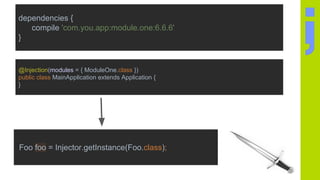
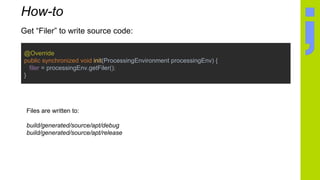
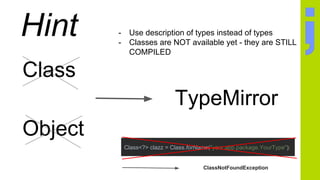
The document discusses annotation processing in Java, including libraries that are useful for annotation processing like Google AutoService and Square JavaPoet. It provides an overview of the basic structure of an annotation processor class and explains how to access elements from the source code being processed. It also covers how to generate new source code files using JavaPoet and write them out using the Filer. Debugging annotation processors is discussed.














![AnnotationProcessor
for (AnnotationMirror annotationMirror : ((DeclaredType)module).asElement().getAnnotationMirrors()) {
for (Map.Entry<? extends ExecutableElement, ? extends AnnotationValue> entry :
annotationMirror.getElementValues().entrySet()) {
// use the entry with AnnotationValueVisitor
}
}
Get annotations from TypeMirror:
final String[] annotationParam = new String[1];
final AnnotationValueVisitor valueVisitor = new AnnotationValueVisitor();
valueVisitor.setFunction(new Function<TypeMirror, Void>() {
@Nullable @Override public Void apply(@Nullable TypeMirror param) {
TypeMirror moduleClass = param; //assembles modules list
return null;
}
});
annotationParam[0] = entry.getKey().getSimpleName().toString();
entry.getValue().accept(valueVisitor, null);
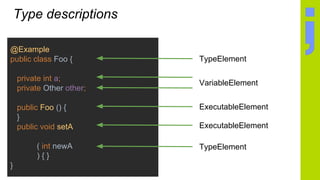
@Annotation(param = { Sample.class })
Class<?>[] param()
Sample.class](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/daggerate-170317080438/85/Daggerate-your-code-Write-your-own-annotation-processor-24-320.jpg)






![Debugging
● Annotation processing cannot
be debugged directly
● Compile project with gradle
in debug mode
● Attach to the compile process
from IDE
● [OPTIONAL] configure scripts
to launch debug from IDE
Detailed tutorial here](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/daggerate-170317080438/85/Daggerate-your-code-Write-your-own-annotation-processor-31-320.jpg)

