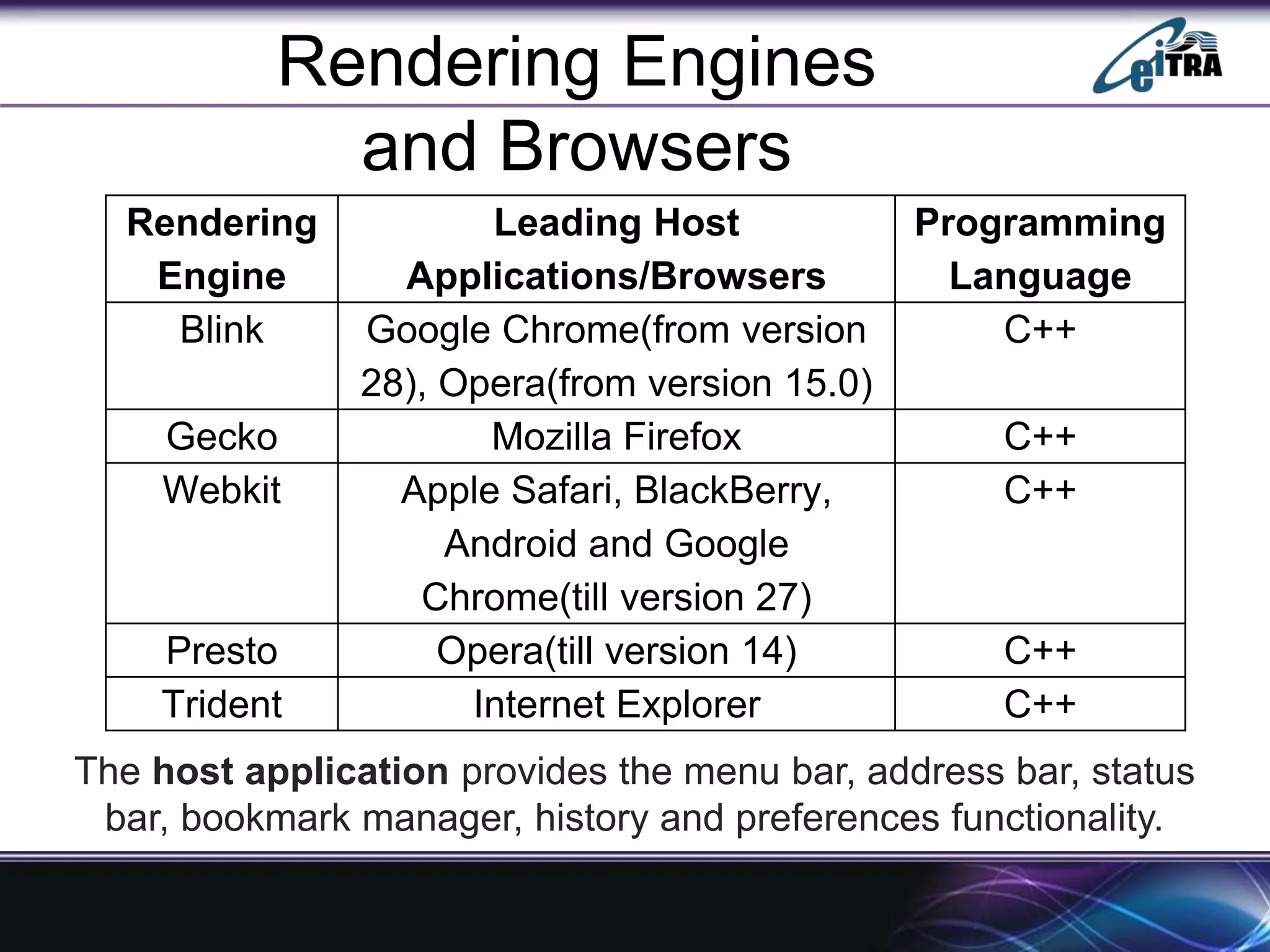
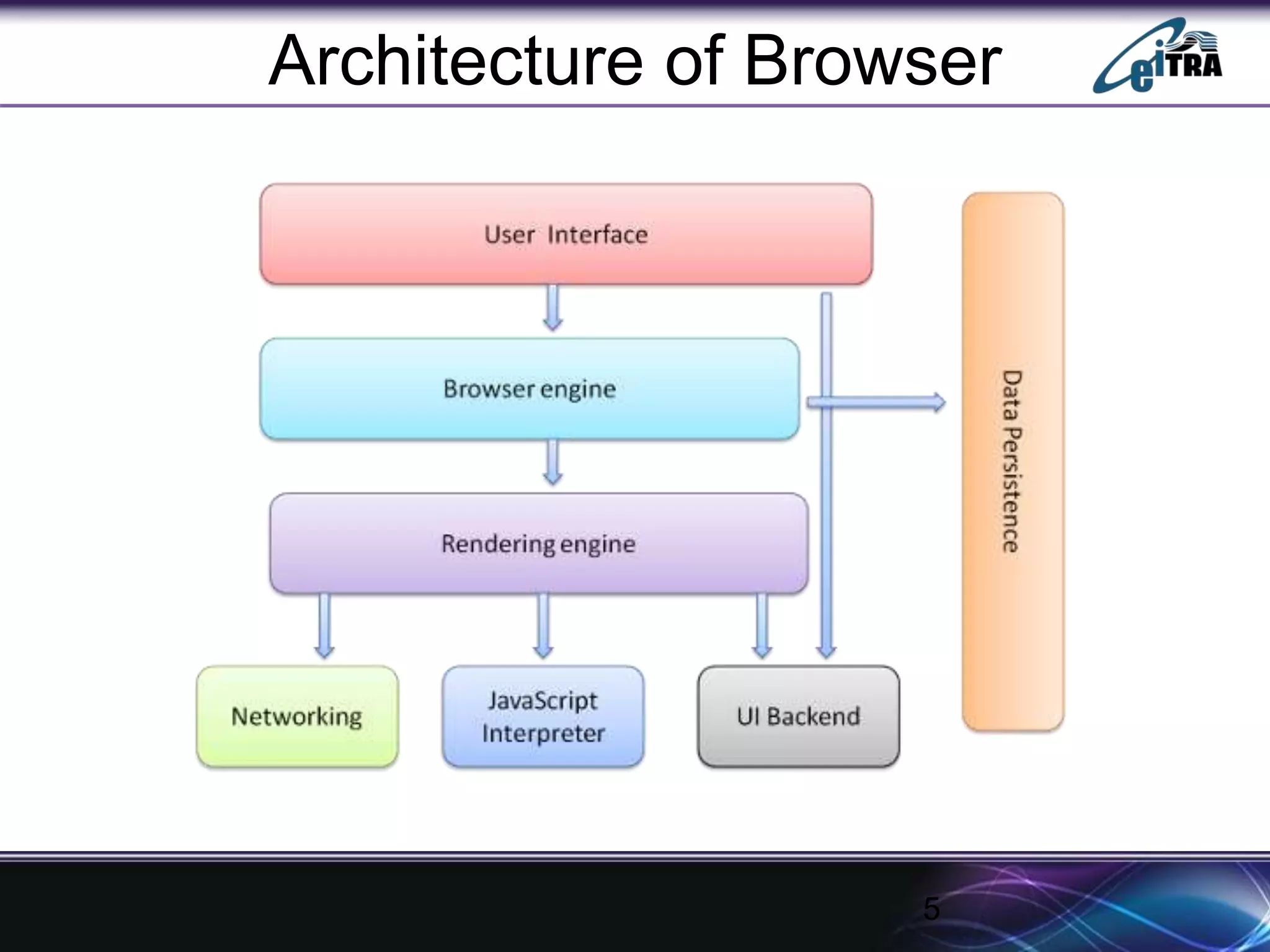
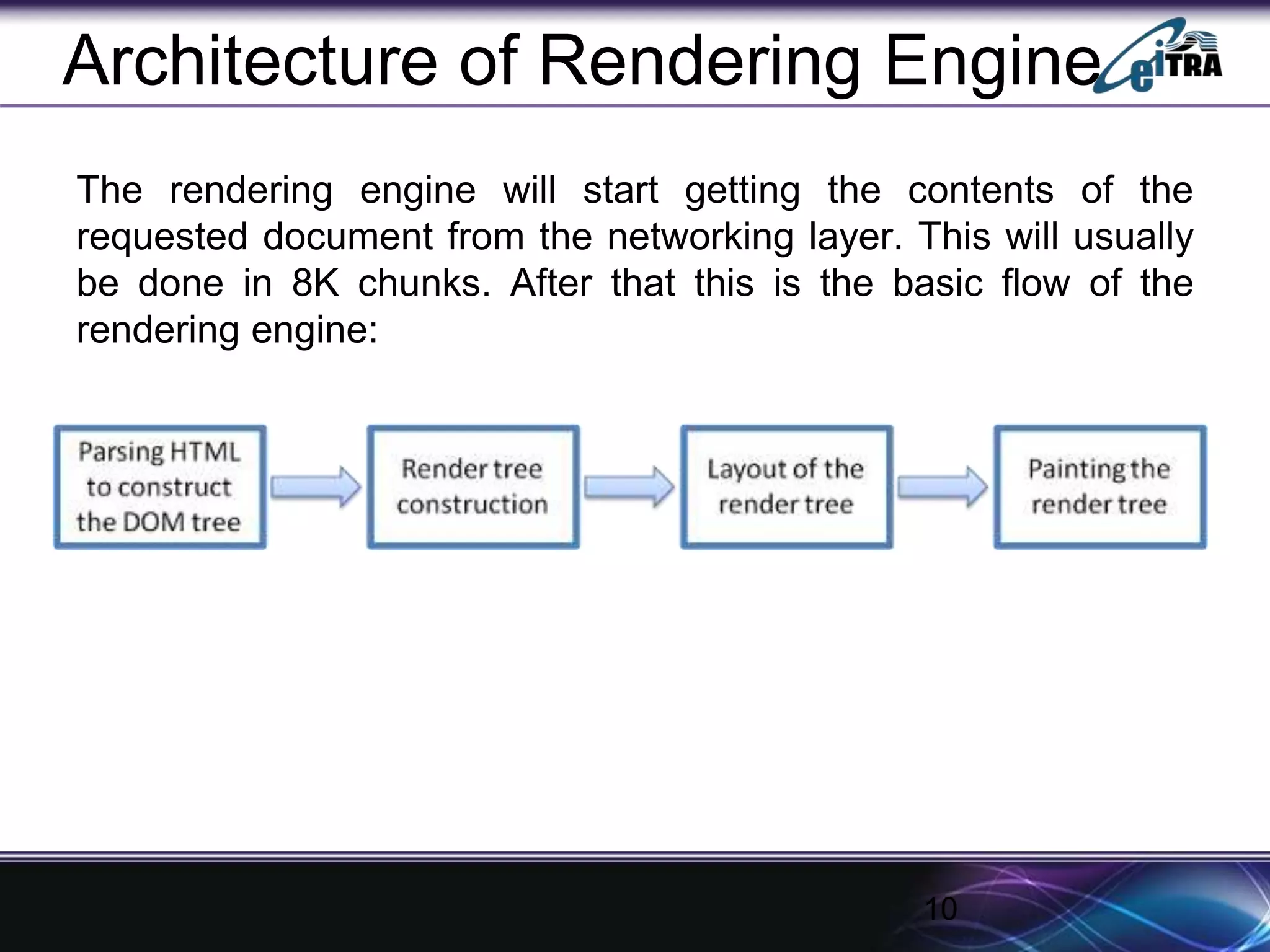
