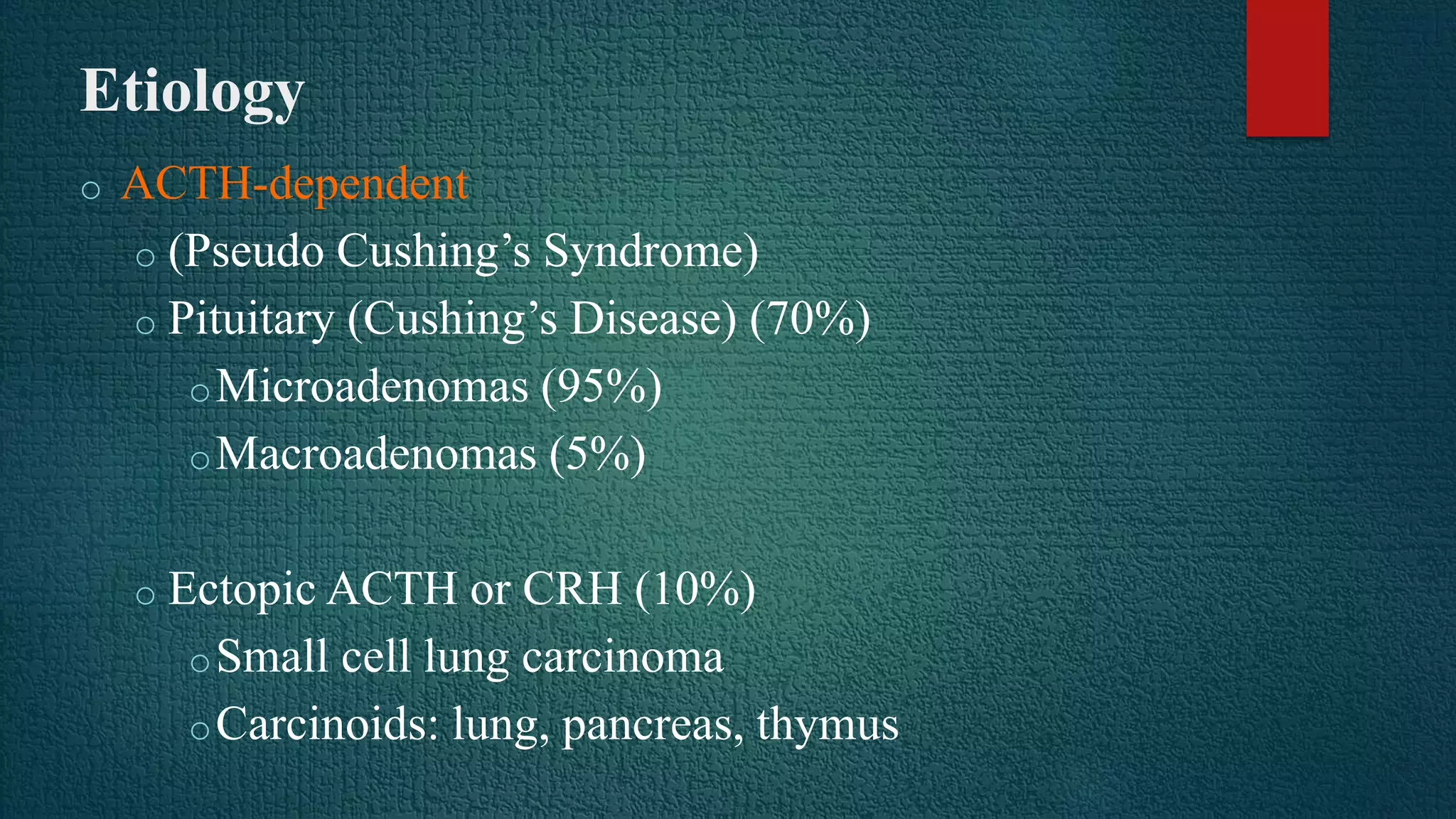
Cushing's syndrome results from prolonged exposure to excess glucocorticoids and is associated with poor suppressibility of cortisol production with dexamethasone. The most common cause is exogenous glucocorticoid administration, while endogenous causes include pituitary adenomas (70%), adrenal adenomas or carcinomas (15%), and ectopic ACTH secretion (10%). Diagnosis involves tests like the overnight low-dose dexamethasone suppression test and 24-hour urine free cortisol. Treatment depends on the underlying cause, and may include transphenoidal pituitary surgery, adrenalectomy, pituitary irradiation, or medical therapy with cortisol synthesis inhibitors.