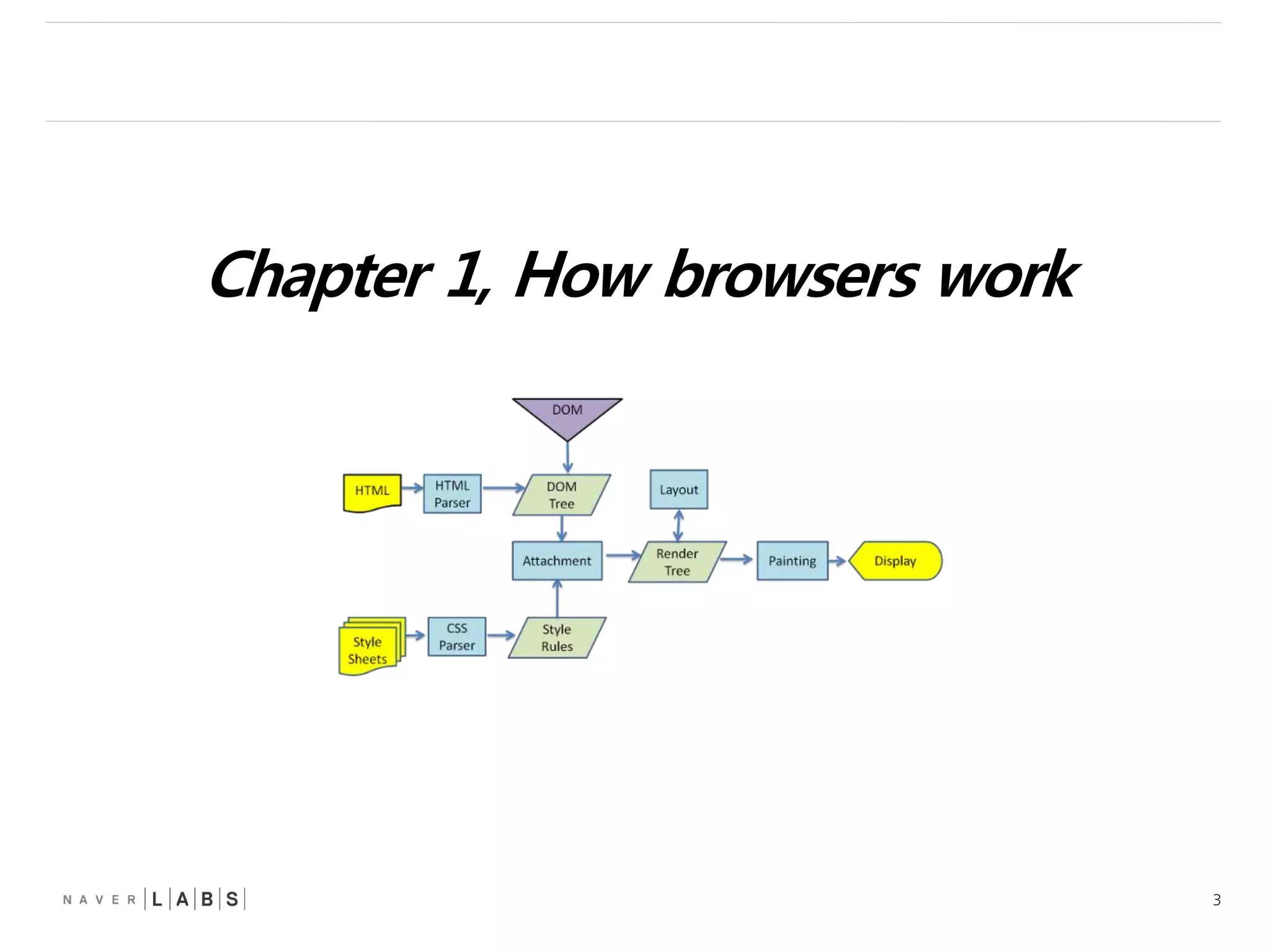
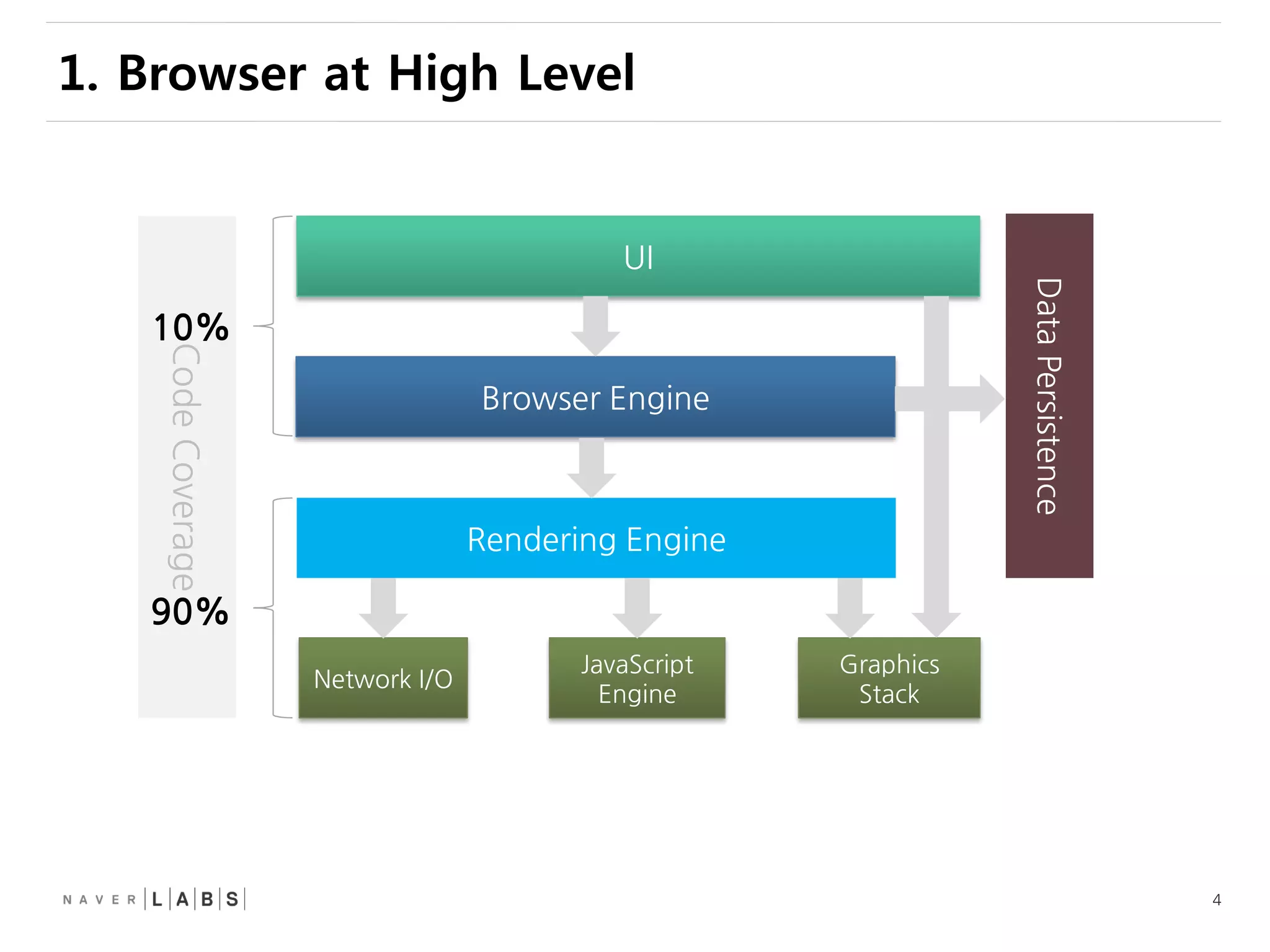
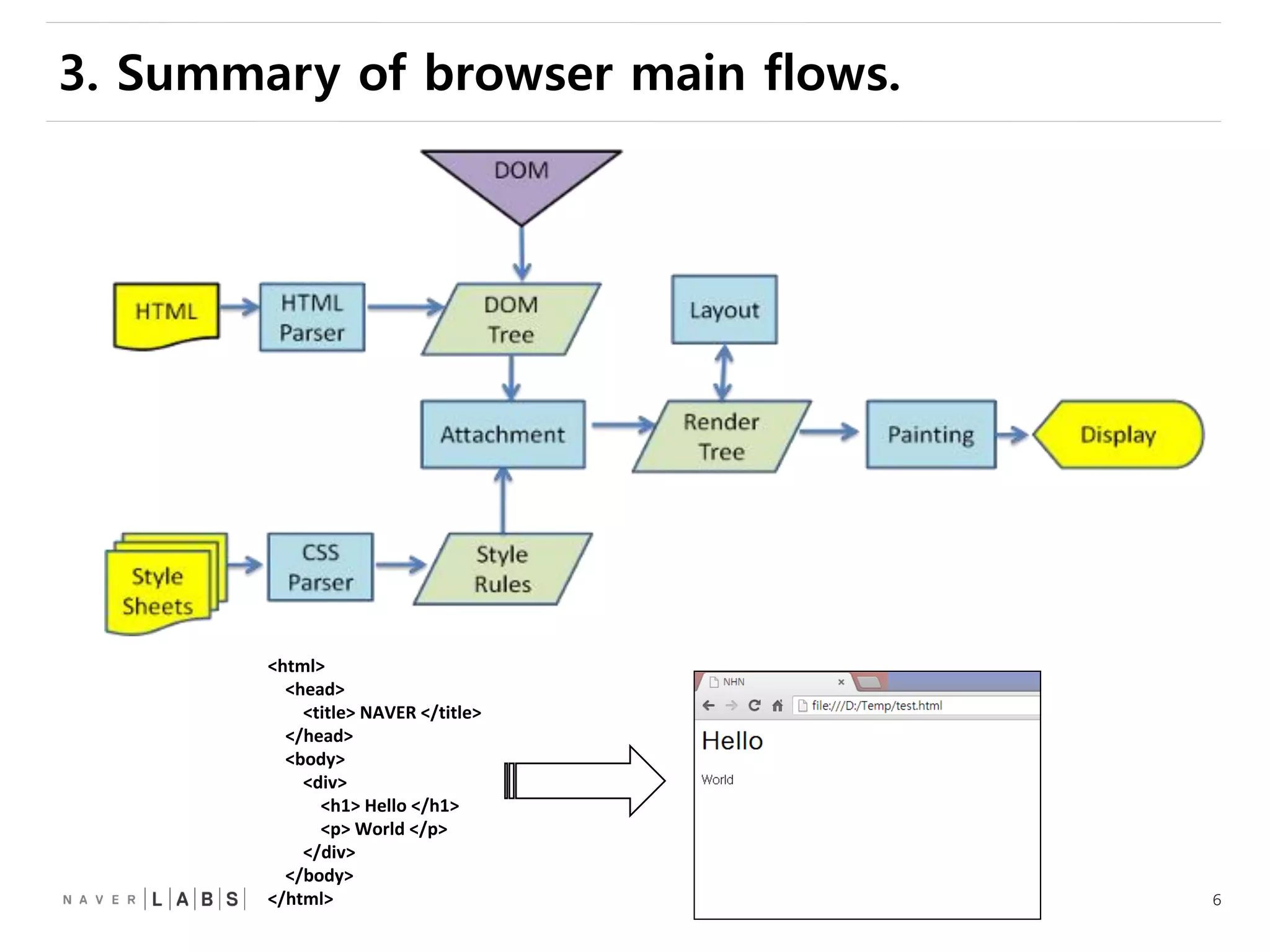
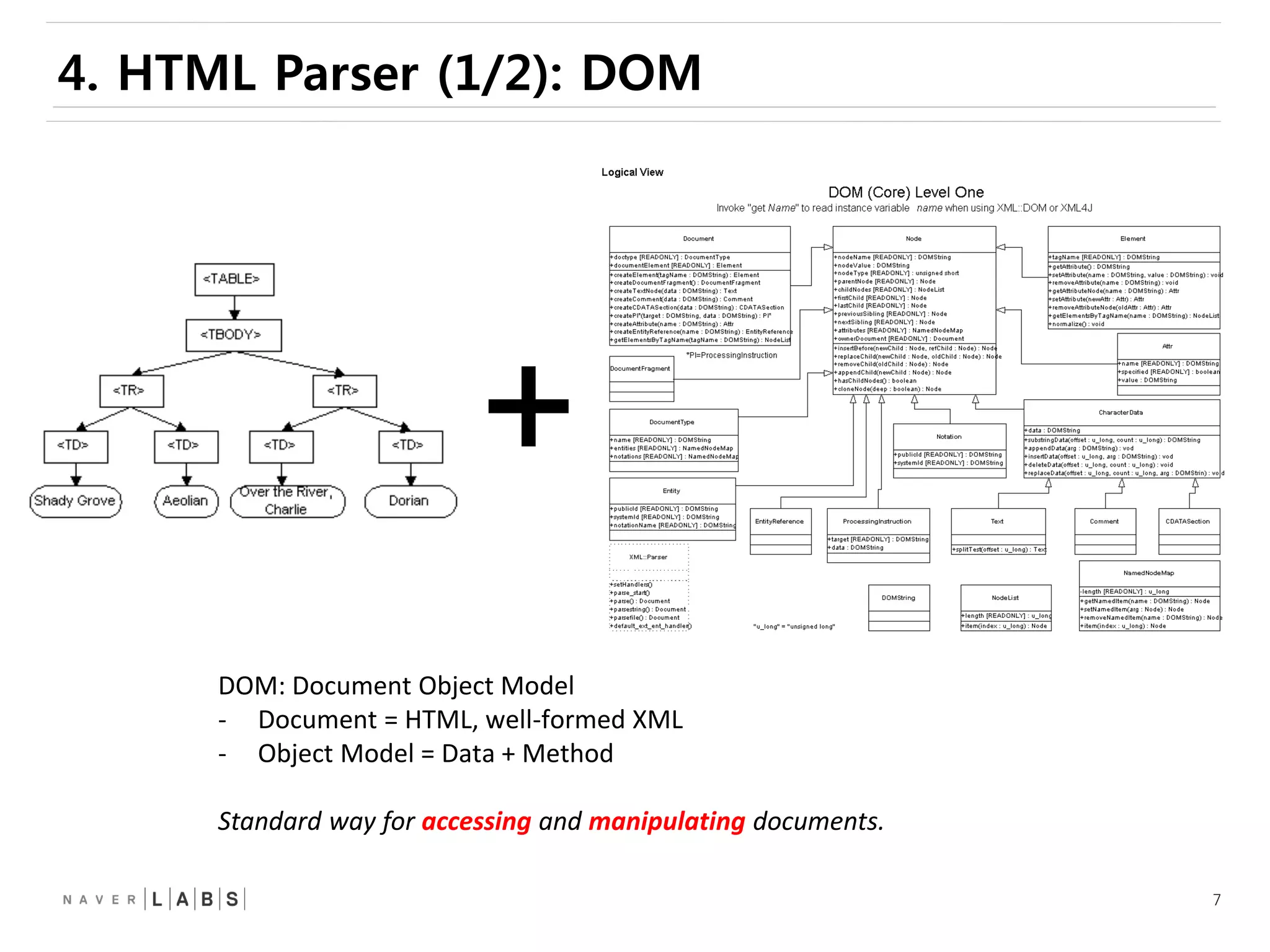
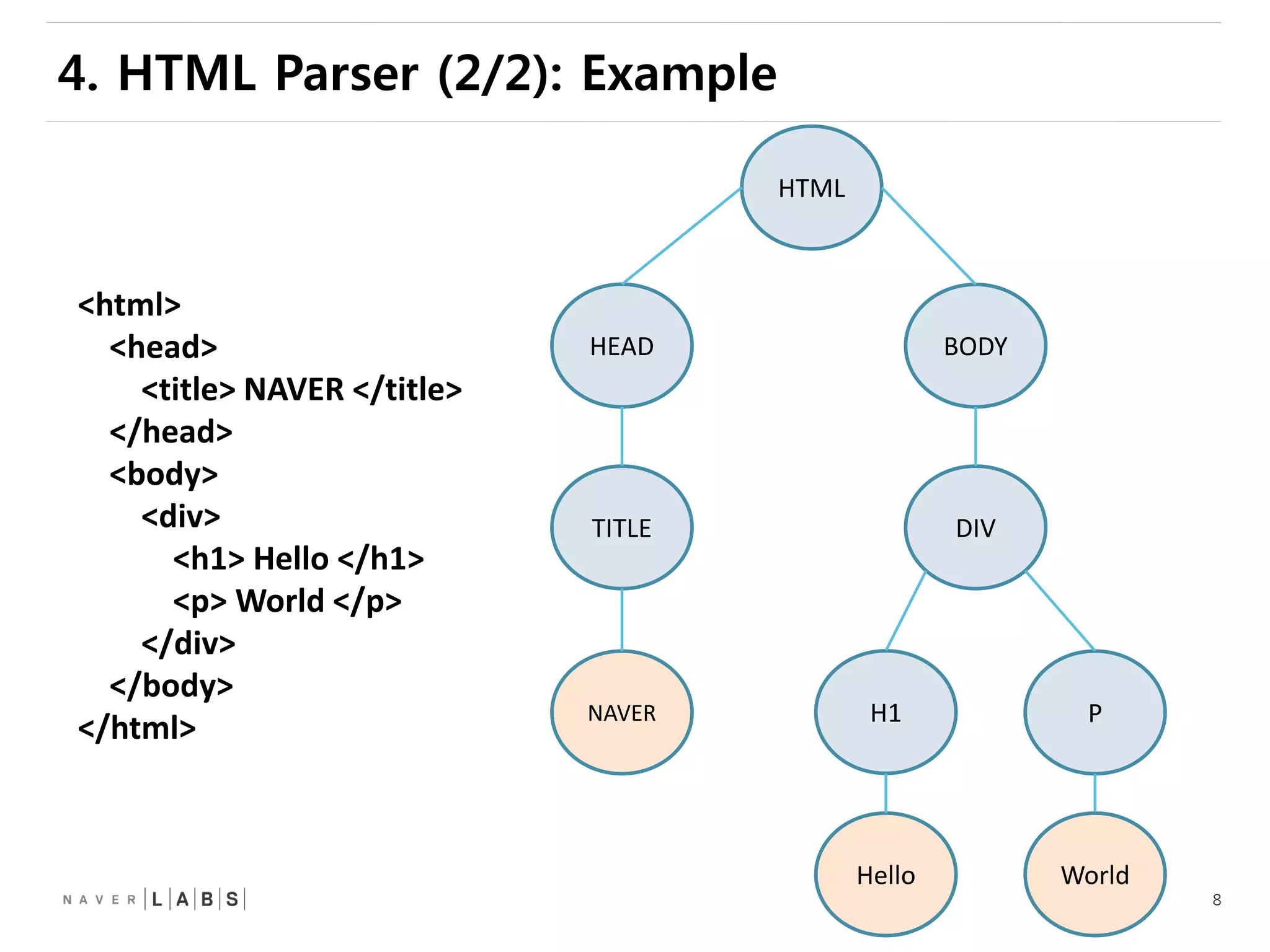