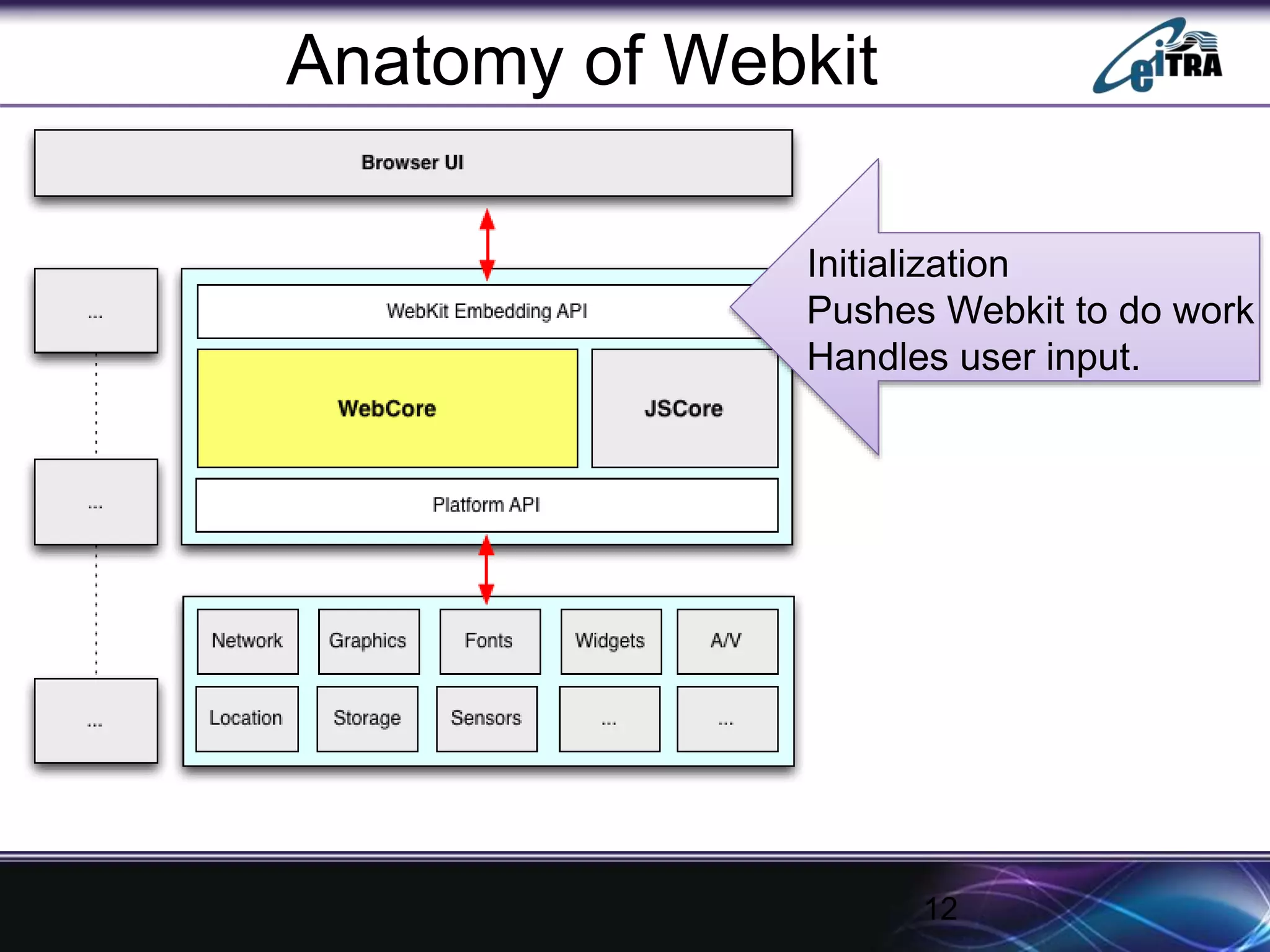
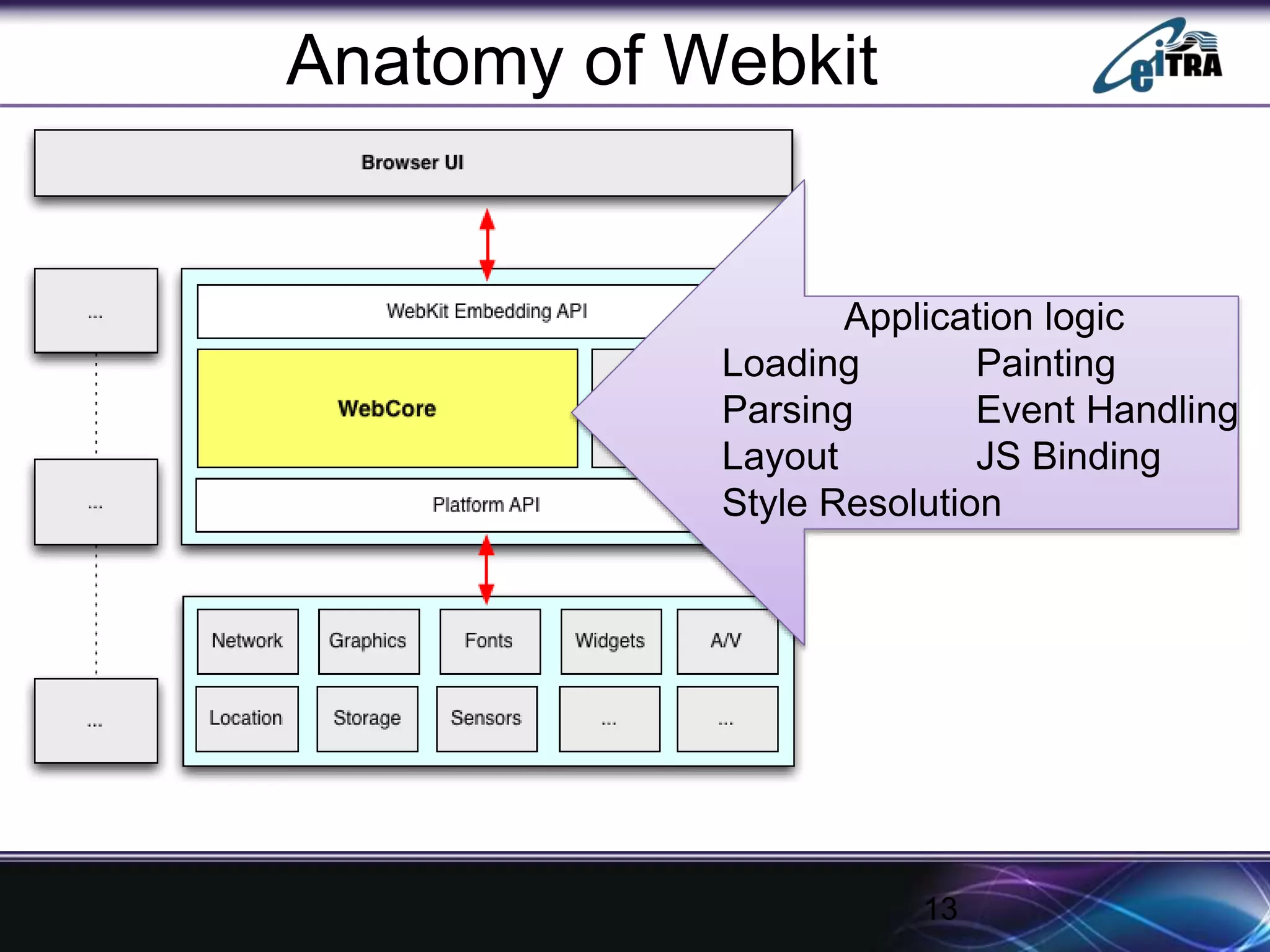
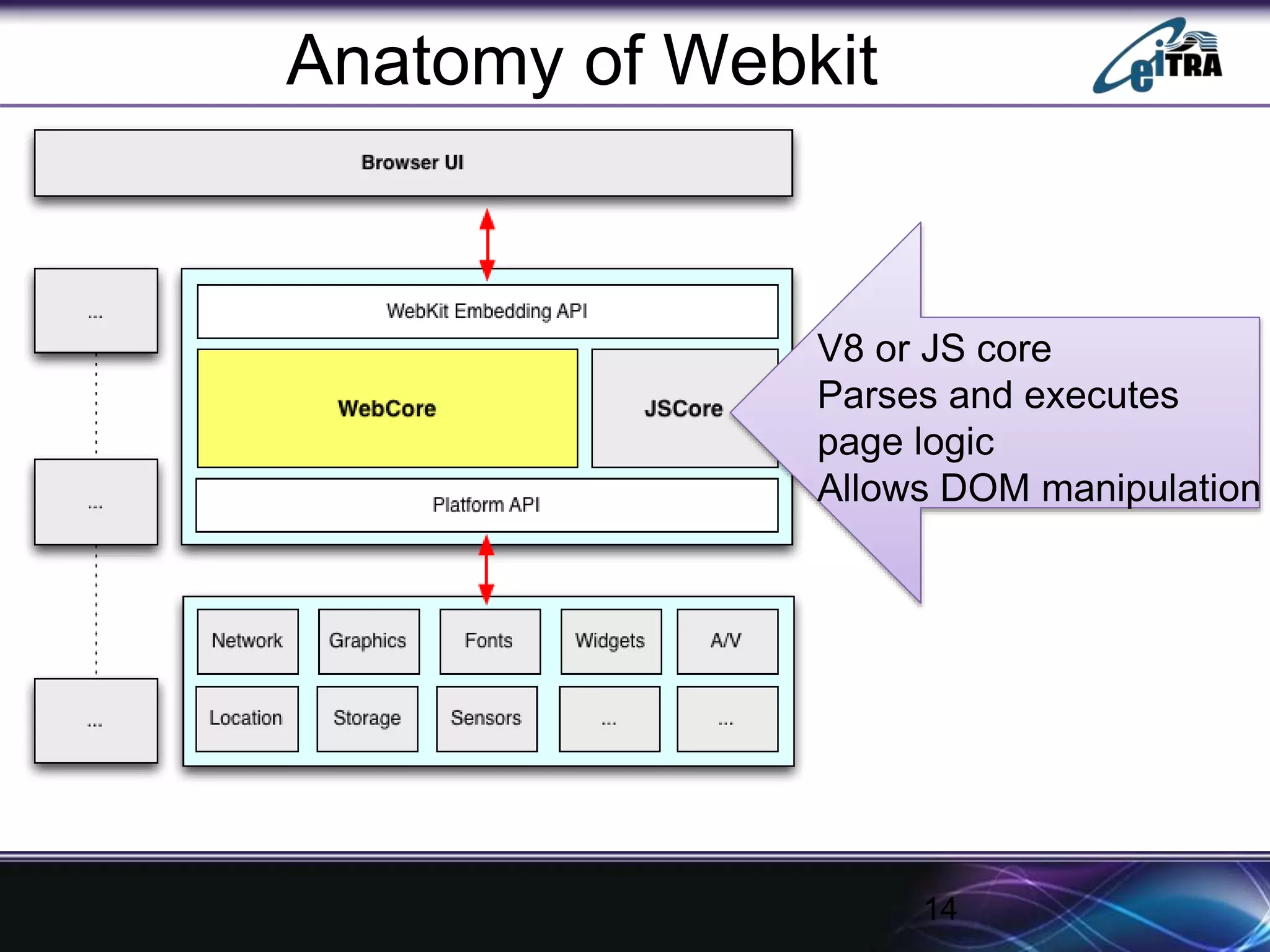
