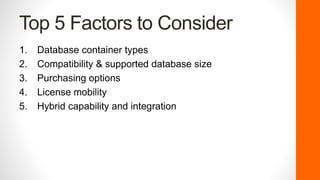
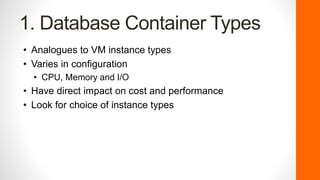
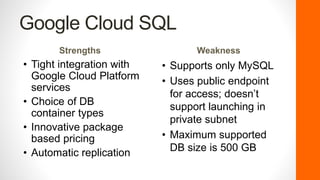
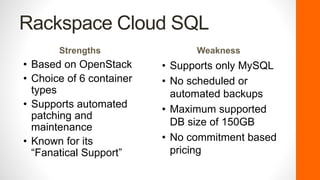
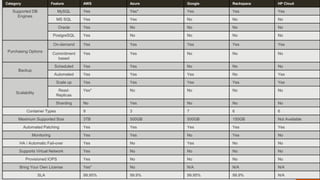
The document discusses the evolution and current landscape of cloud databases, focusing primarily on managed relational database services (DBaaS). It outlines key factors to consider when choosing a cloud database, including database container types, compatibility, purchasing options, license mobility, and hybrid integration. The top cloud database providers highlighted are Amazon RDS, Google Cloud SQL, Microsoft Azure SQL Database, and Rackspace Cloud SQL, each with their strengths and weaknesses.