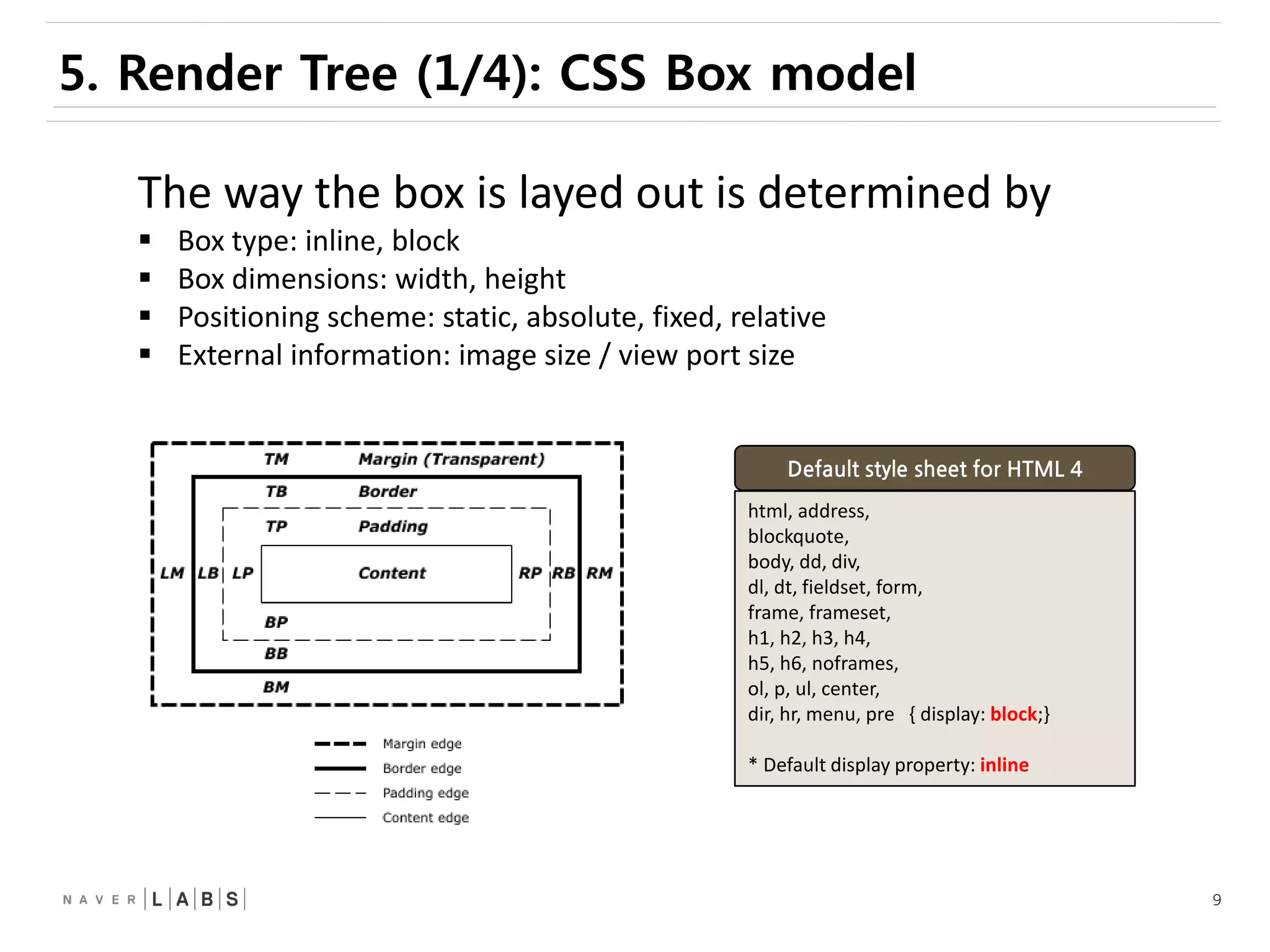
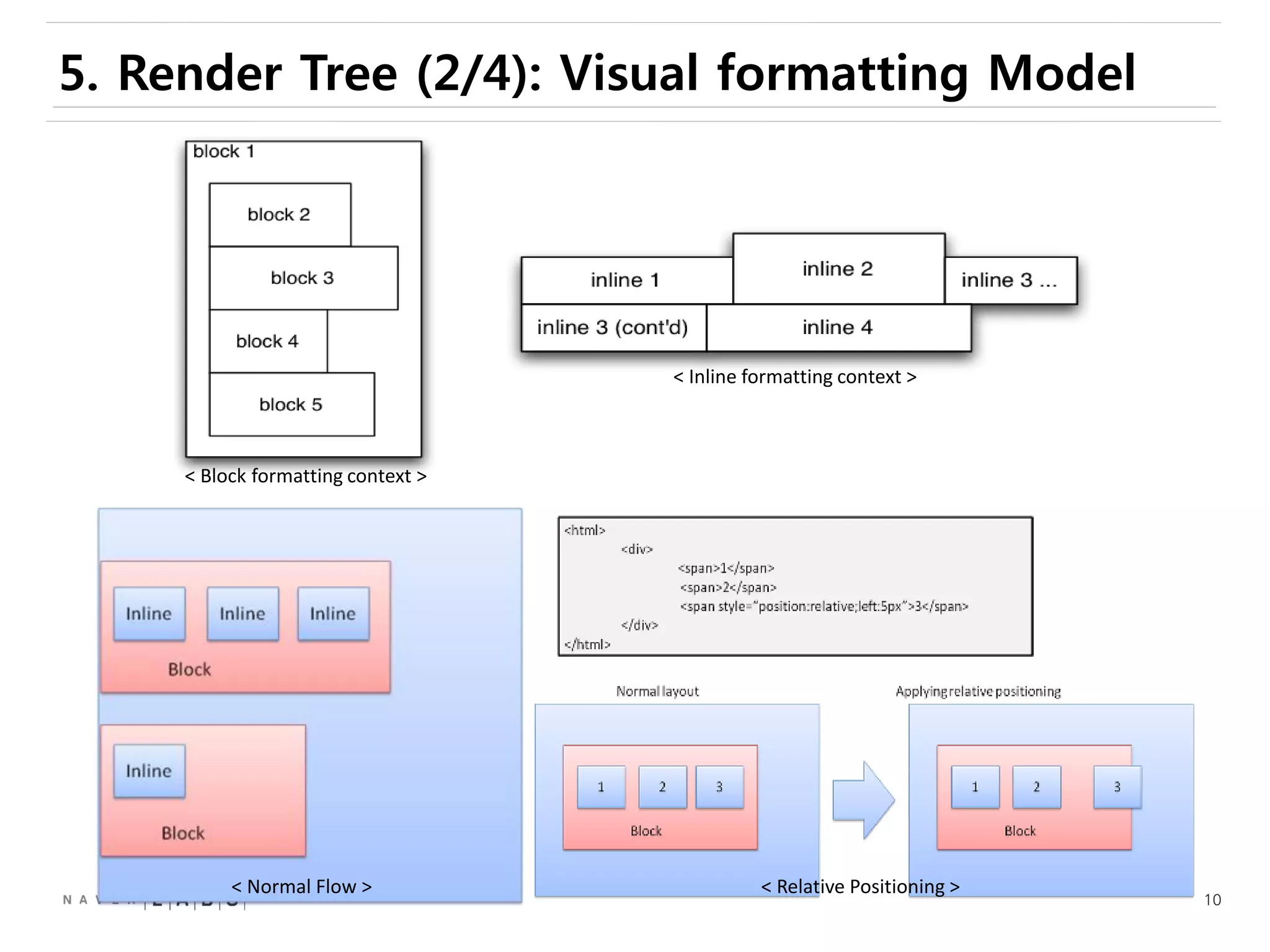
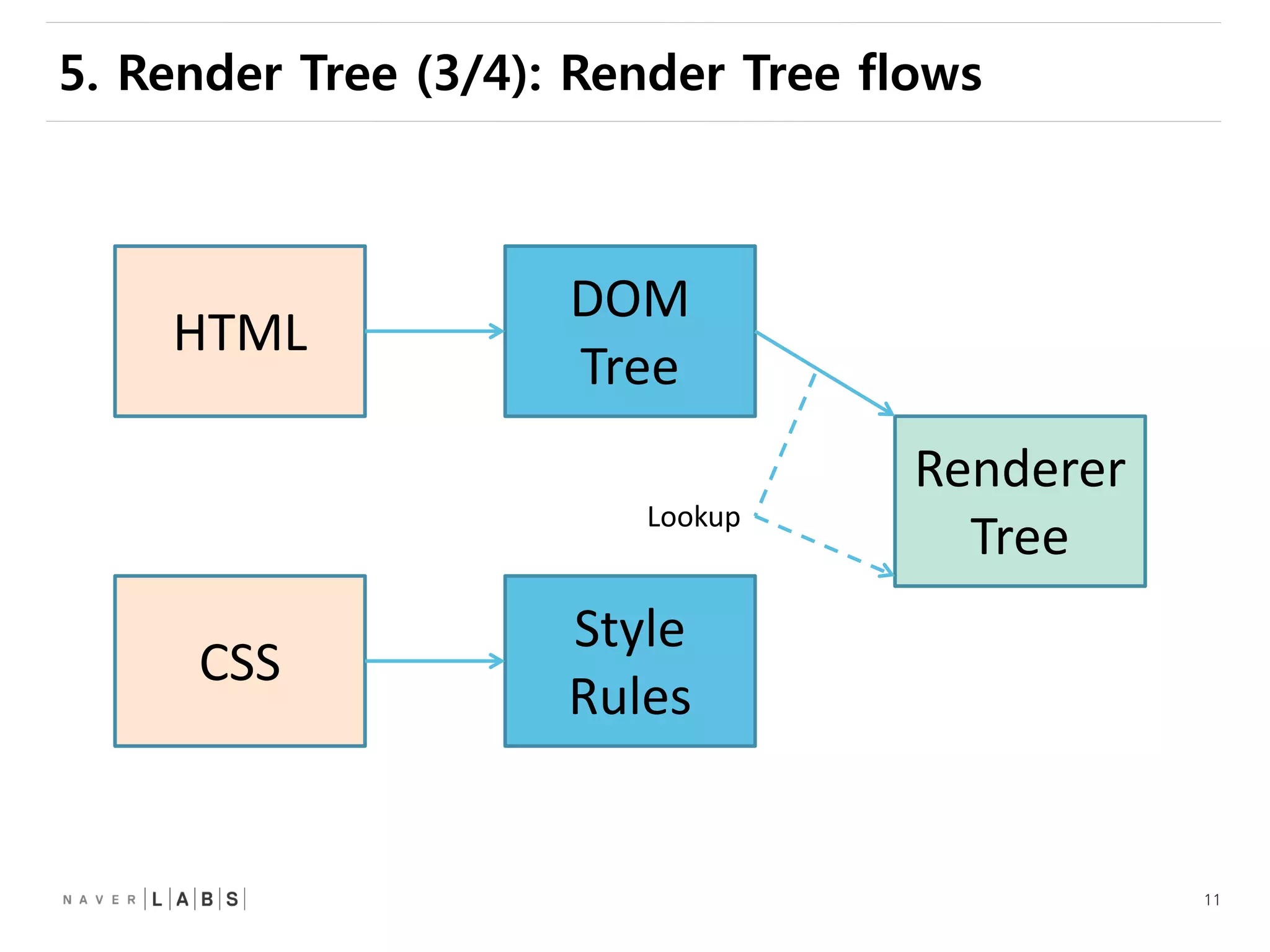
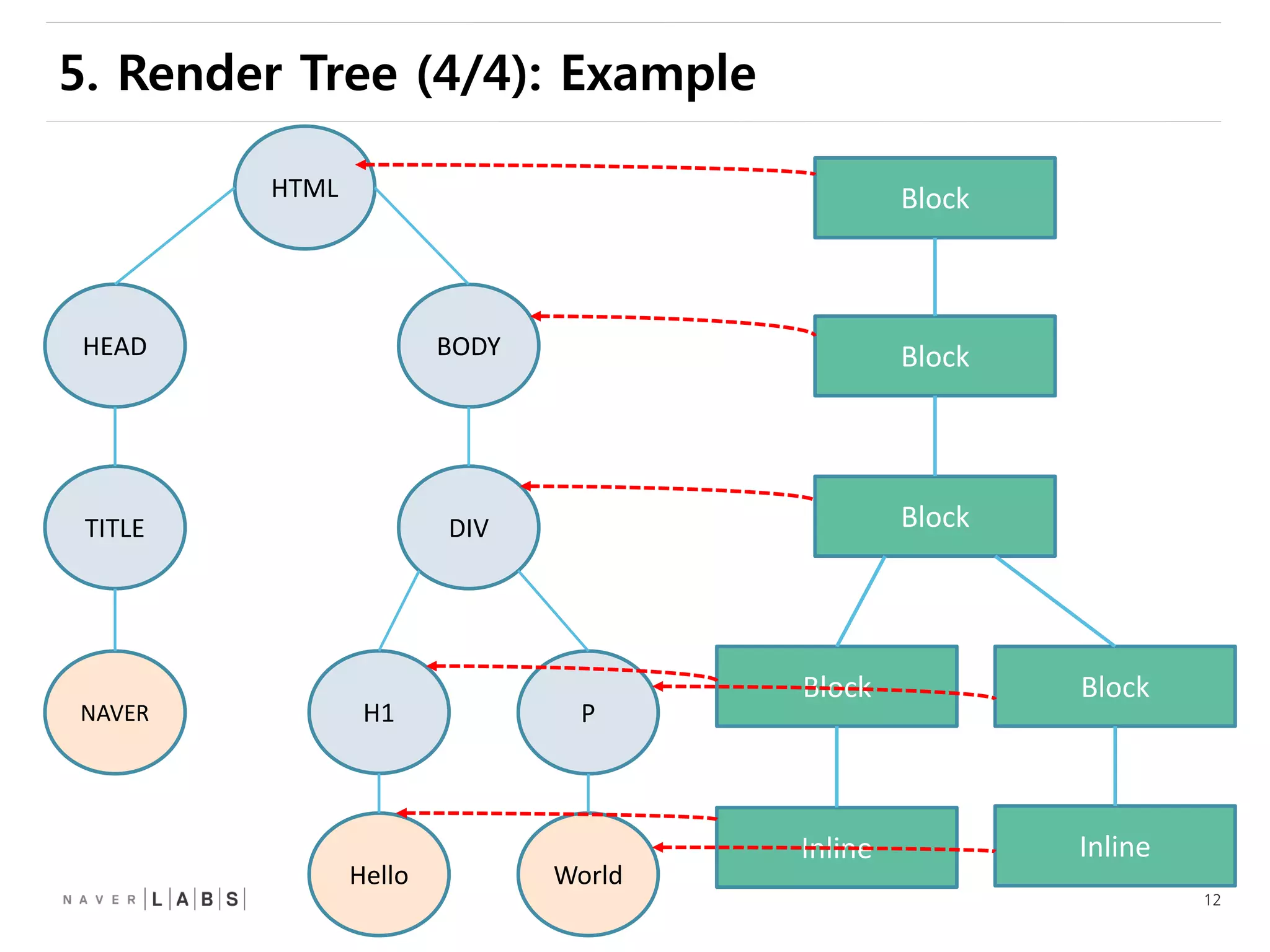