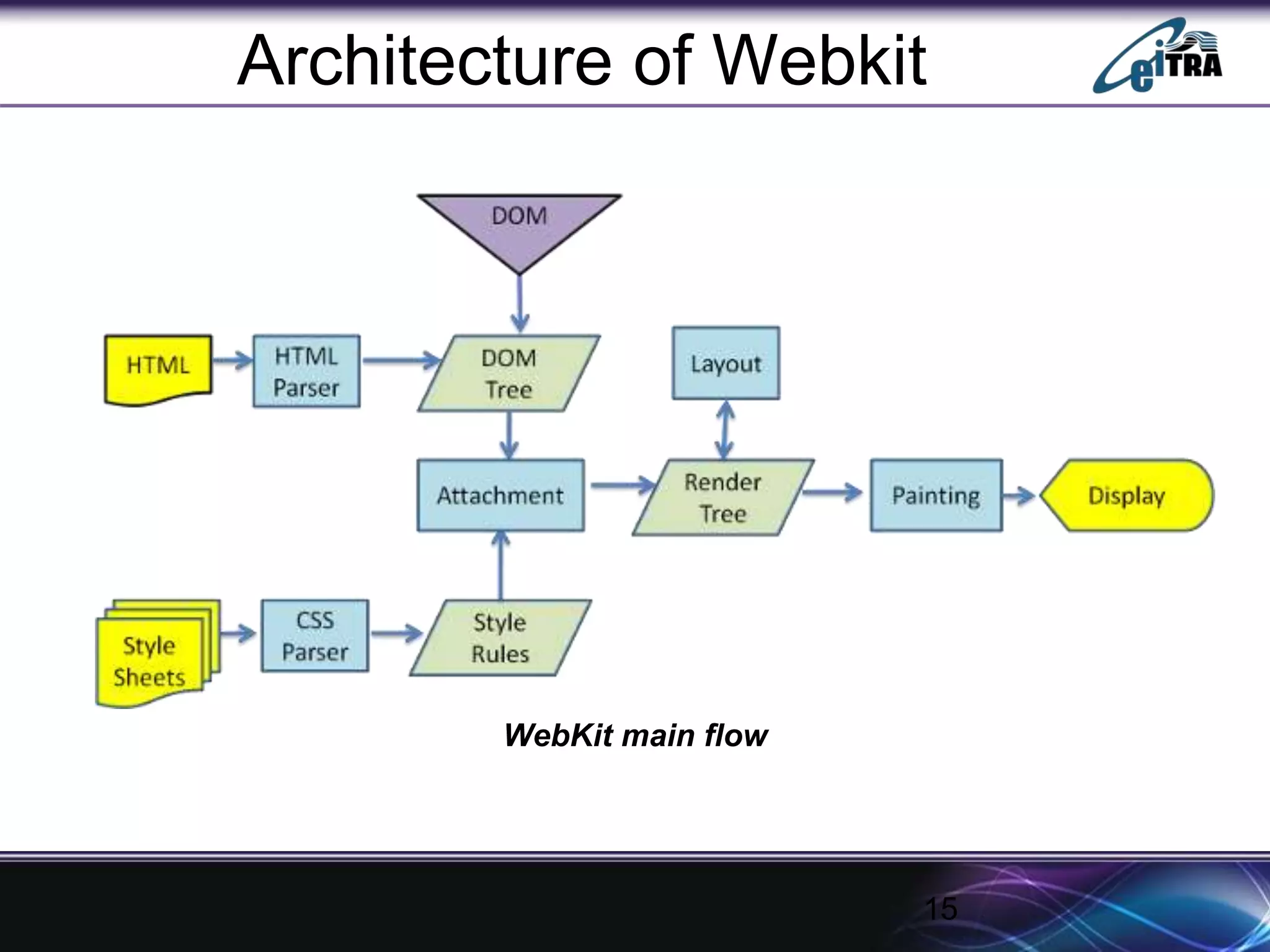
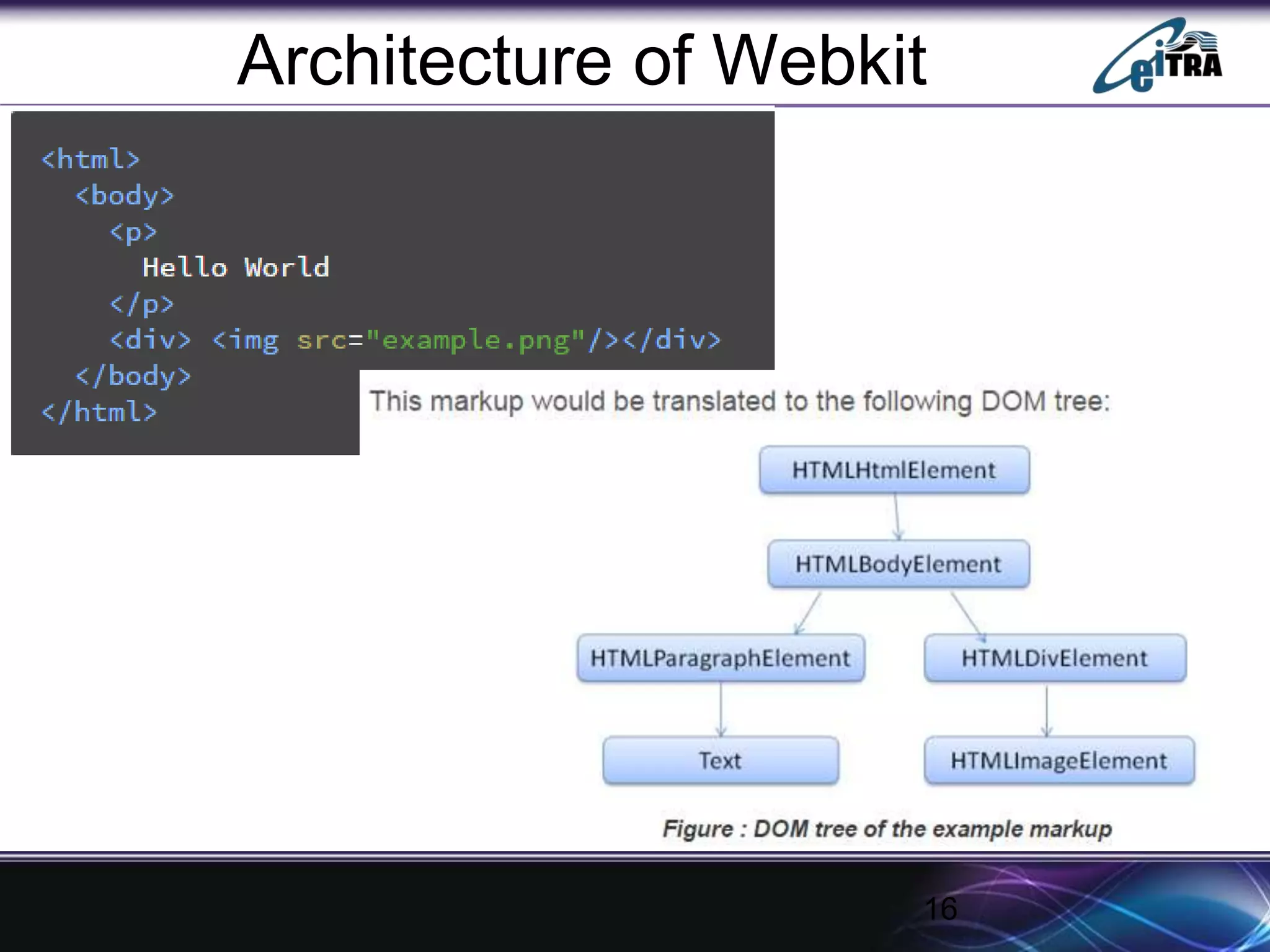
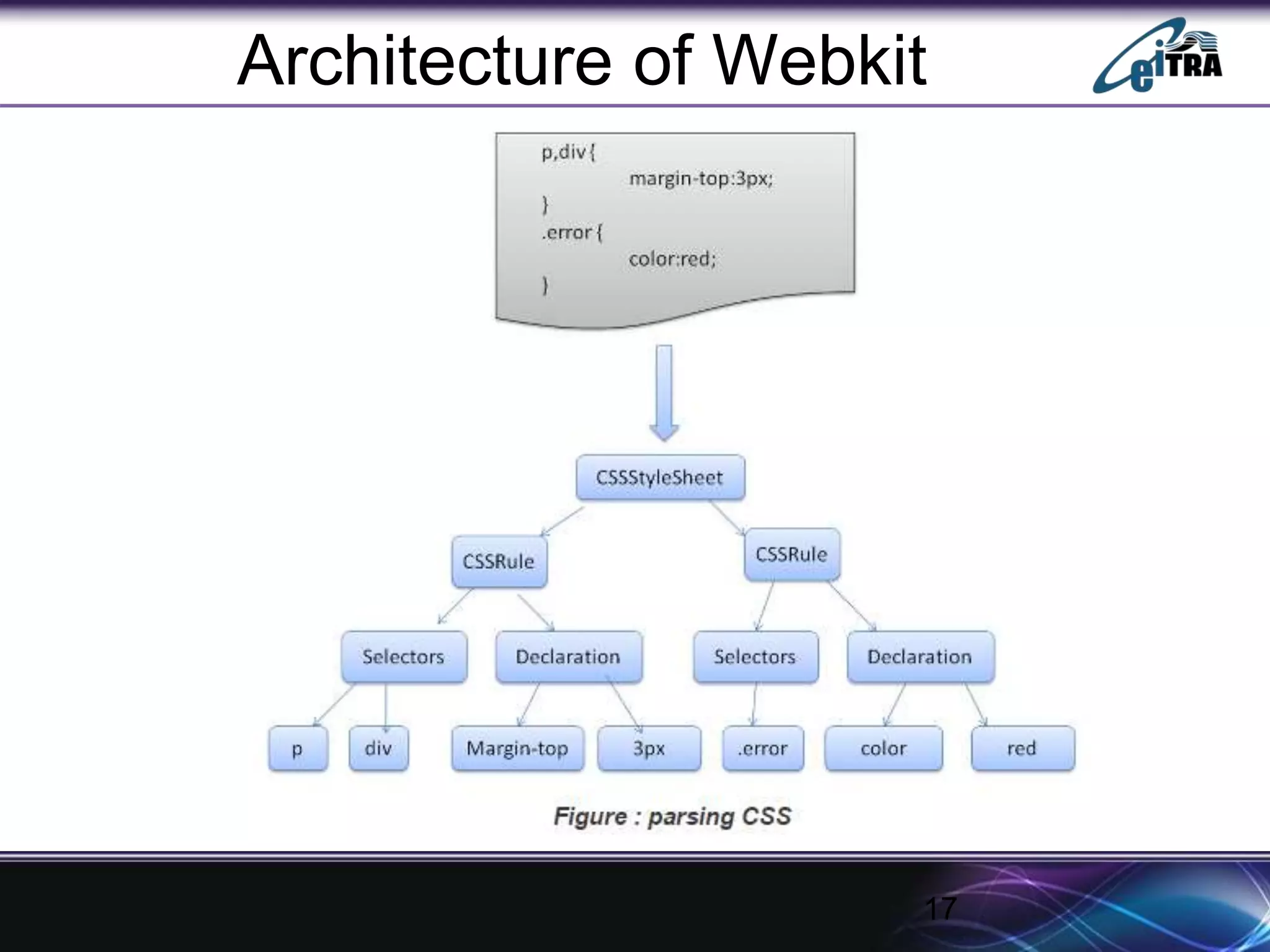
