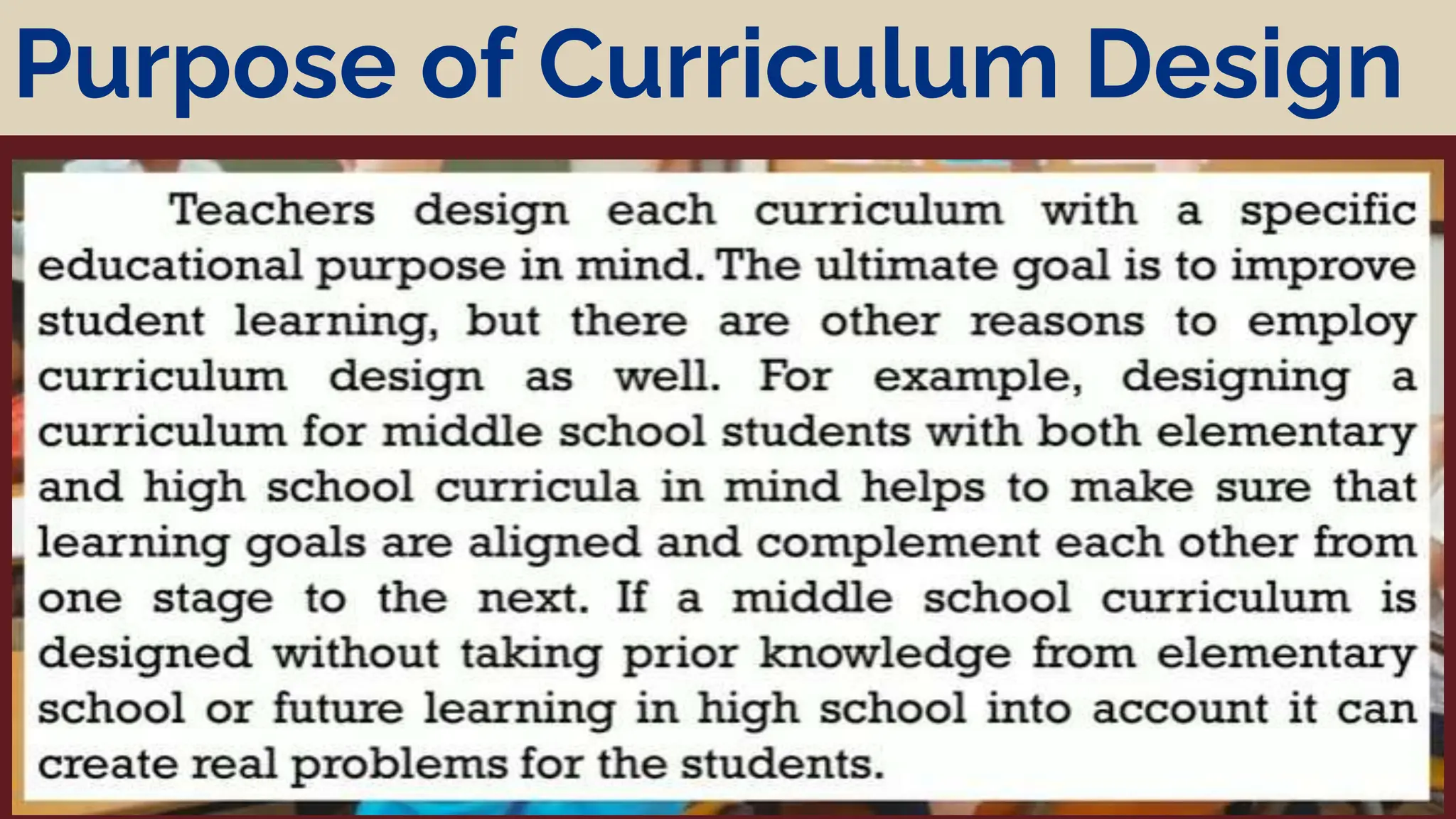
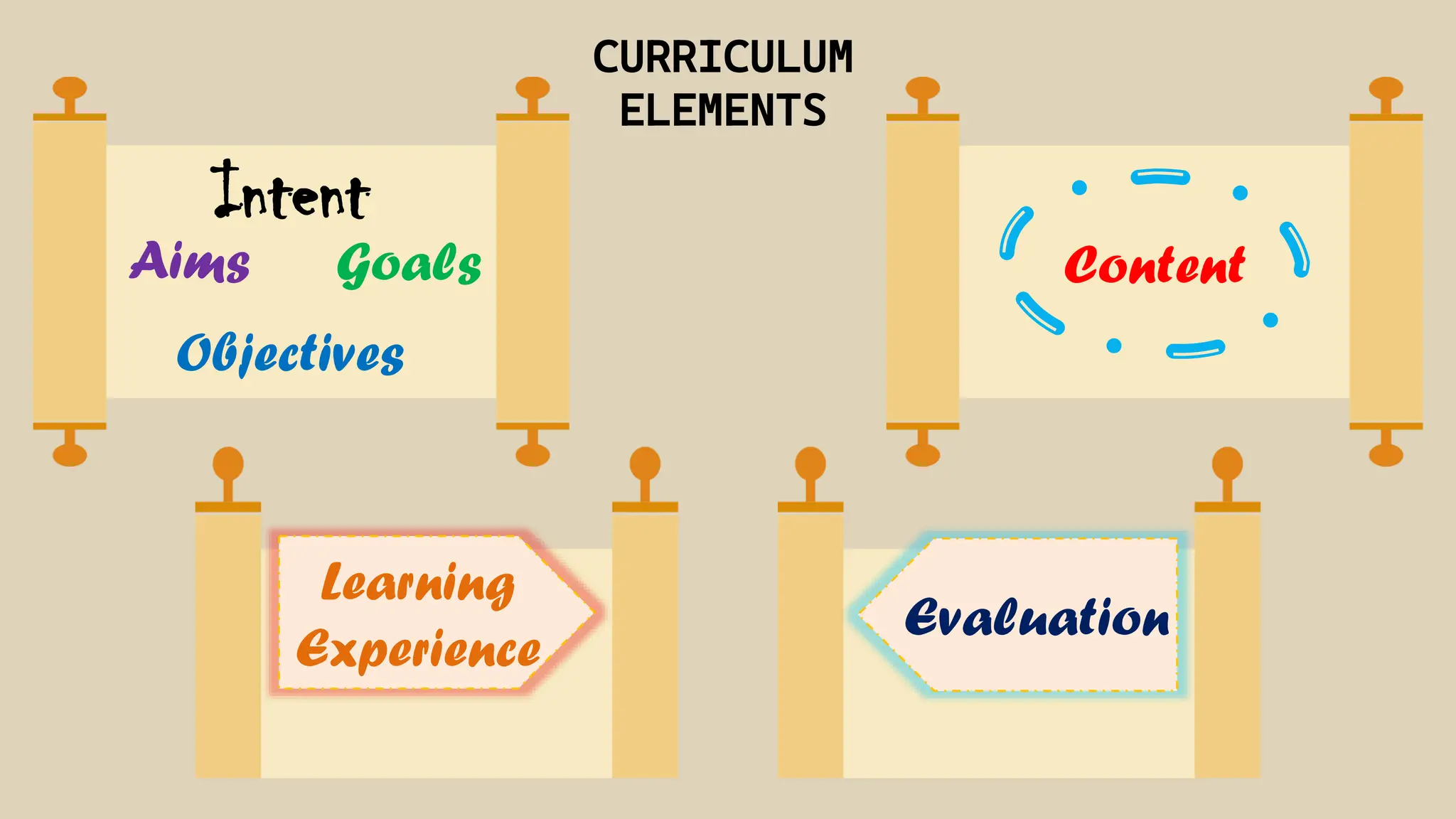
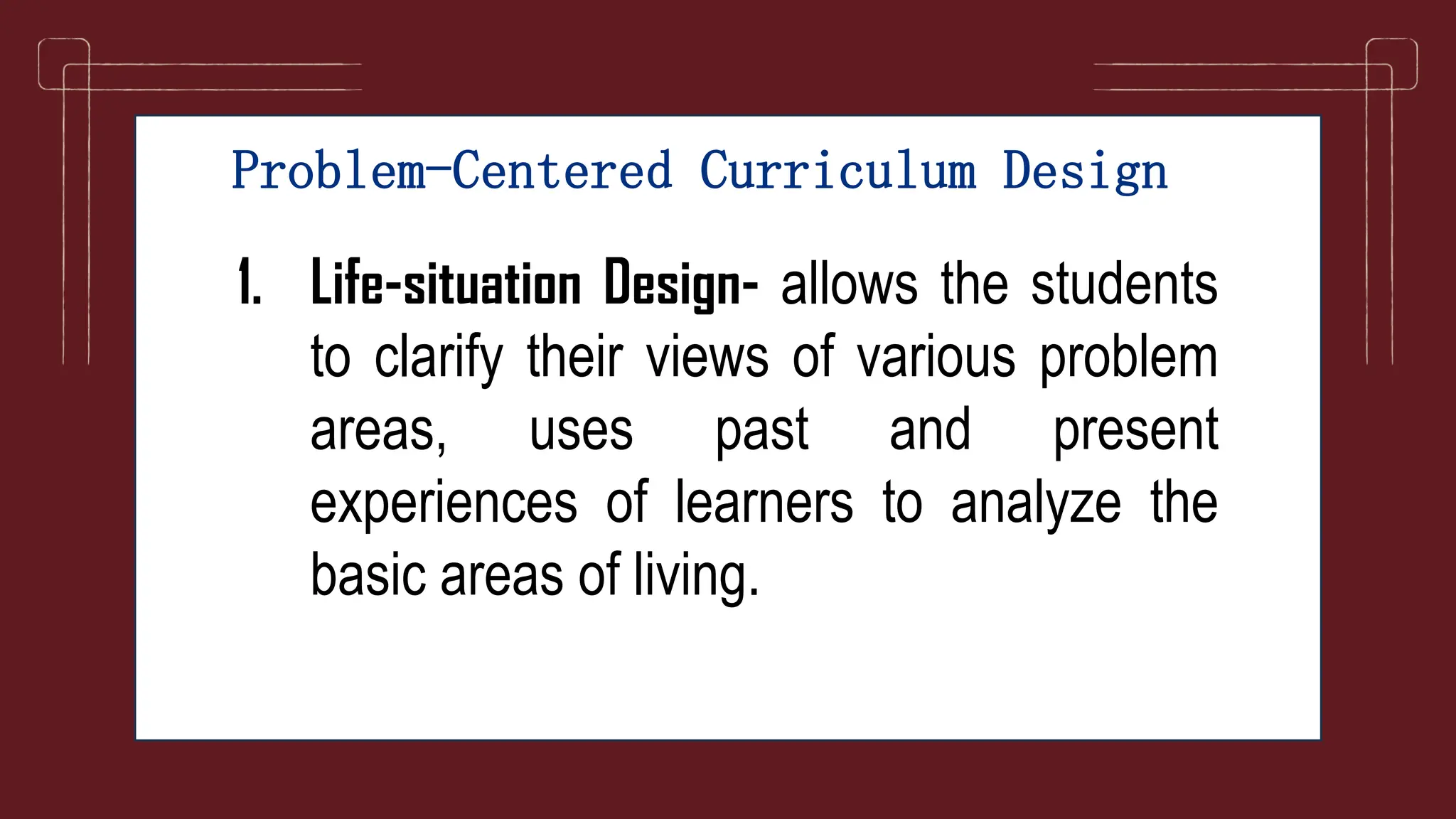
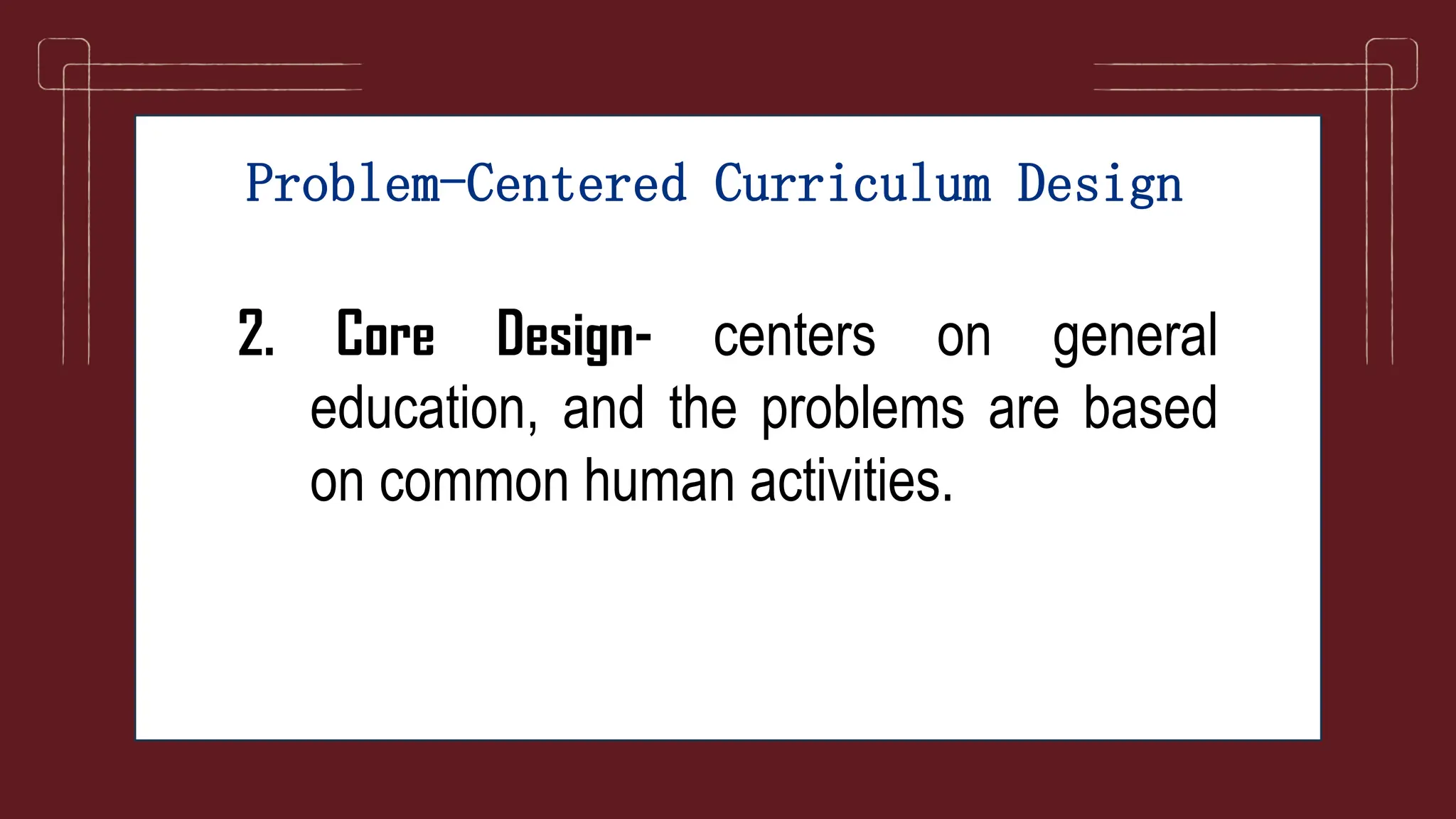
The document discusses different models of curriculum design including subject-centered, learner-centered, and problem-centered approaches. Subject-centered curriculum focuses on content divided into separate subjects. Learner-centered designs emphasize the needs and interests of students, such as child-centered and experience-centered models. Problem-centered curricula draw on social issues and student abilities, like life-situation and core designs.