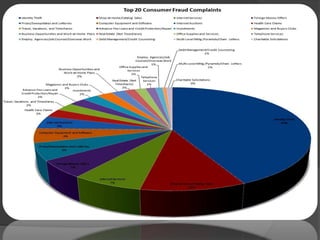
This document provides an overview of cyber crime. It begins with introductions and history, then covers categories and types of cyber crimes like hacking, viruses, and cyber terrorism. It discusses cyber criminals and security measures. Prevention tips are outlined, along with cyber law and recent amendments. The conclusion emphasizes that successful response requires cooperation between technology and law enforcement.