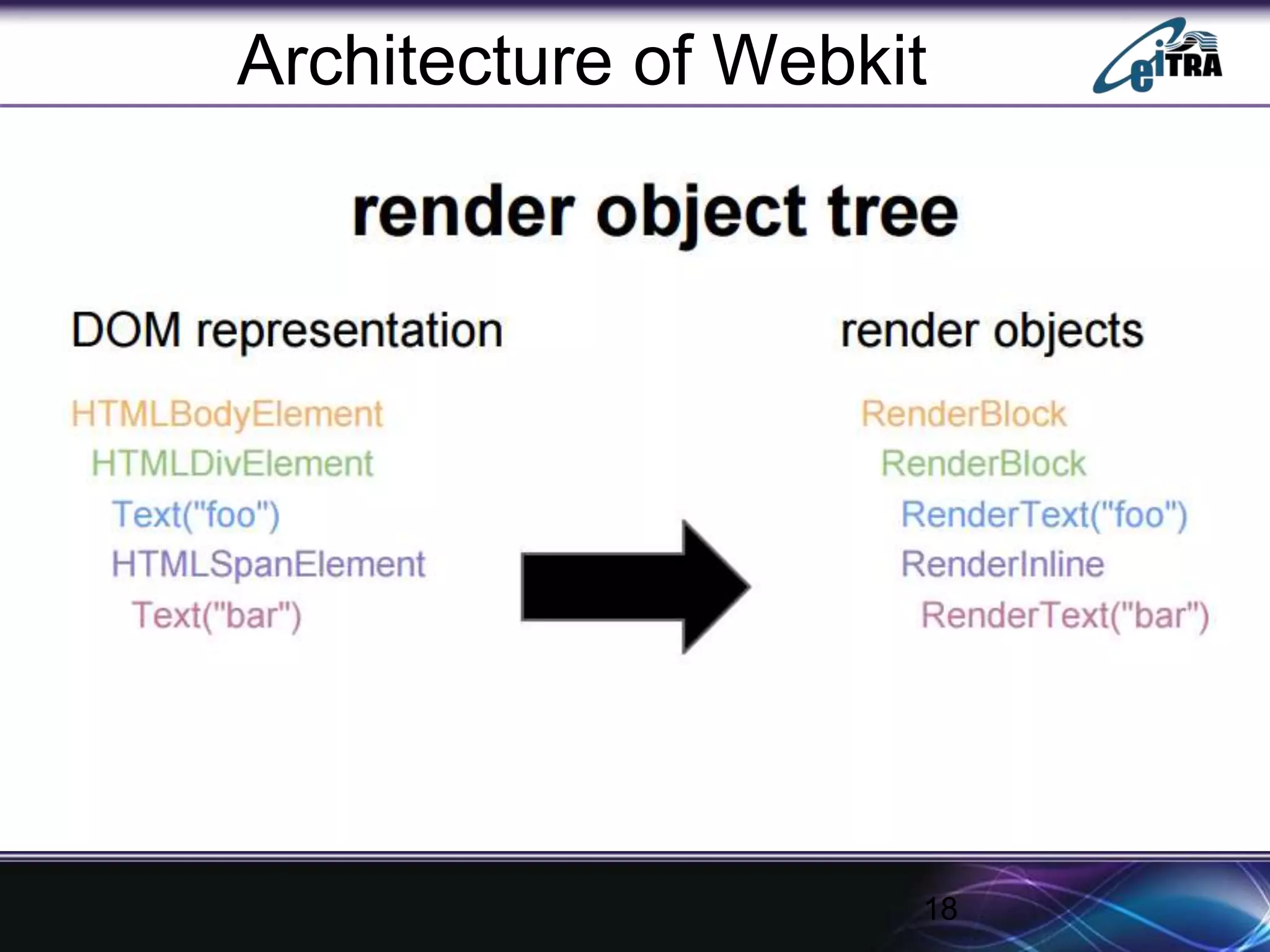
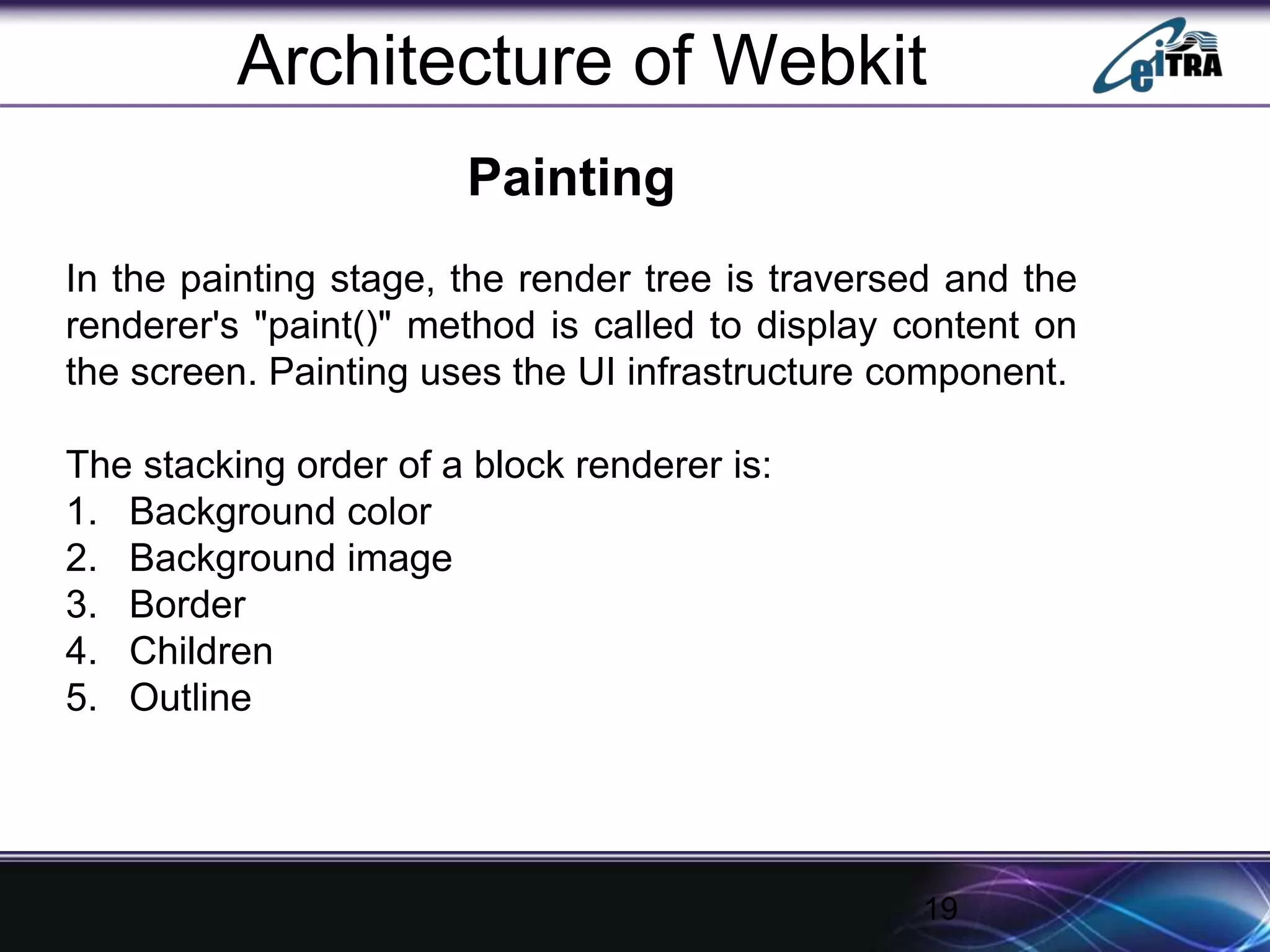
The document details the architecture and functioning of rendering engines in web browsers, explaining their role in translating and displaying web content. It covers different rendering engines associated with popular browsers, including Blink, Gecko, and WebKit, and outlines the general flow of operations from URL retrieval to graphical representation. Additionally, it describes the components involved in the browsing experience, such as the browser engine, user interface, and networking functionalities.