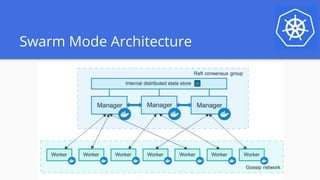
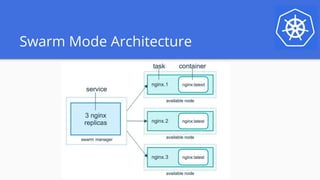
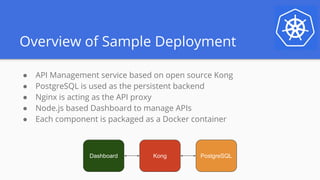
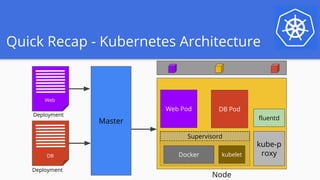
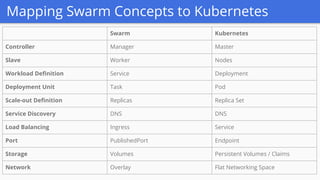
The document outlines a webinar series focused on migrating swarm applications to Kubernetes, featuring expert-led sessions on key concepts and practical guidance. It covers the architecture of swarm mode, comparisons to Kubernetes components, and provides resources for participants, including Google Cloud credits. The session aims to help attendees transition to Kubernetes with practical examples and insights into application deployment and management.