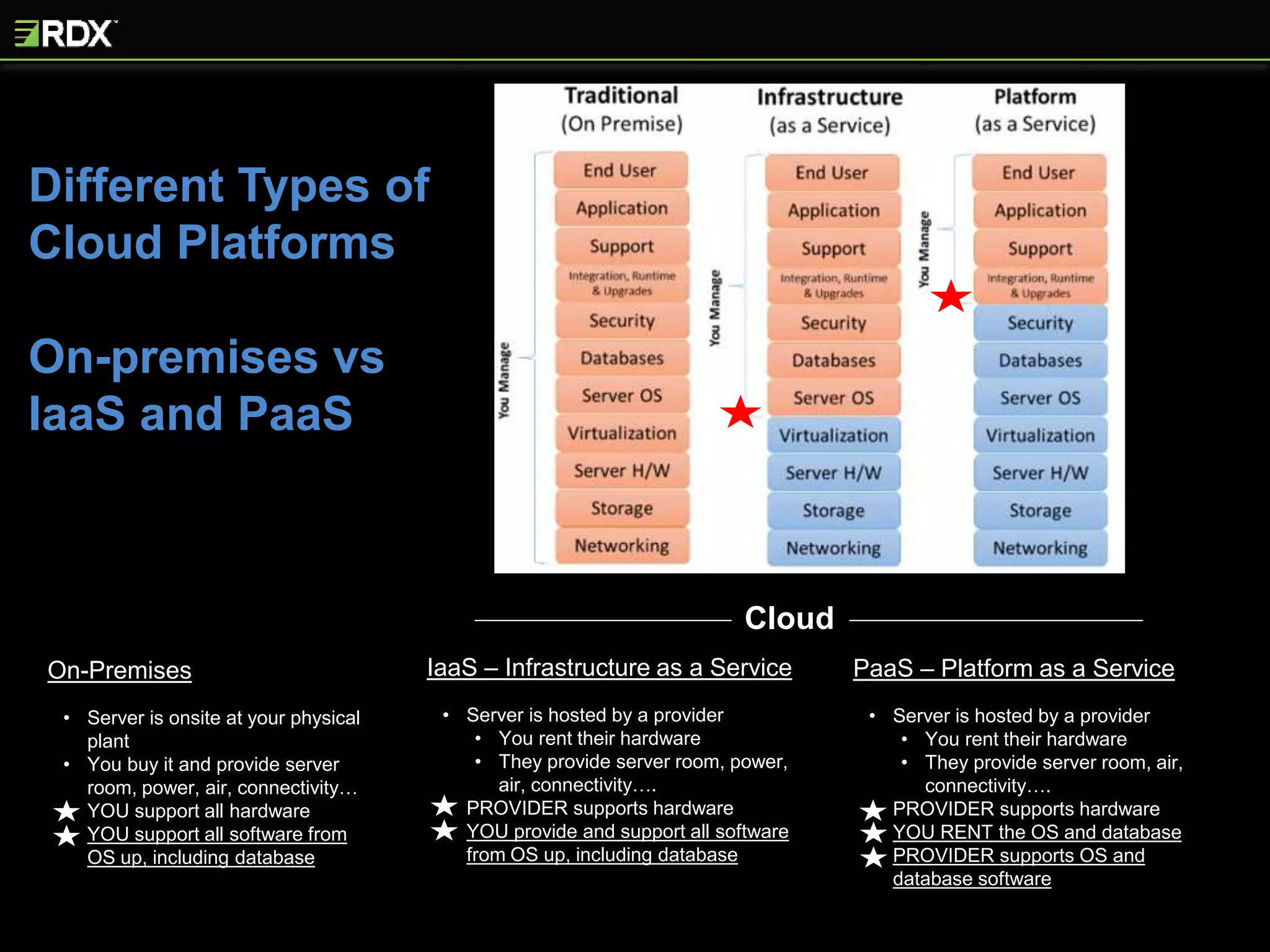
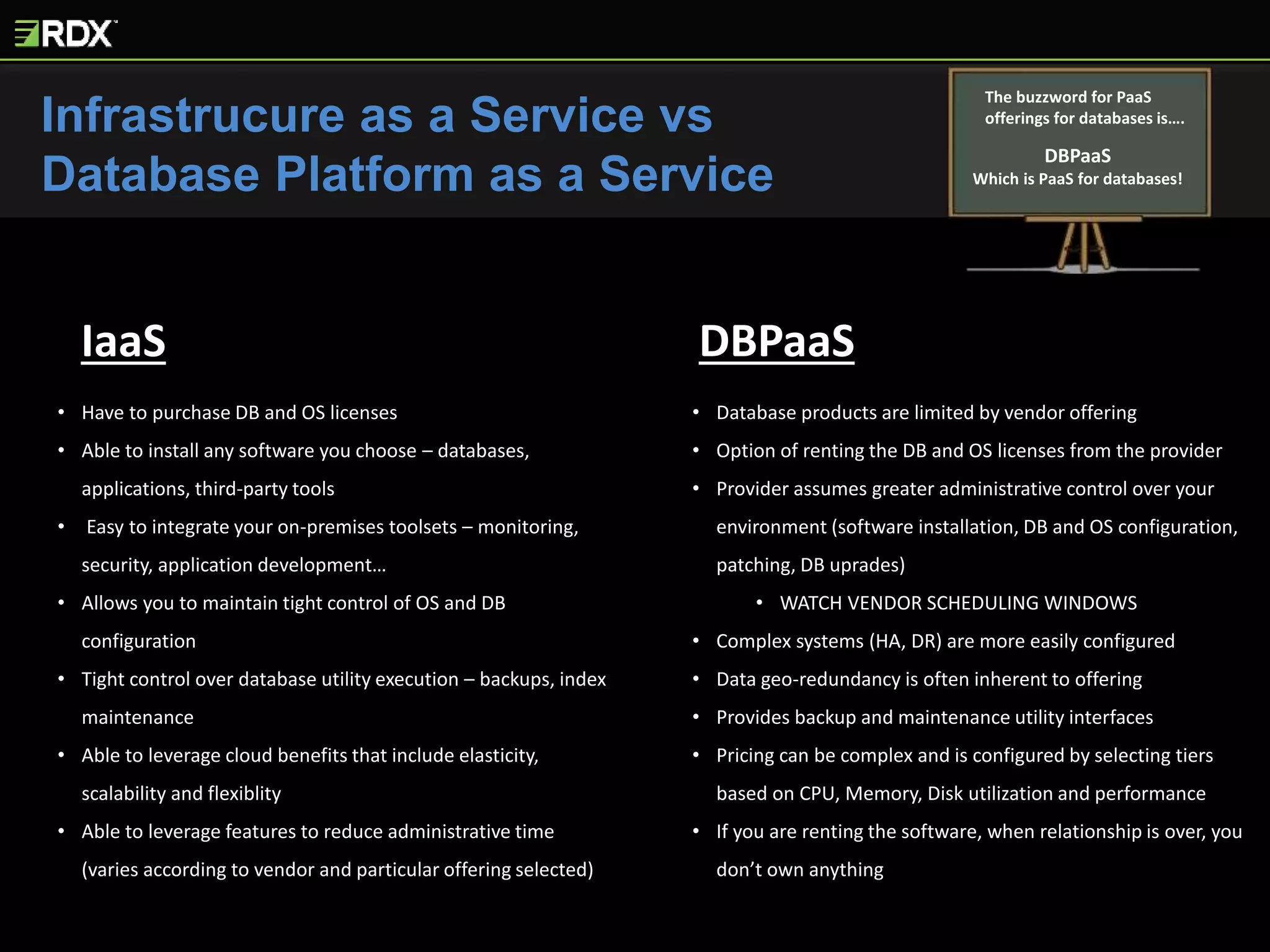
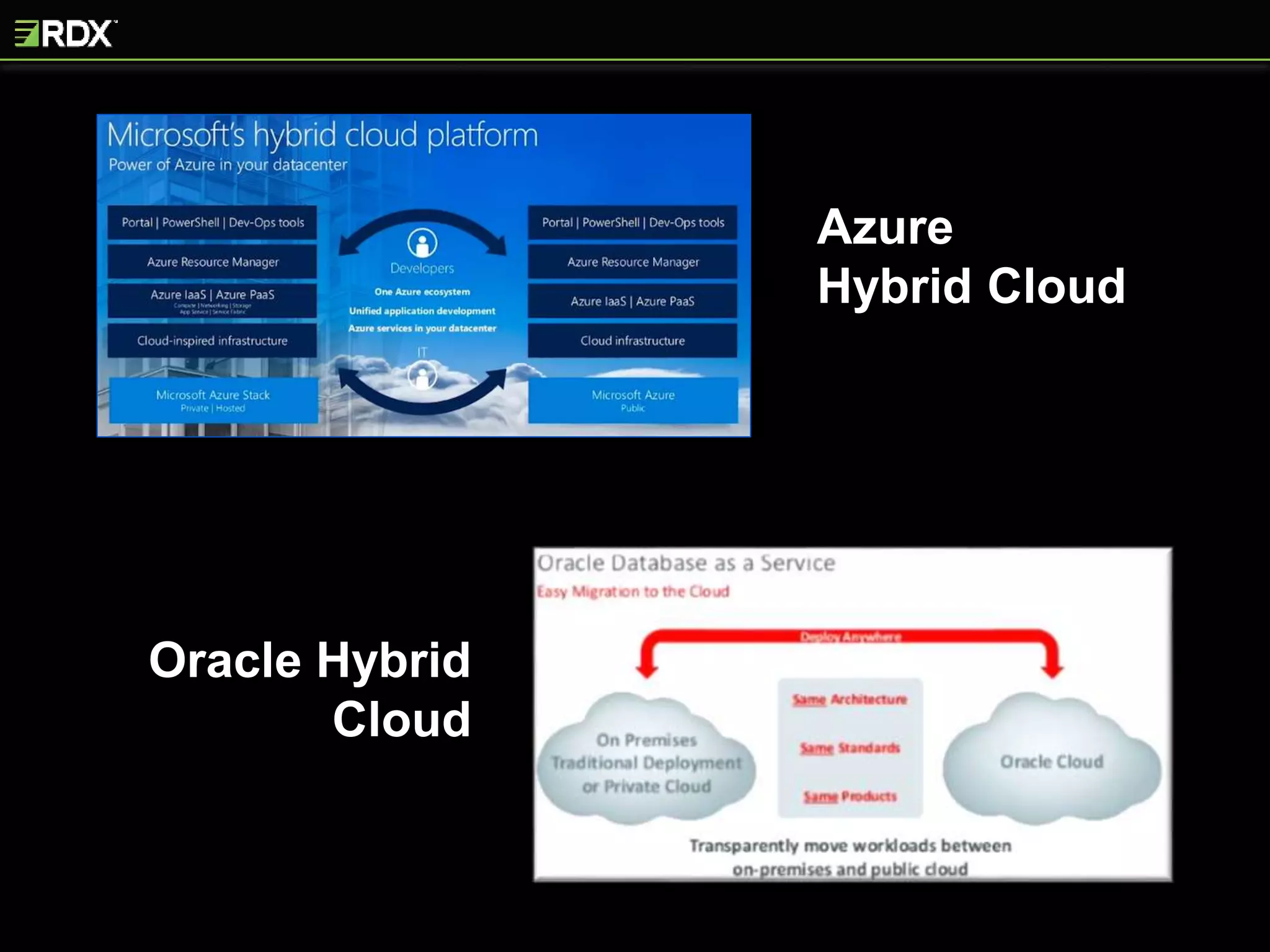
