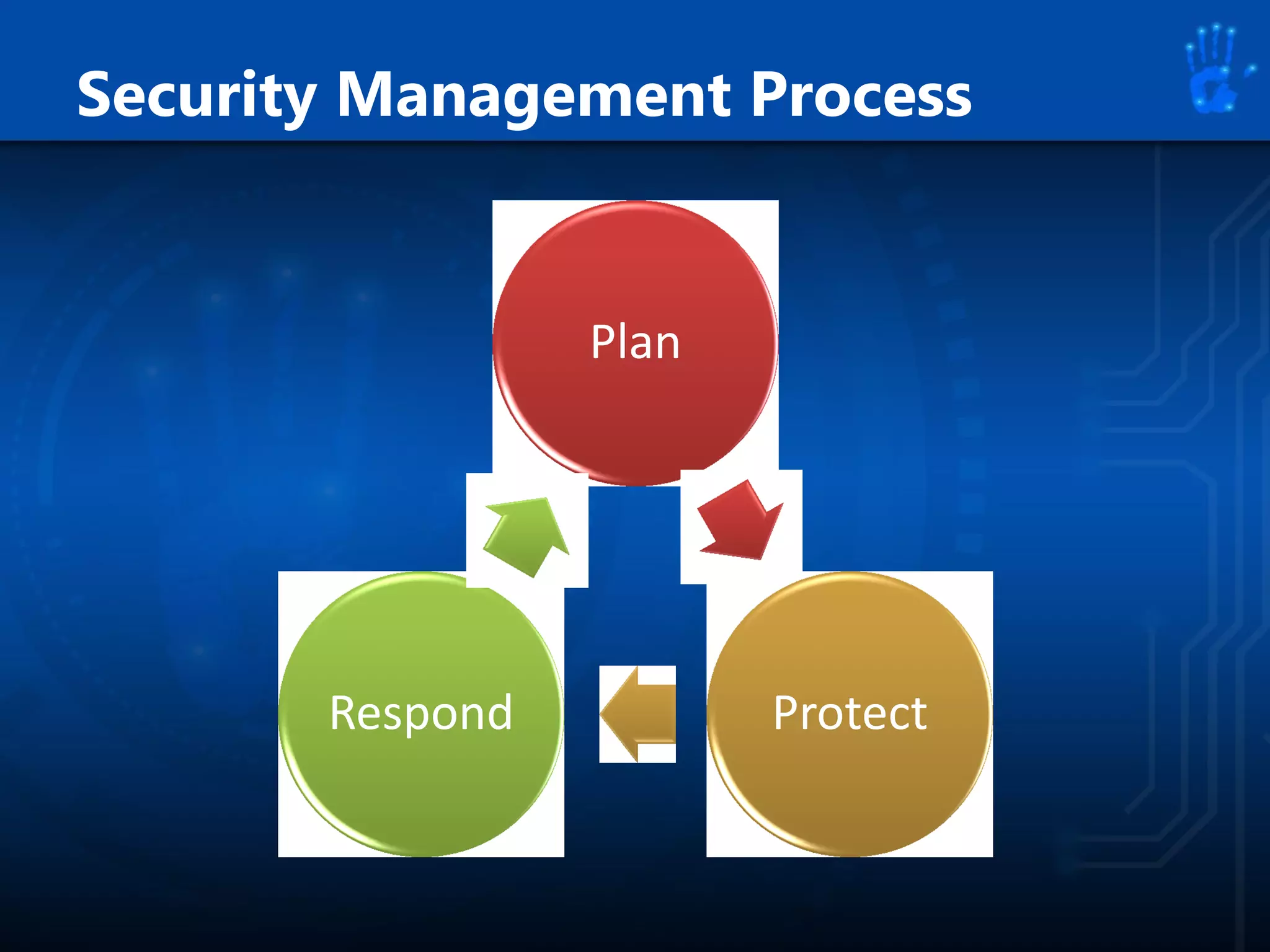