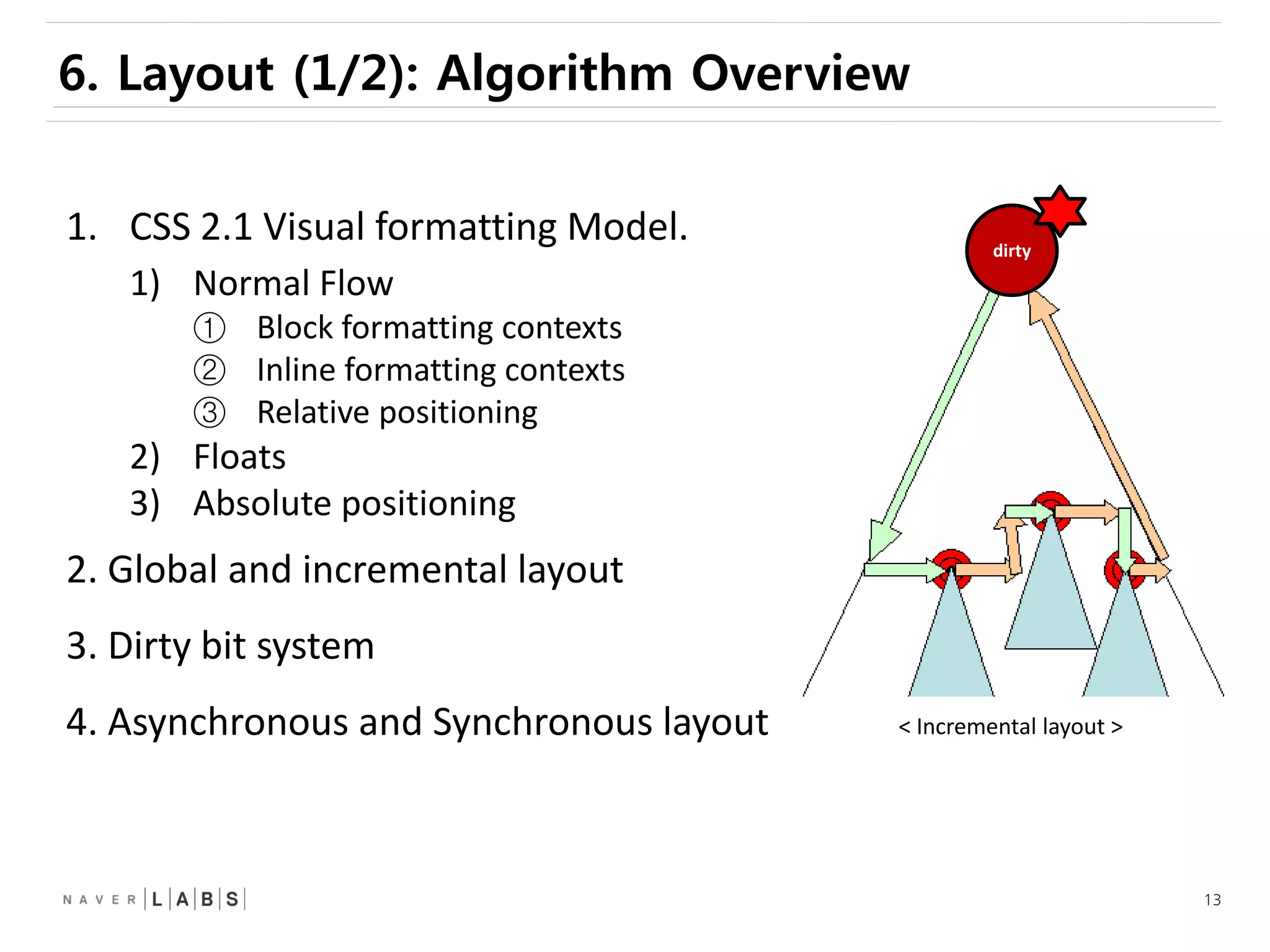
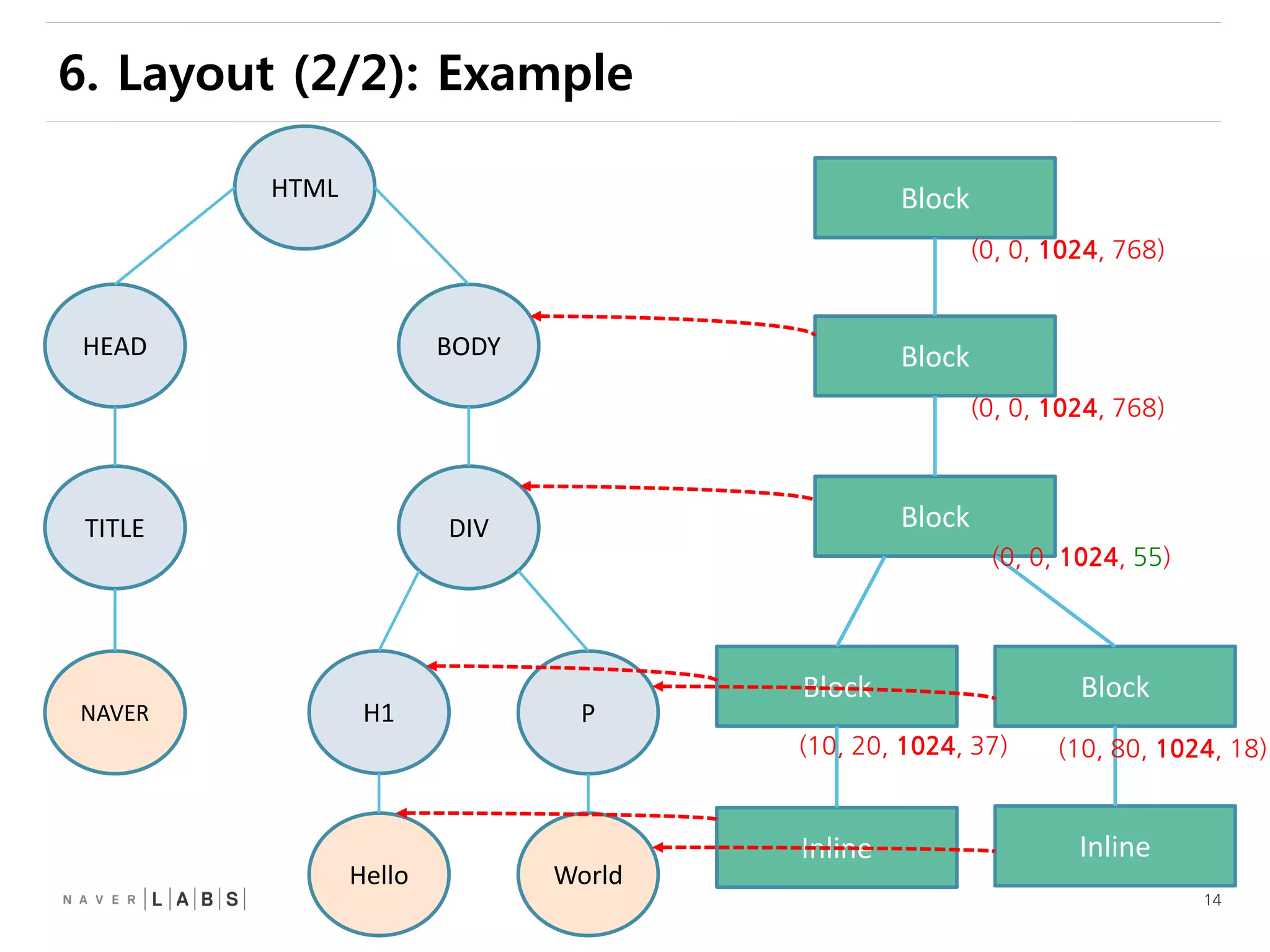
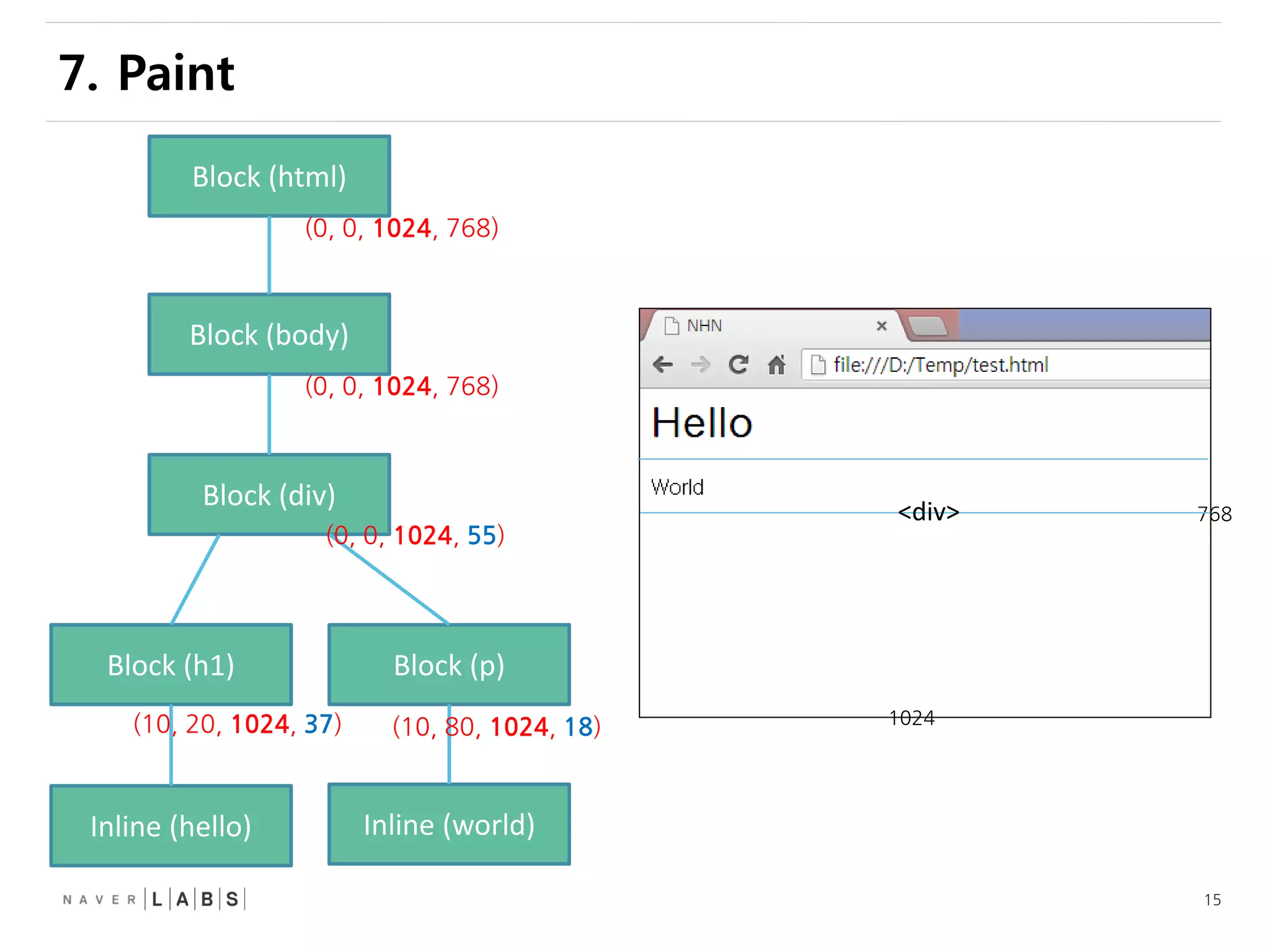
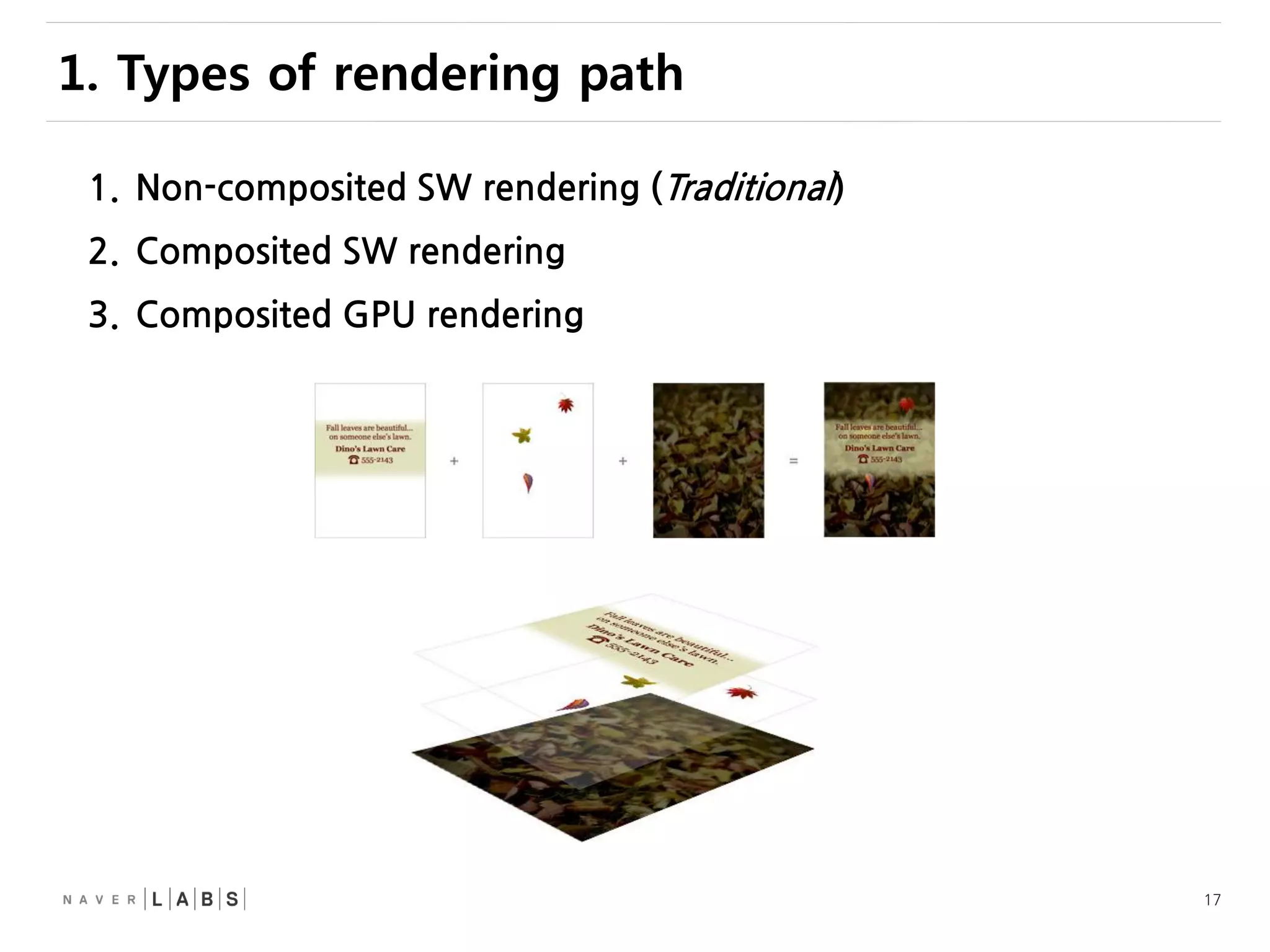
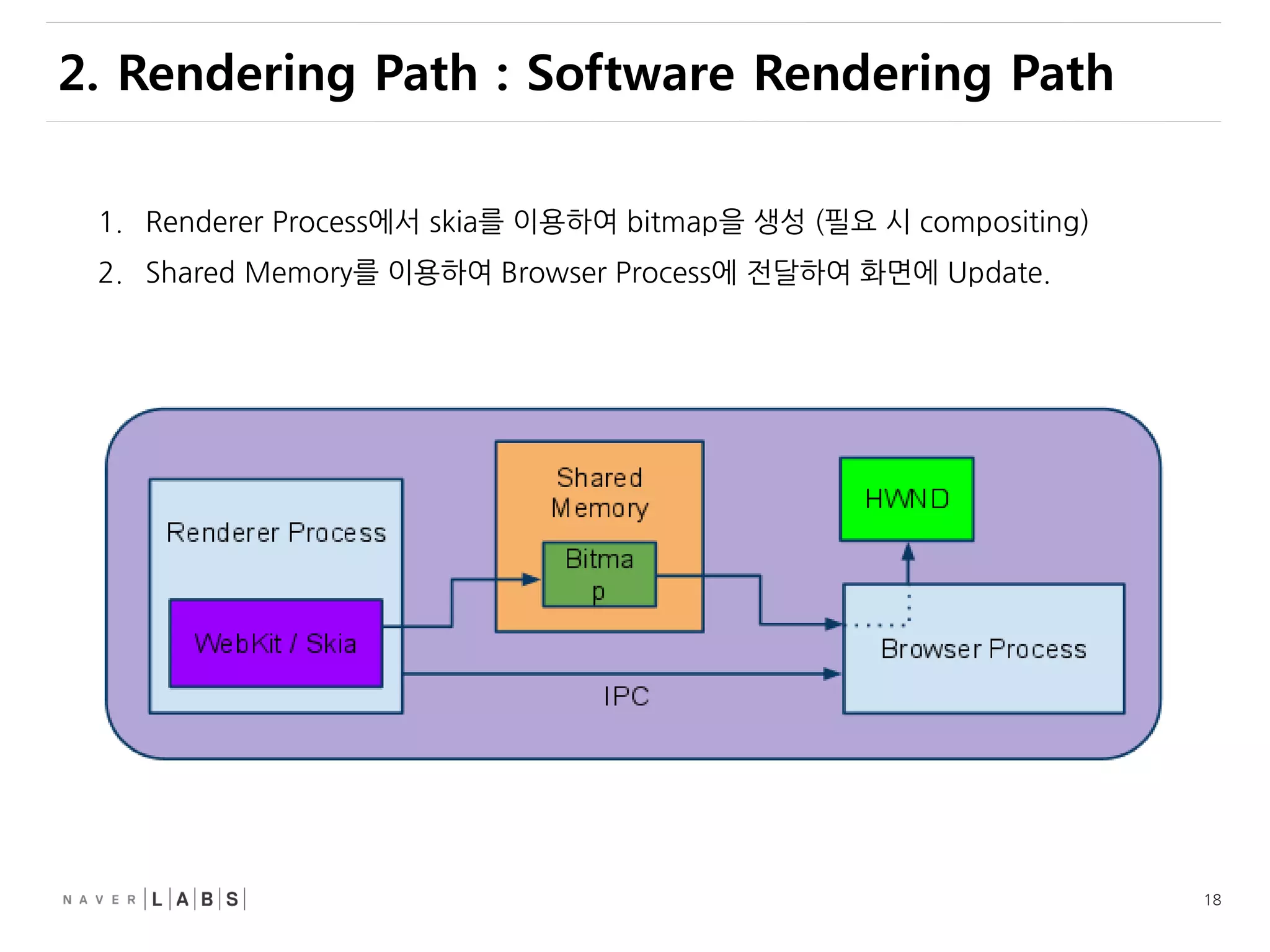
