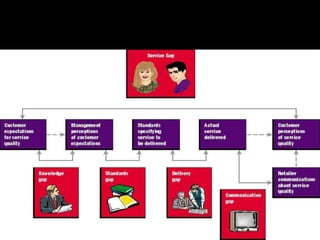
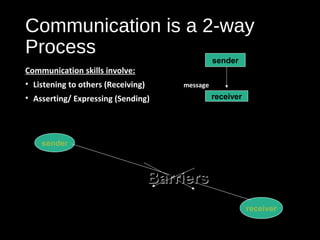
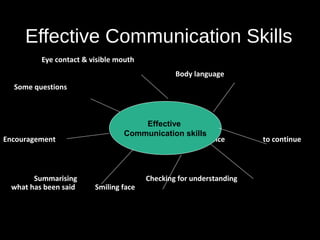
This document provides an overview of key concepts for effective customer service. It discusses closing common service gaps through standards, delivery, communication and knowledge. Good customer service involves communicating effectively with customers through skills like active listening, questioning, and using positive body language. Maintaining high service standards, dealing with special customer needs, and planning for good customer experiences are also covered. The document provides guidance for presenting a positive organizational image and dealing with difficult customer situations.