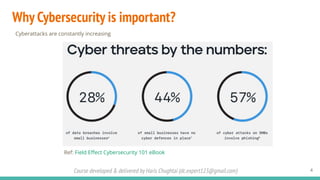
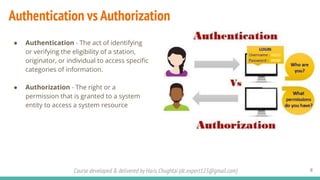
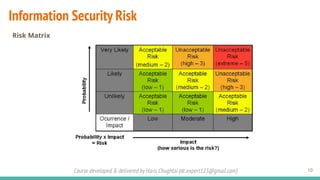
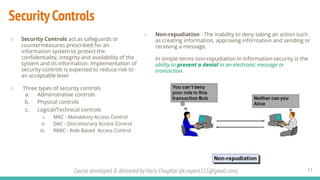
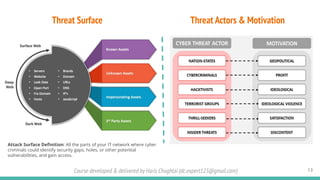
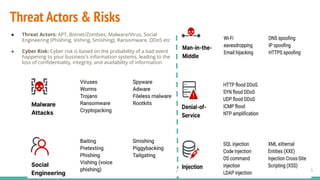
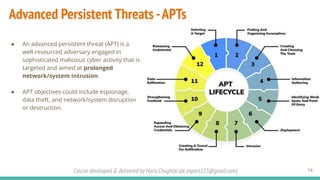
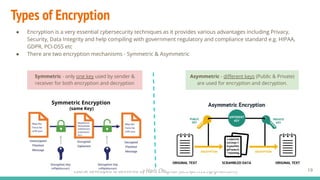
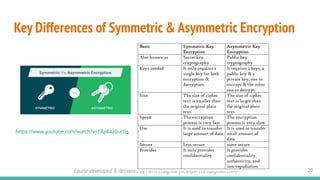
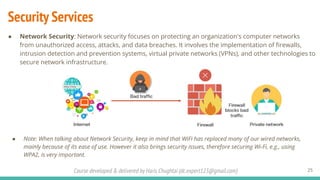
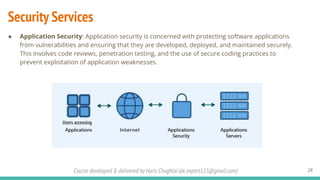
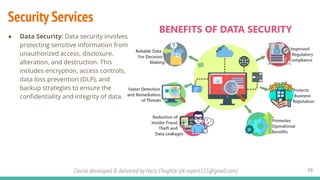
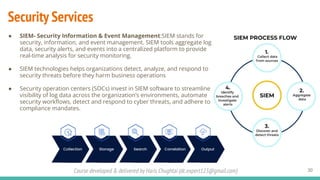
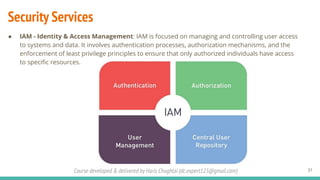
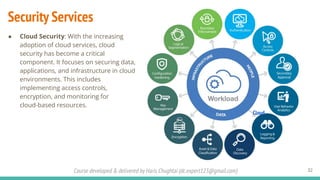
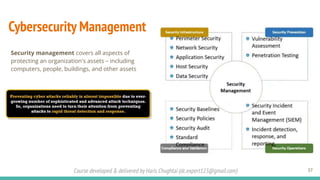
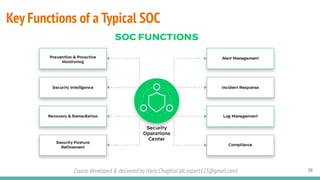
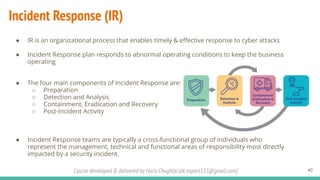
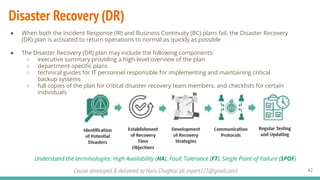
The document outlines a cybersecurity fundamentals course developed and delivered by Haris Chughtai, covering key concepts including the cybersecurity framework, the CIA triad (confidentiality, integrity, and availability), data privacy and protection, various types of security services, and risk management. It delves into common cyber threats, attack vectors, and defensive strategies involving encryption, identity management, and incident response. The course also emphasizes the importance of understanding roles, processes, and technologies in mitigating cybersecurity risks.