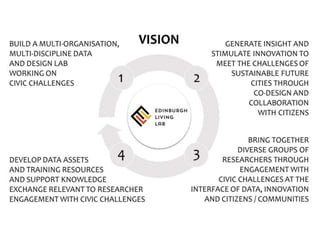
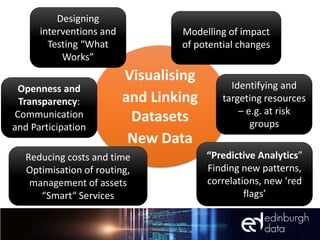
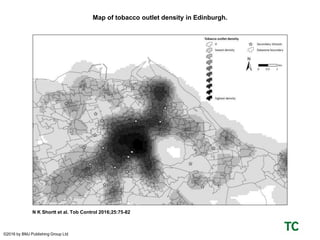
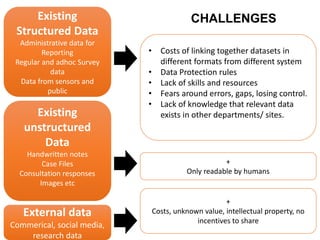
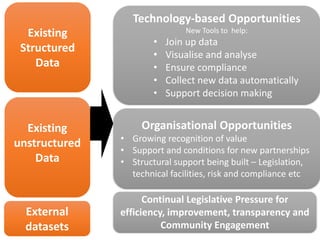
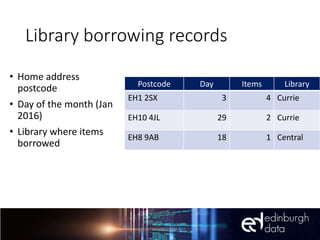
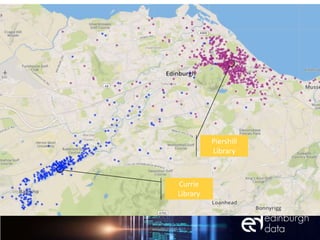
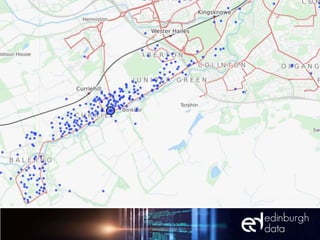
The document discusses the role of data and innovation in the public sector, highlighting the integration of various datasets to enhance decision-making and service delivery. It emphasizes the challenges of linking structured and unstructured data, as well as the importance of collaboration between public authorities, academia, and communities. Examples from cities like Edinburgh and Newcastle illustrate how data can be utilized for targeted interventions and community-oriented services.