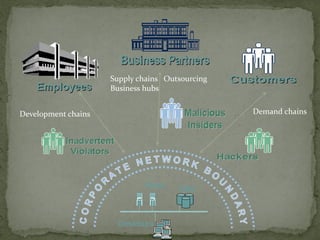
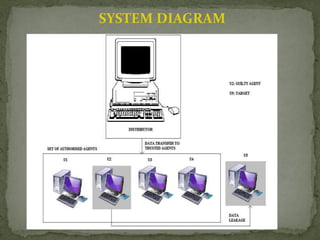
The document discusses data leakage from organizations to external parties. It proposes using watermarking and fake data objects to detect the source of leaks. The system would include modules for data allocation, fake objects, data distribution, and identifying guilty agents. The goal is to distribute data intelligently to improve detection of agents responsible for leaks, while satisfying data requests. Challenges include some data not supporting watermarks and dynamic agent requests.




![Watermarking
Overview:
A unique code is embedded in each distributed
copy. If that copy is later discovered in the hands of an
unauthorized party, the leaker can be identified.
Mechanism:
The main idea is to generate a watermark [W(x; y)]
using a secret key chosen by the sender such that W(x;
y) is indistinguishable from random noise for any
entity that does not know the key (i.e., the recipients).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dataleakagedetectionsuveeksha-160107070602/85/Data-leakage-detection-8-320.jpg)