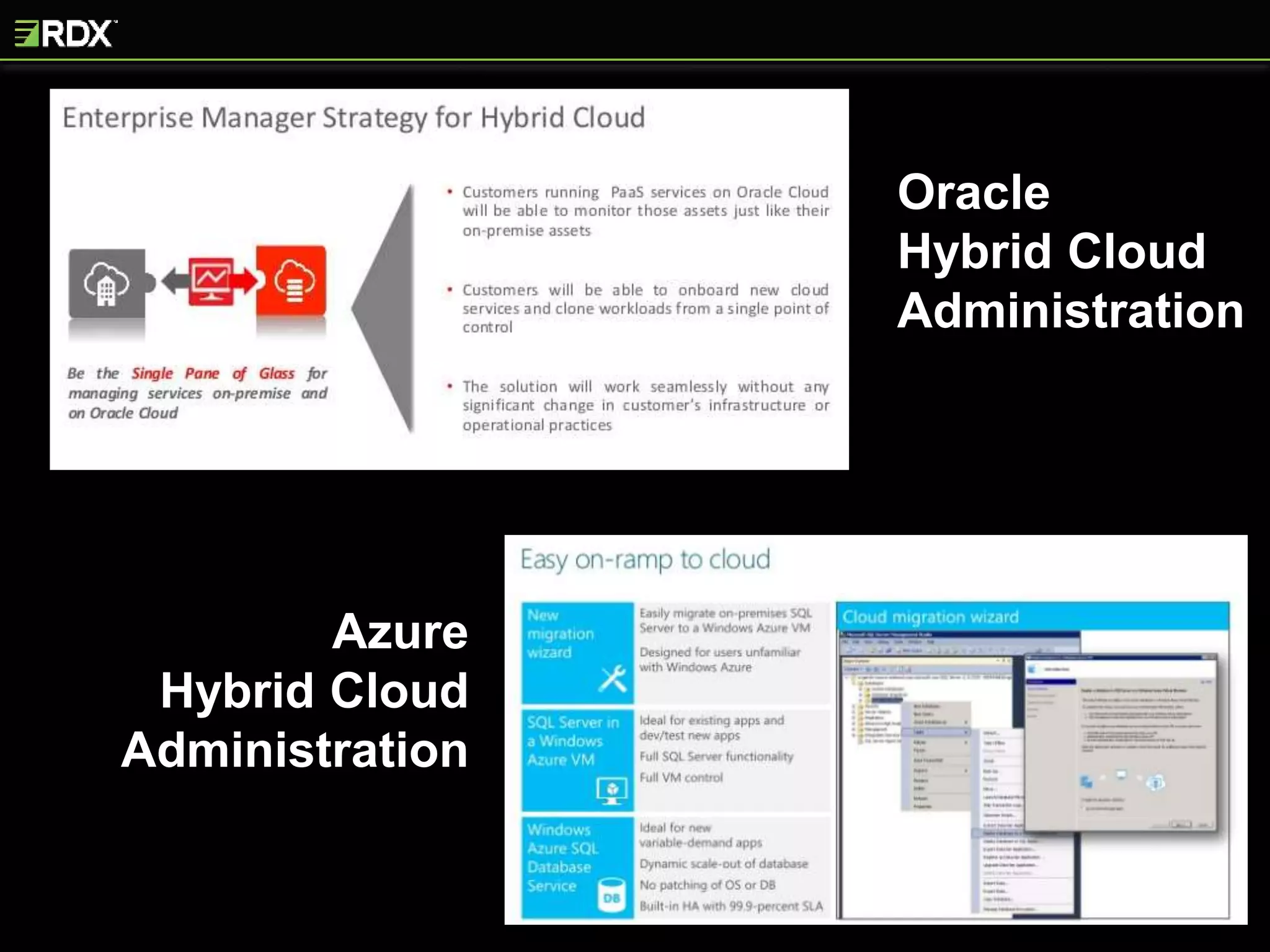
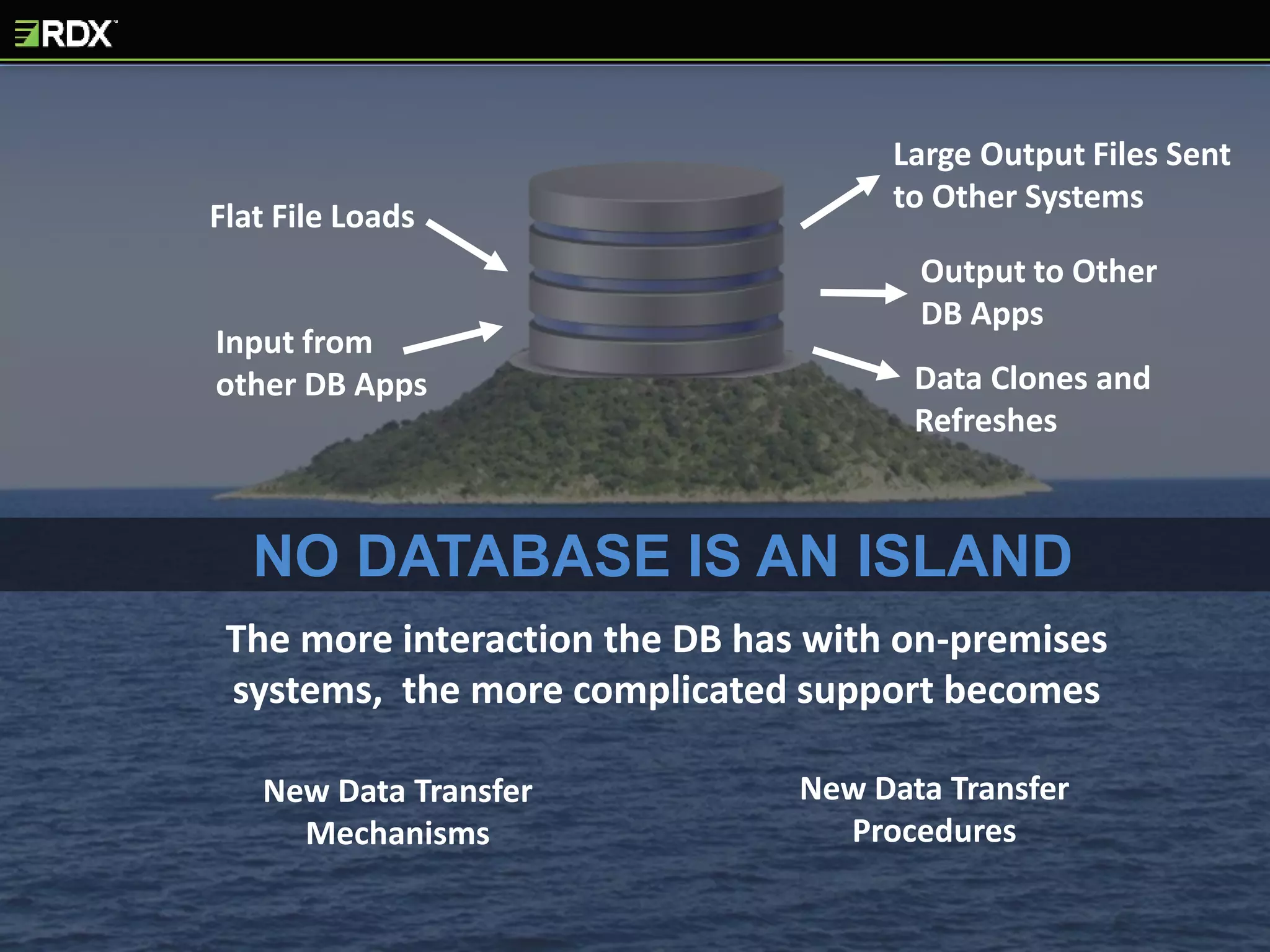
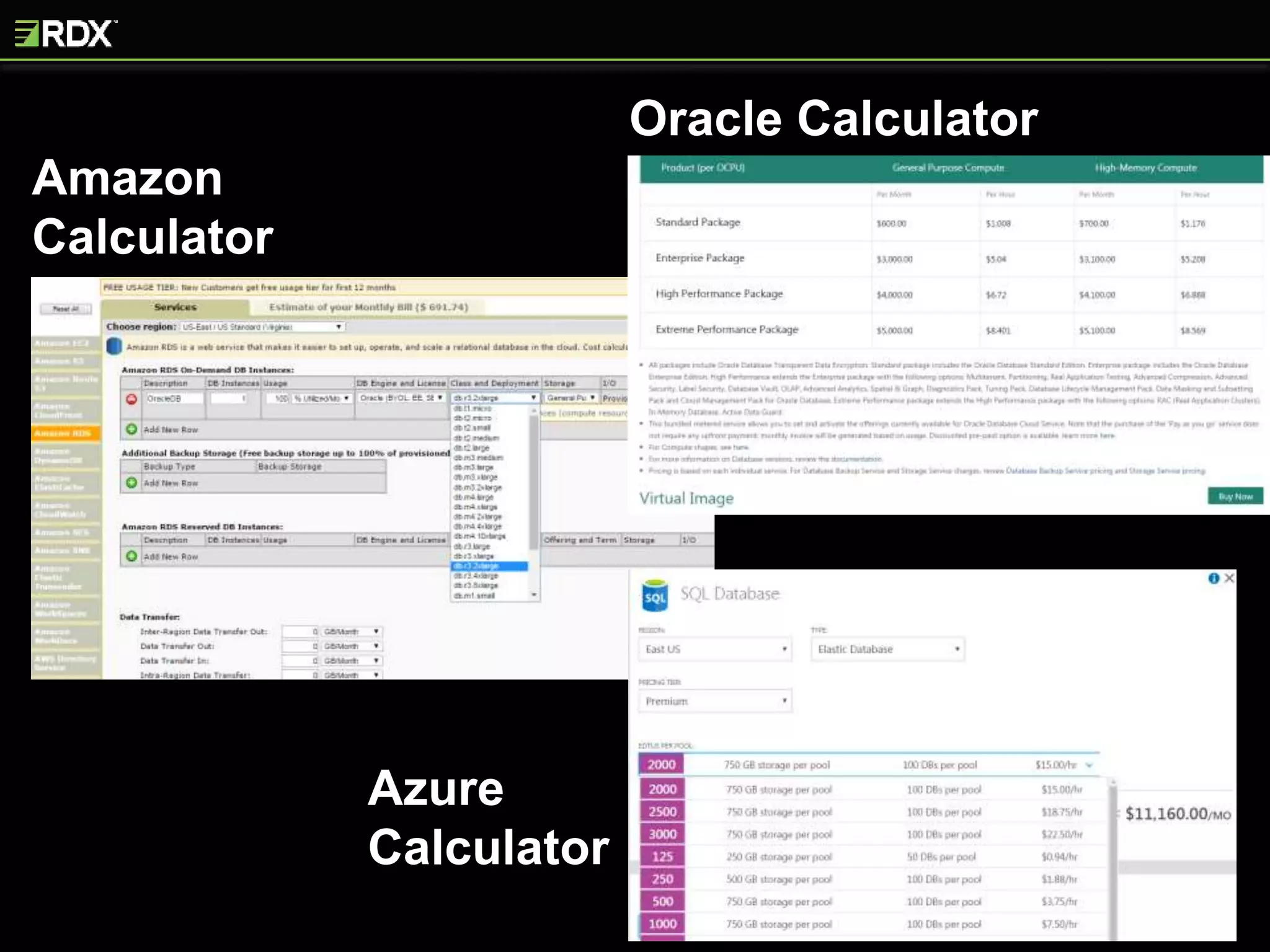
