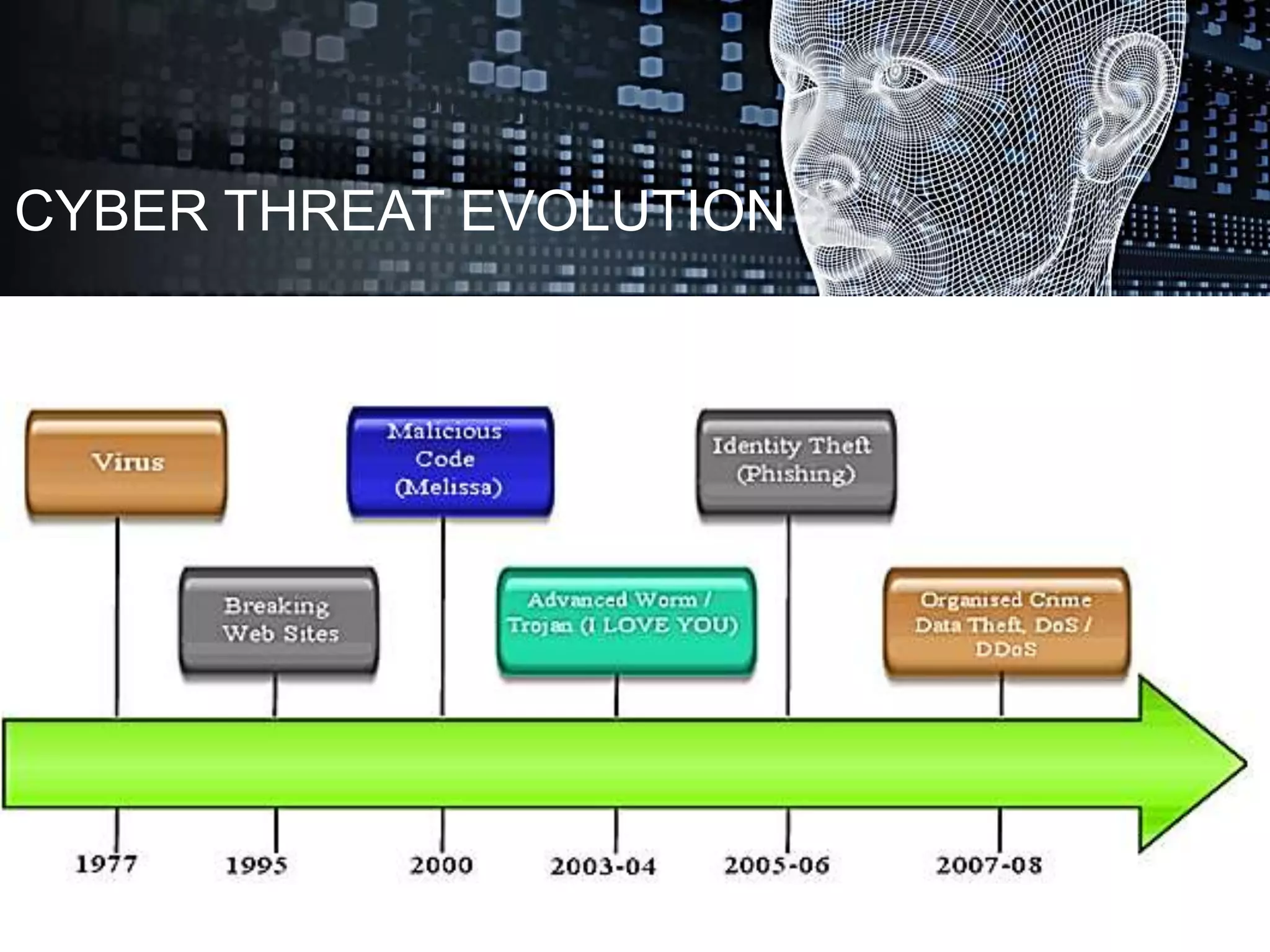
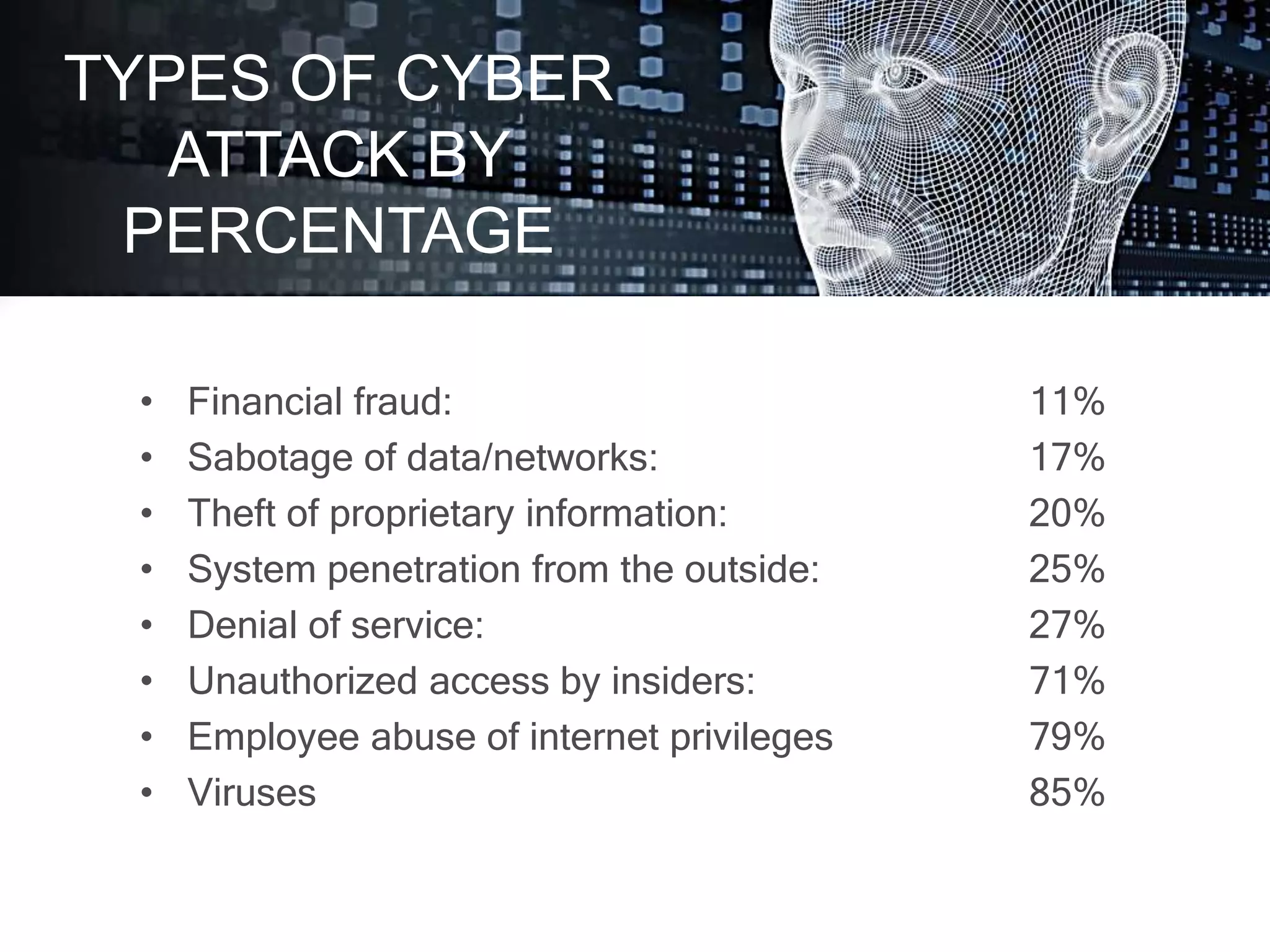
Cyber crime and security refers to illegal activities committed using computers and the internet. It can include hacking, denial of service attacks, virus dissemination, and software piracy. The document discusses the history and evolution of cyber threats and categorizes common types of cyber crimes. It also provides statistics on the most common types of cyber attacks and offers safety tips, emphasizing the importance of cyber security to defend against critical attacks and browse safely.