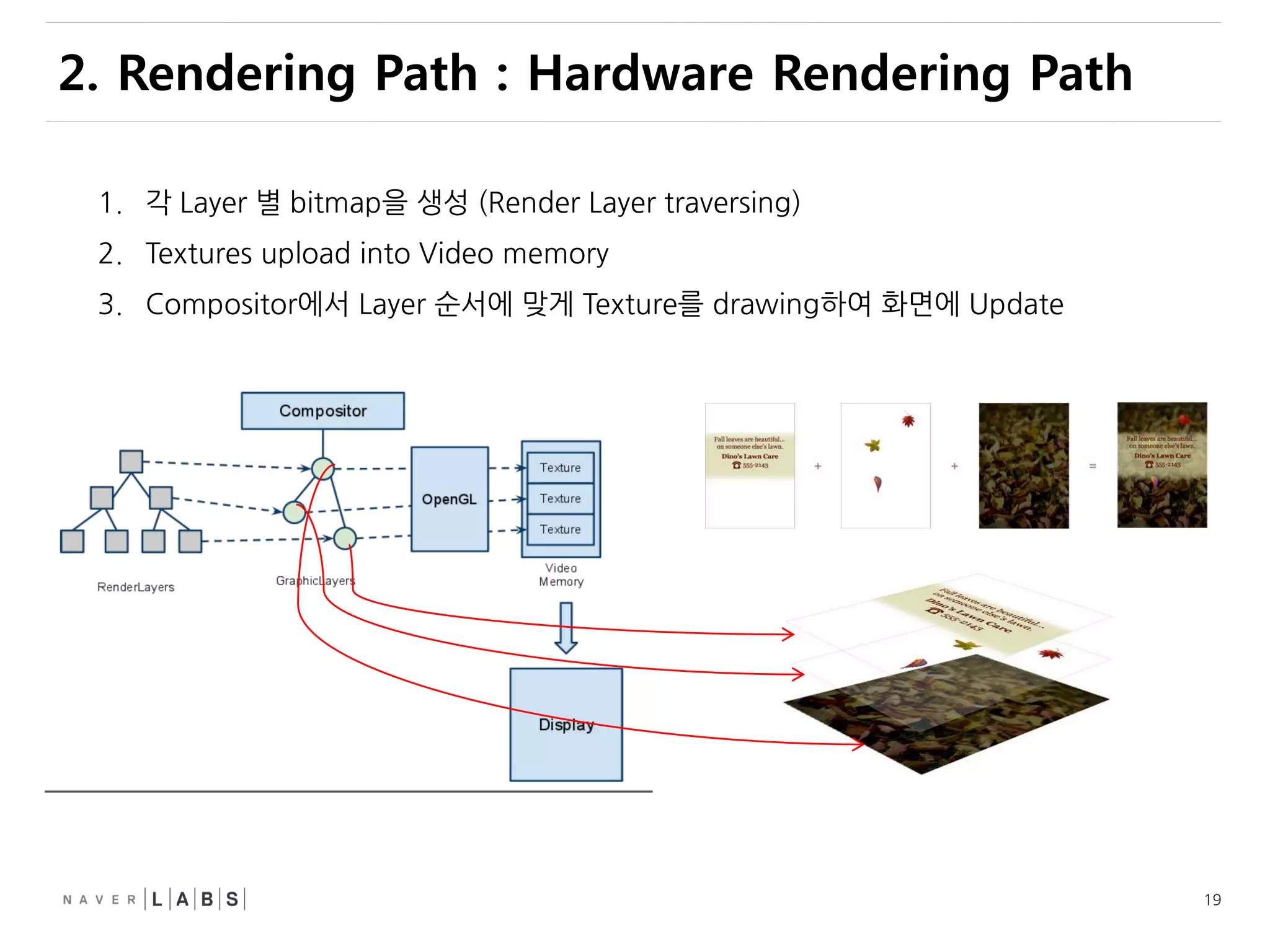
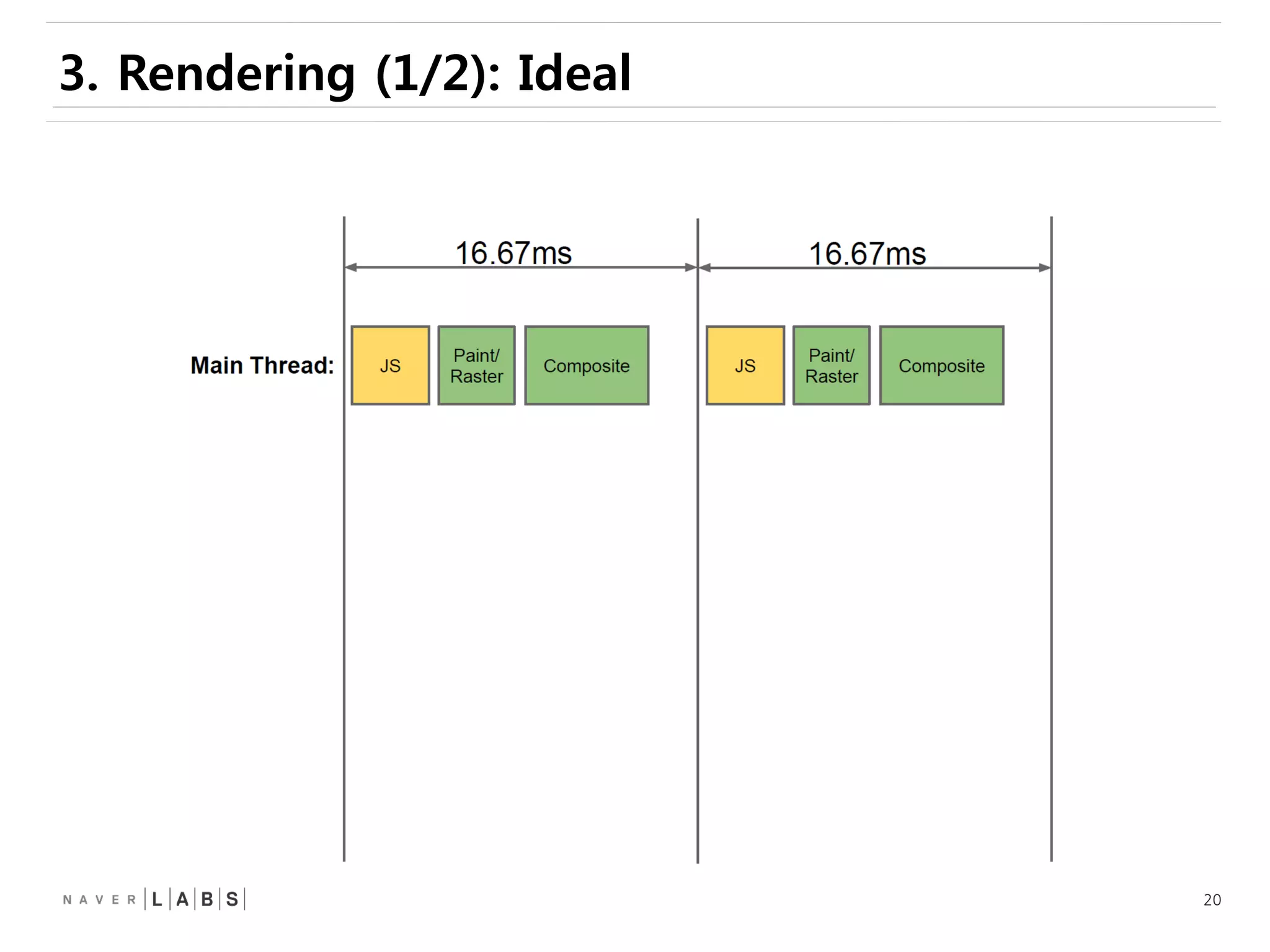
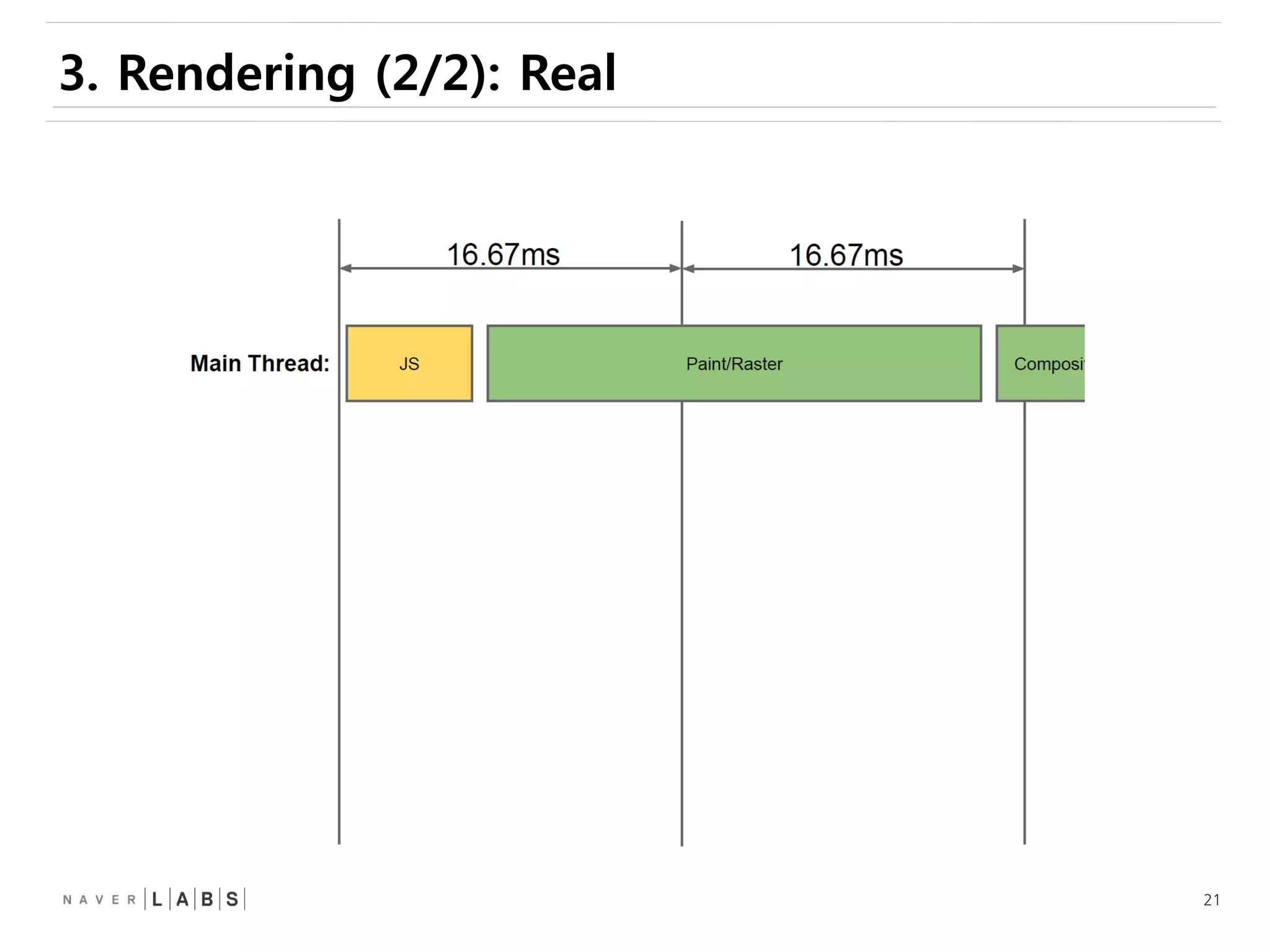
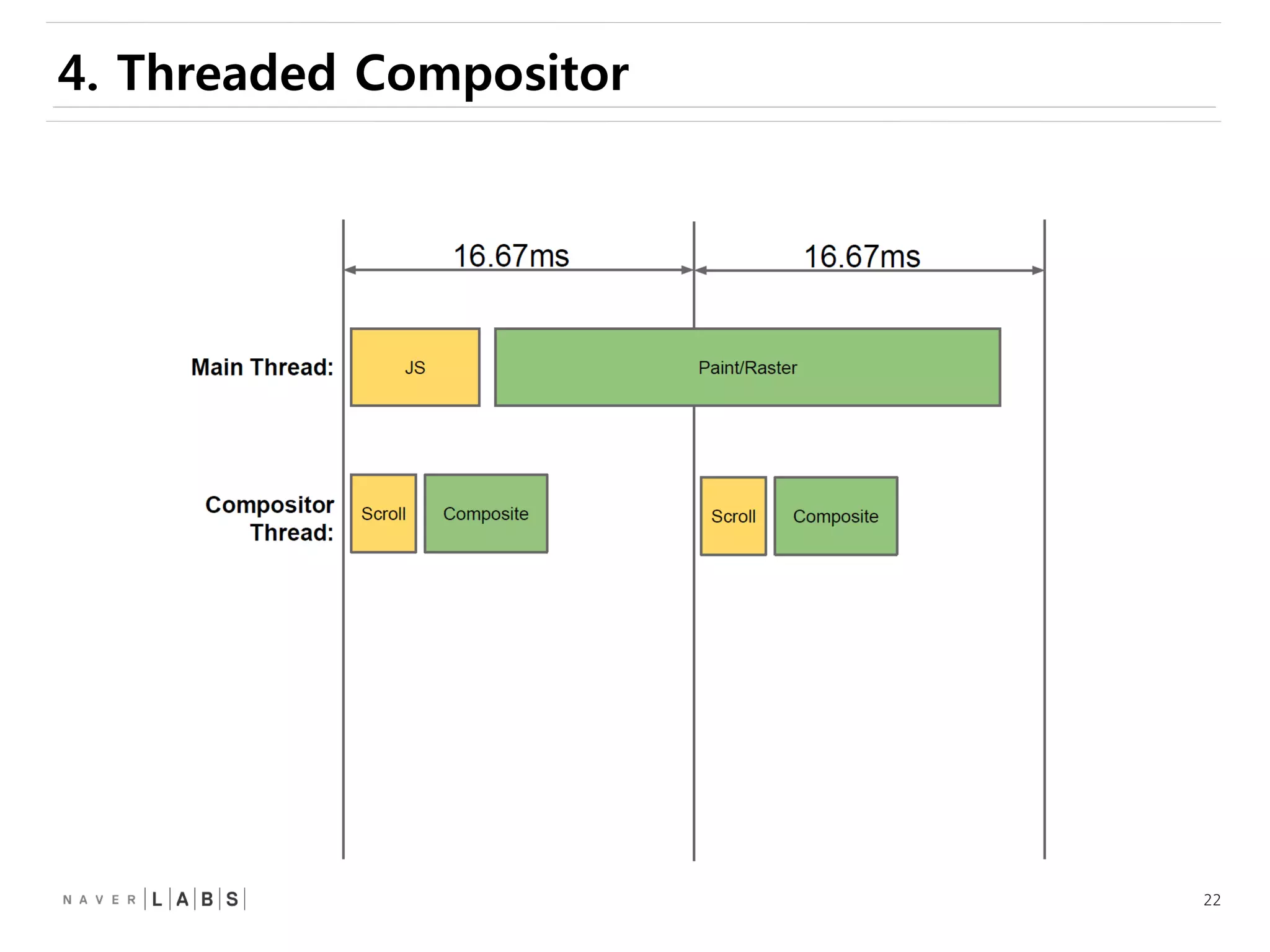
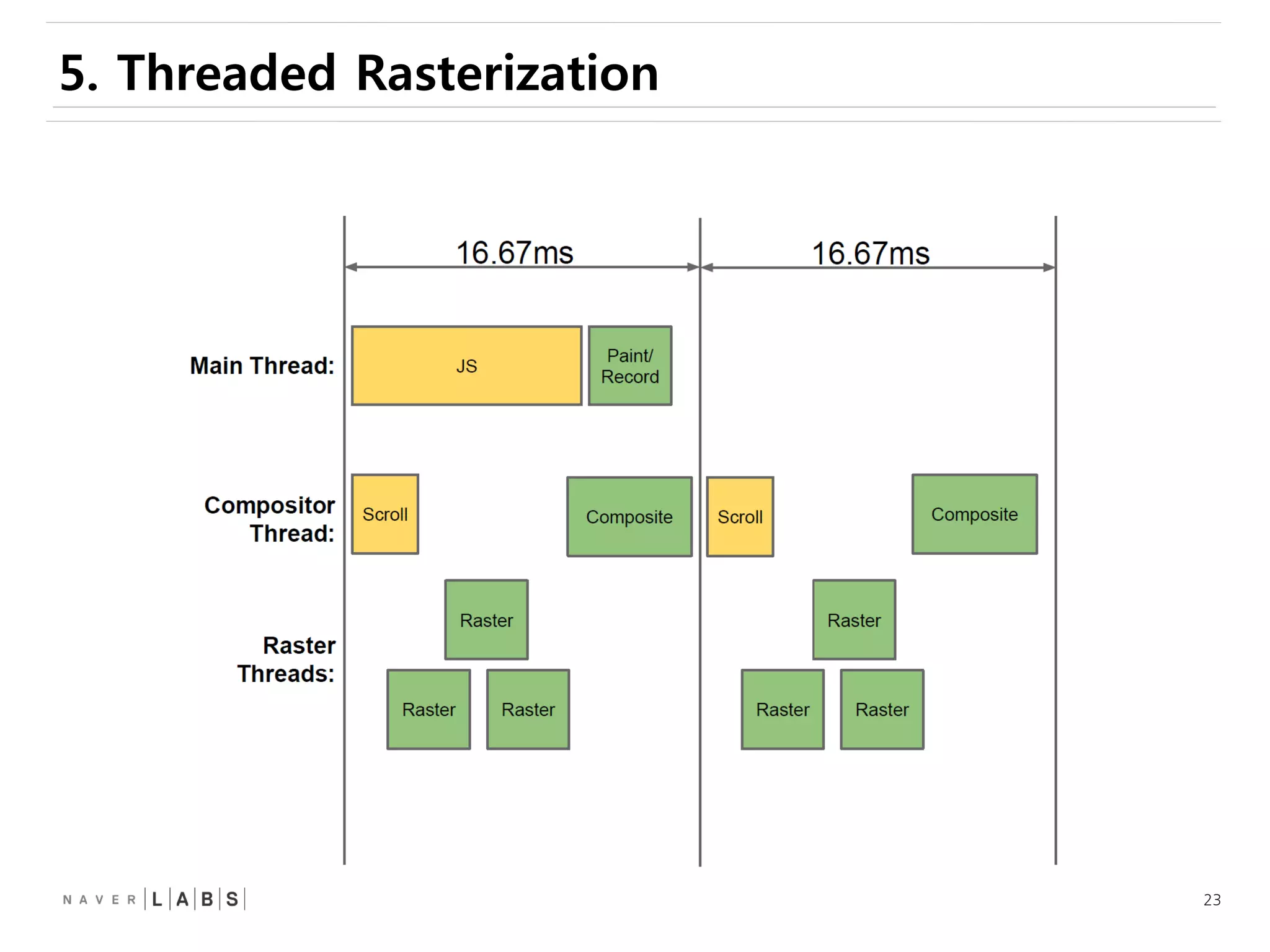