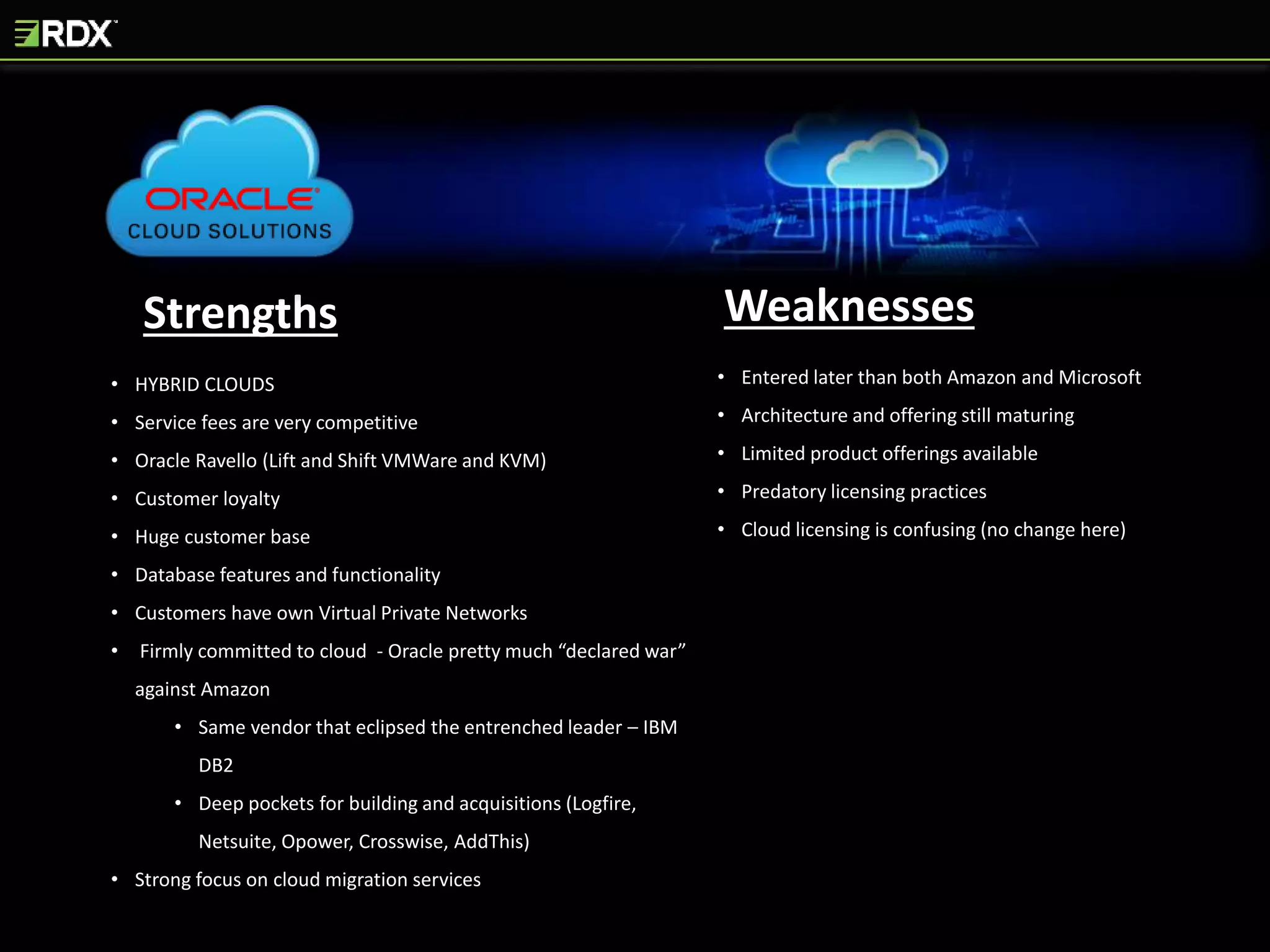
The document provides an extensive evaluation of cloud database management systems (DBMS) including various offerings, pricing models, and architectural distinctions between on-premises, IaaS, and PaaS. It outlines the implications of adopting cloud solutions on organizational support, change management, security, and compliance requirements. Furthermore, it emphasizes the criticality of selecting the right vendor and designing a comprehensive cloud strategy, alongside the assessment of current systems and the training needs for staff.