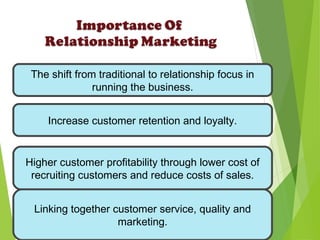
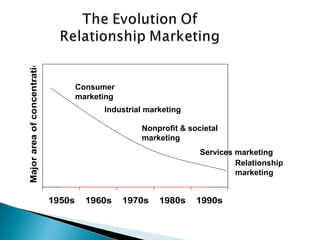
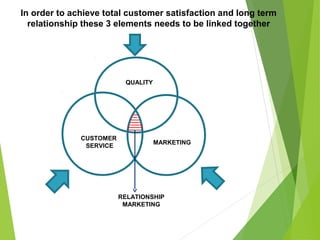
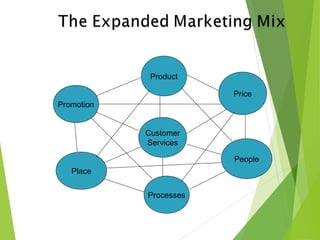
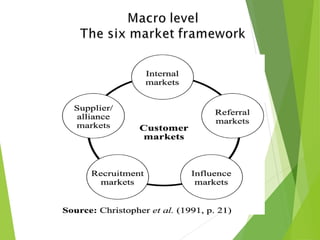
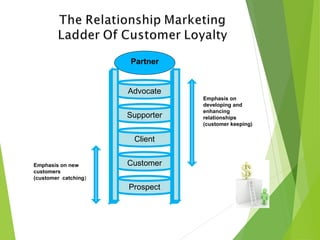
The document outlines the evolution and fundamental concepts of relationship marketing (RM), emphasizing its importance in maximizing customer lifetime value and enhancing long-term relationships. It discusses the transition from traditional marketing approaches to RM, detailing key drivers, principles, and the expanded marketing mix that integrates customer service, quality, and marketing strategies. Furthermore, it highlights the importance of engaging various market domains, including customers, suppliers, and internal stakeholders, to achieve mutual benefits and improved profitability.