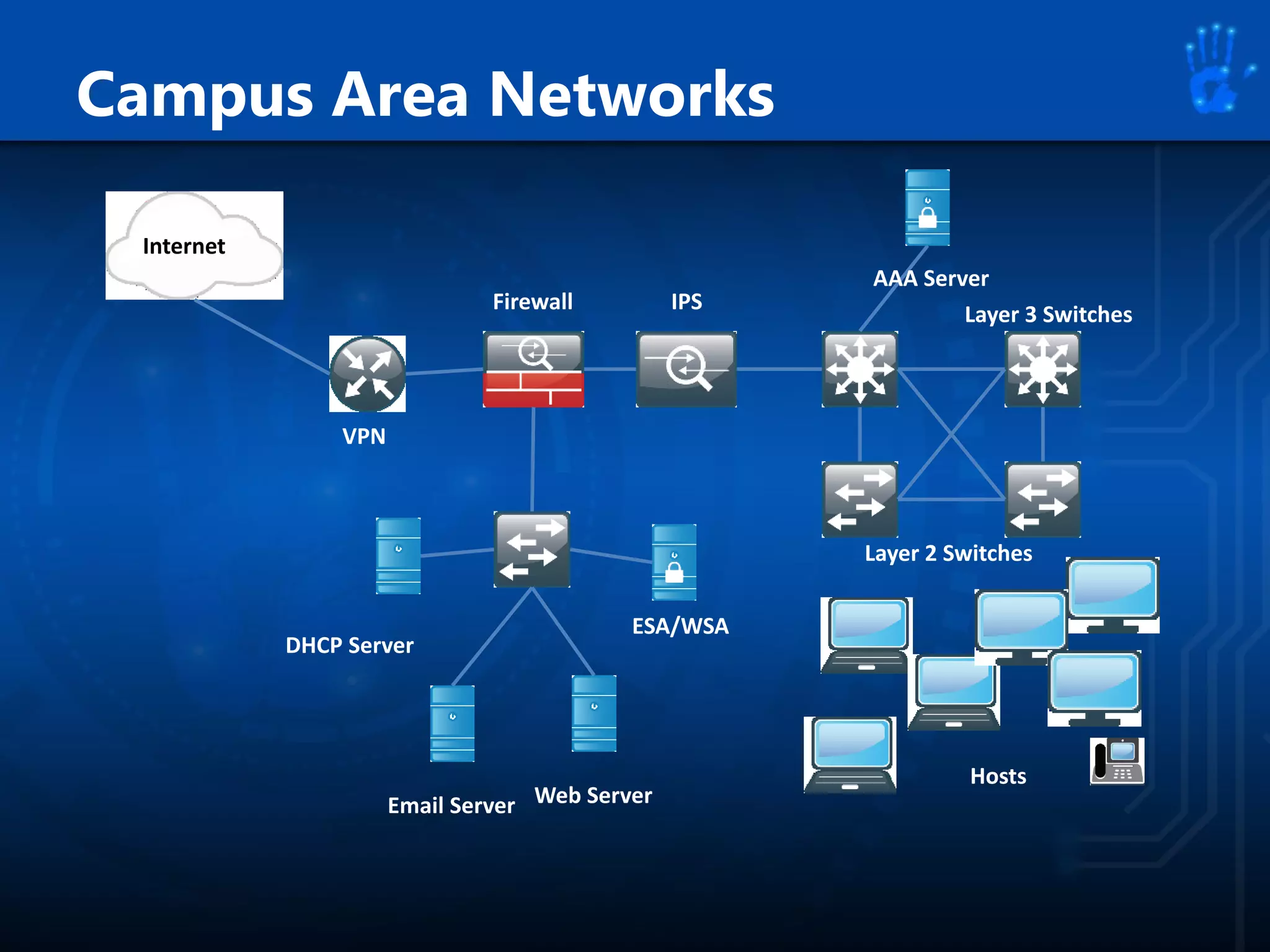
