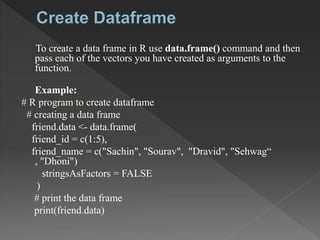
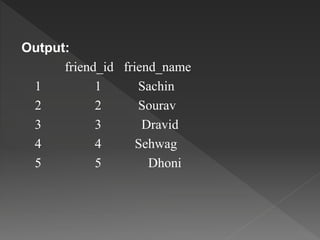
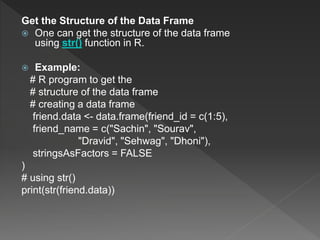
DataFrames in R are used to store tabular data with rows and columns. DataFrames can contain different data types in each column. They are created using the data.frame() function by passing vectors as arguments. Operations that can be performed on DataFrames include creating, accessing and selecting subsets of rows and columns, editing data, and adding or deleting rows and columns. The structure of a DataFrame can be examined using the str() function.