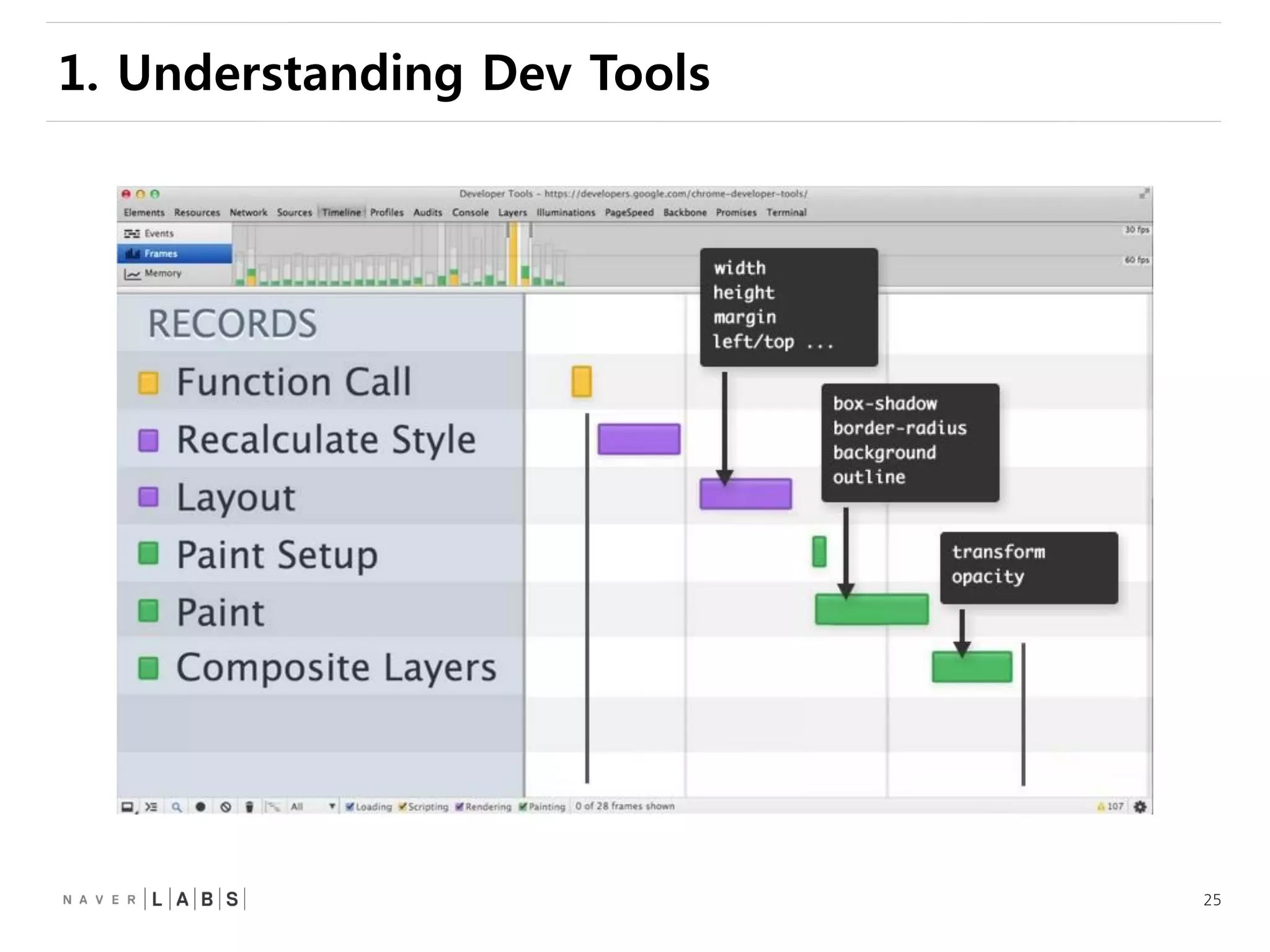
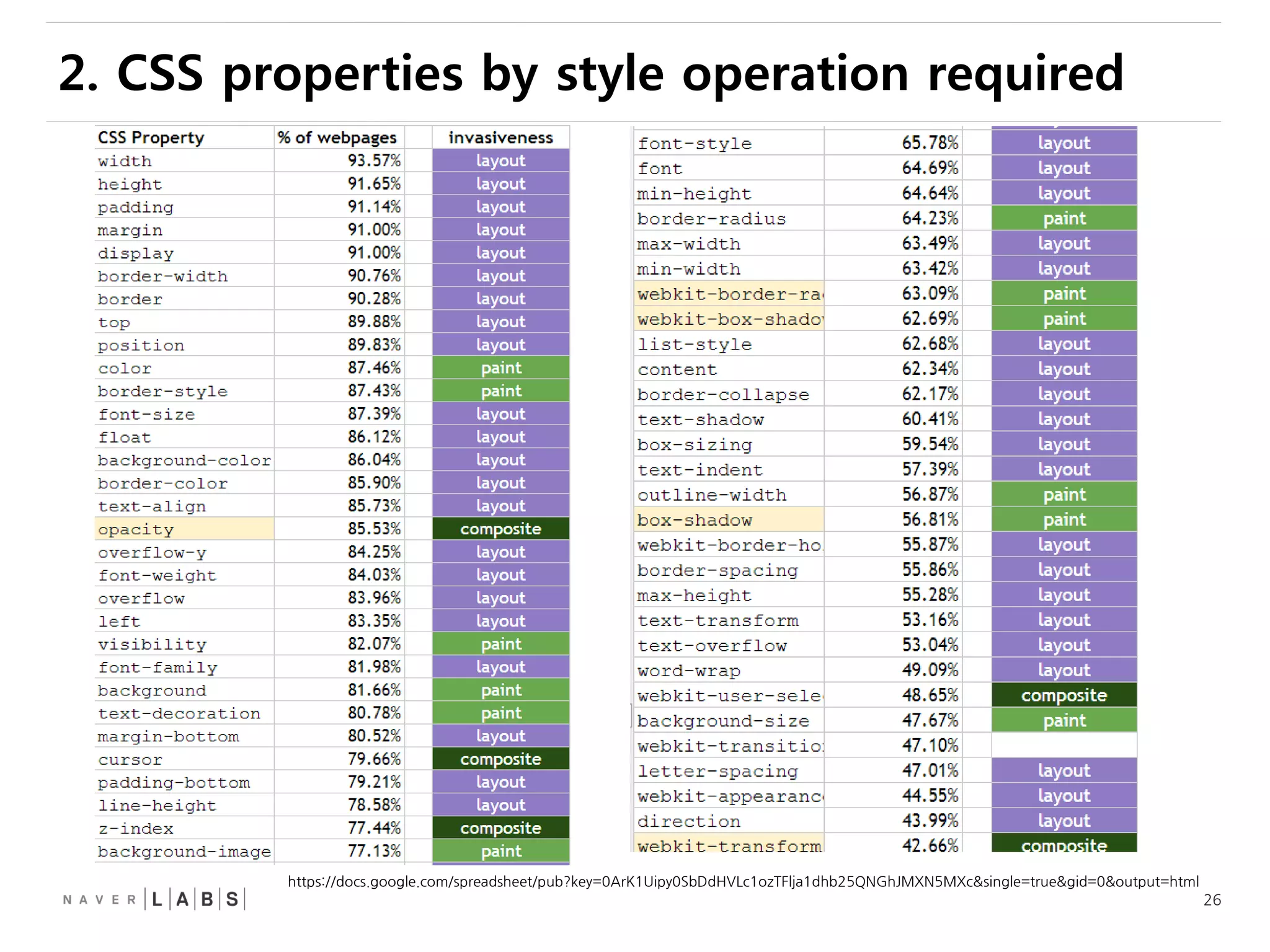
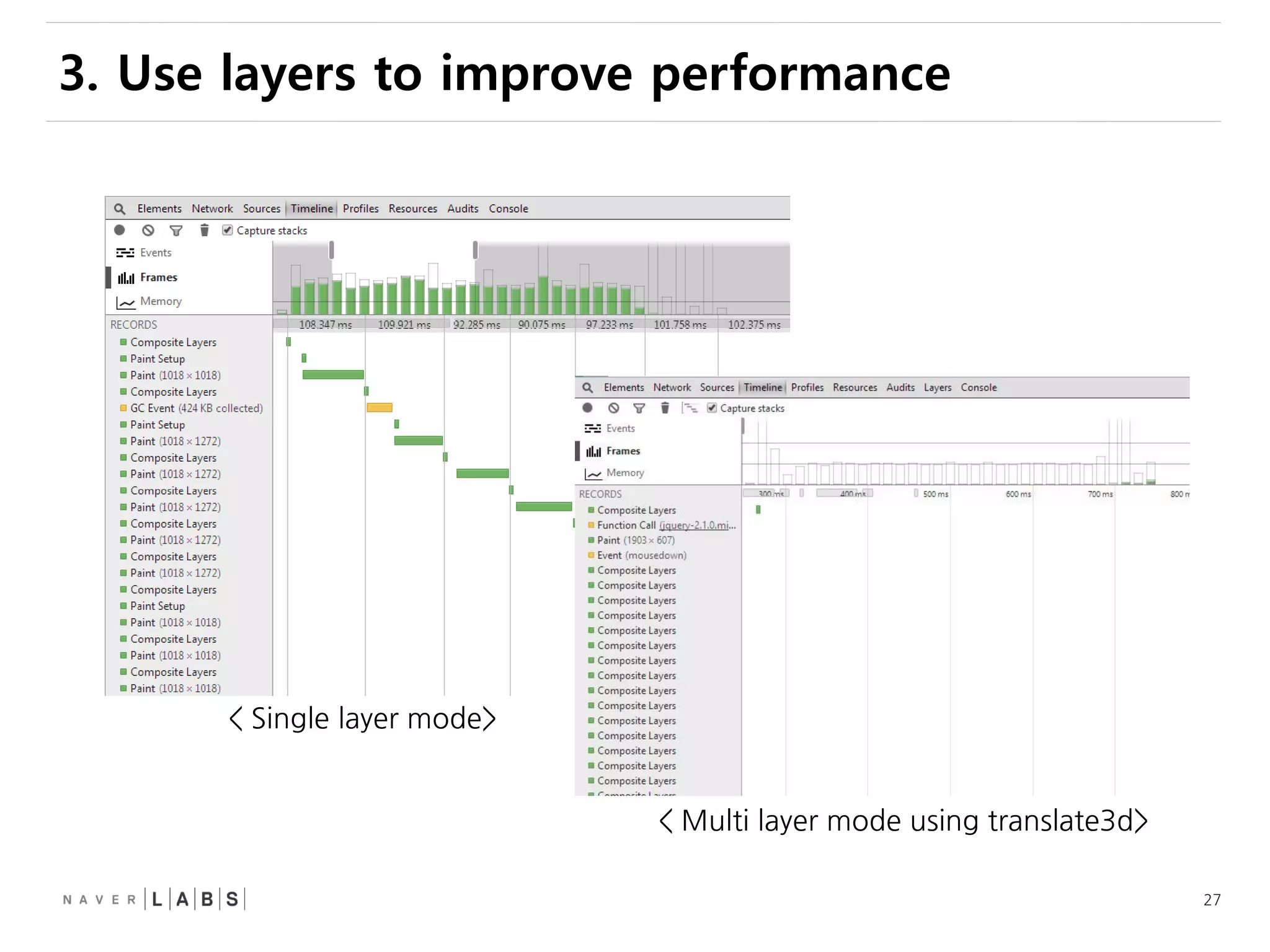
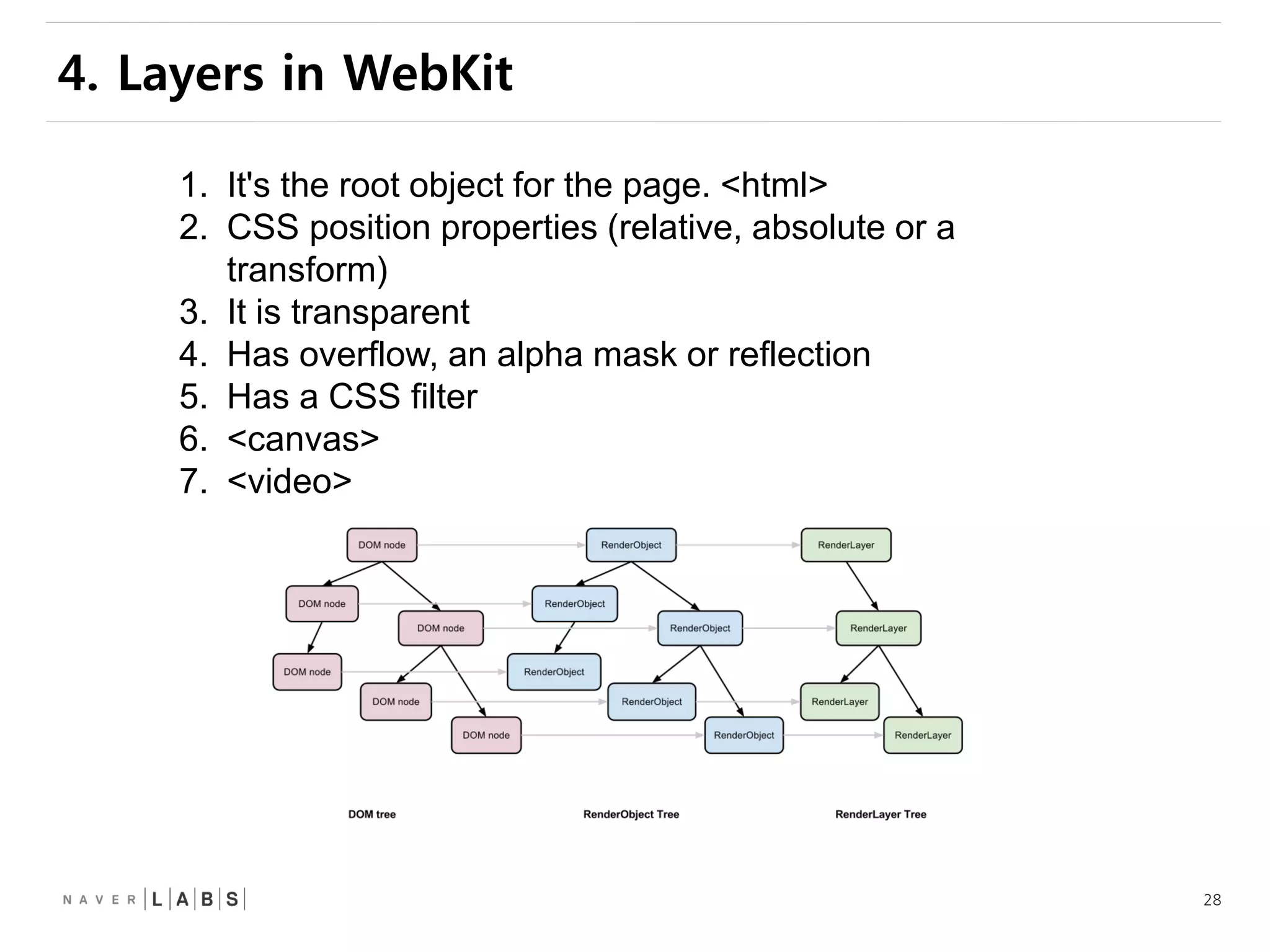
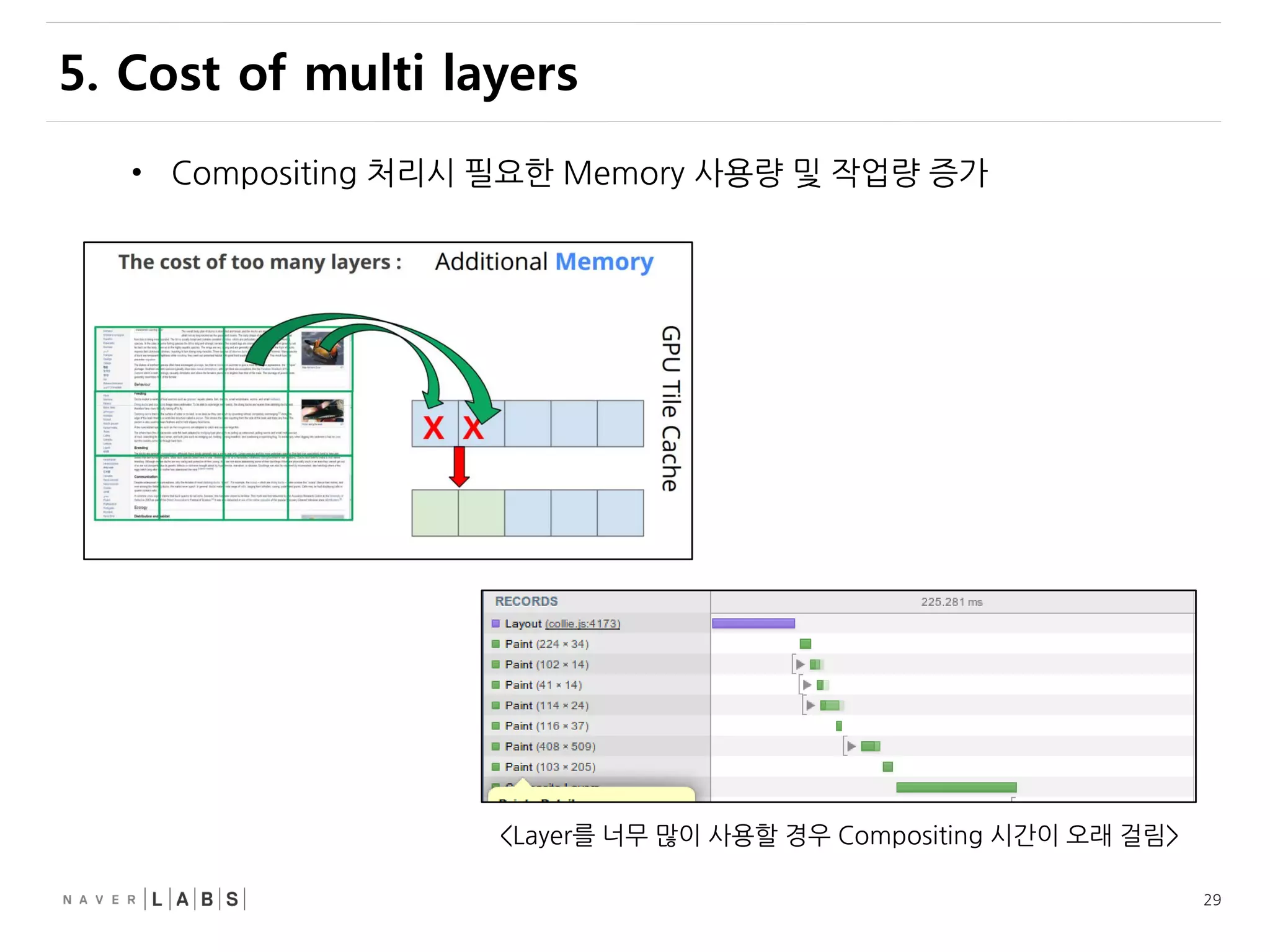
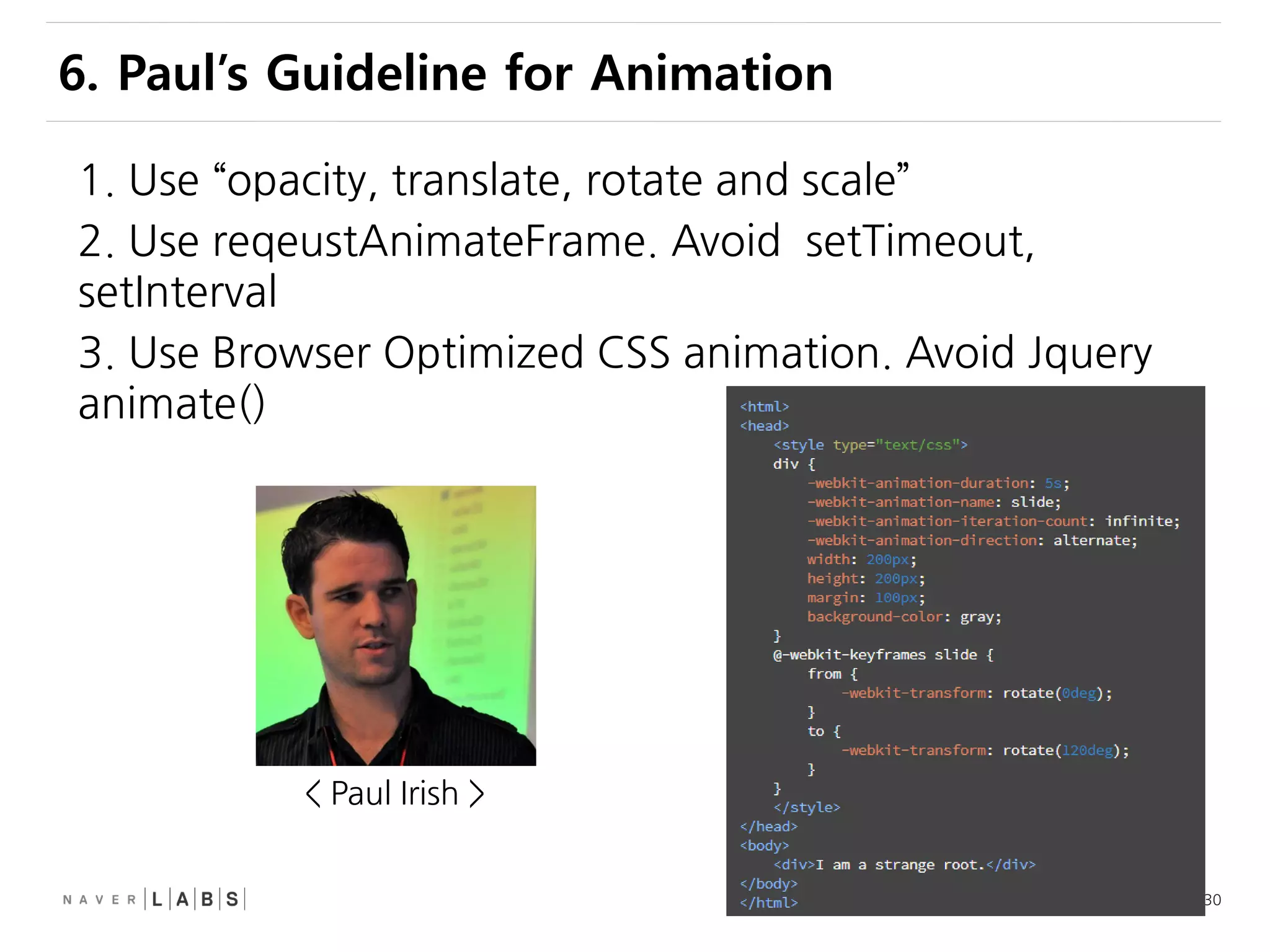
This document discusses how web browsers work and techniques for improving rendering performance. It covers how browsers parse HTML and CSS to build a render tree. The render tree is then laid out and painted to the screen. It also describes different rendering paths including software rendering, hardware accelerated rendering using the GPU, and techniques like layering and compositing. Guidelines are provided for optimizing CSS animations and using developer tools to analyze rendering performance.