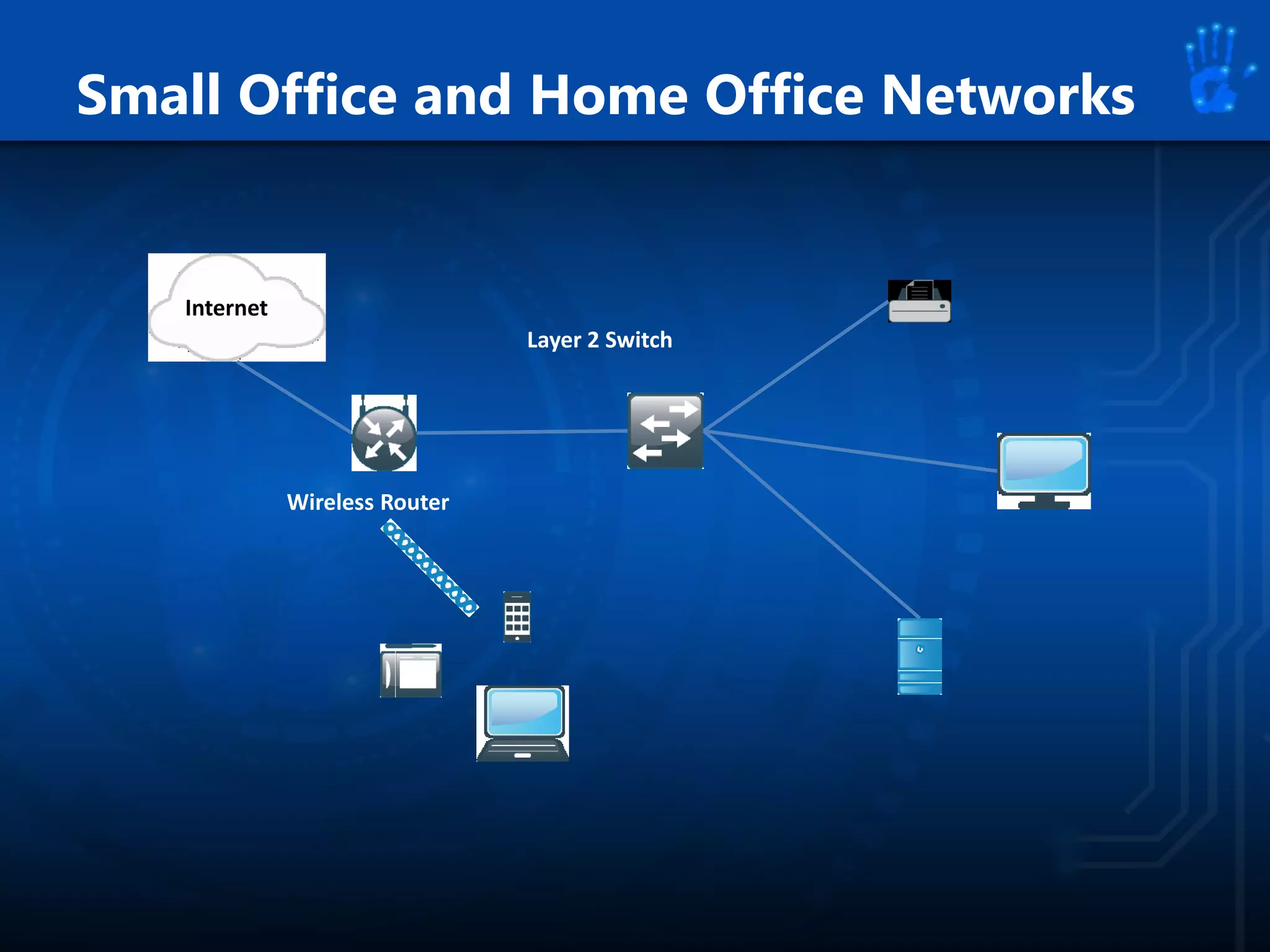
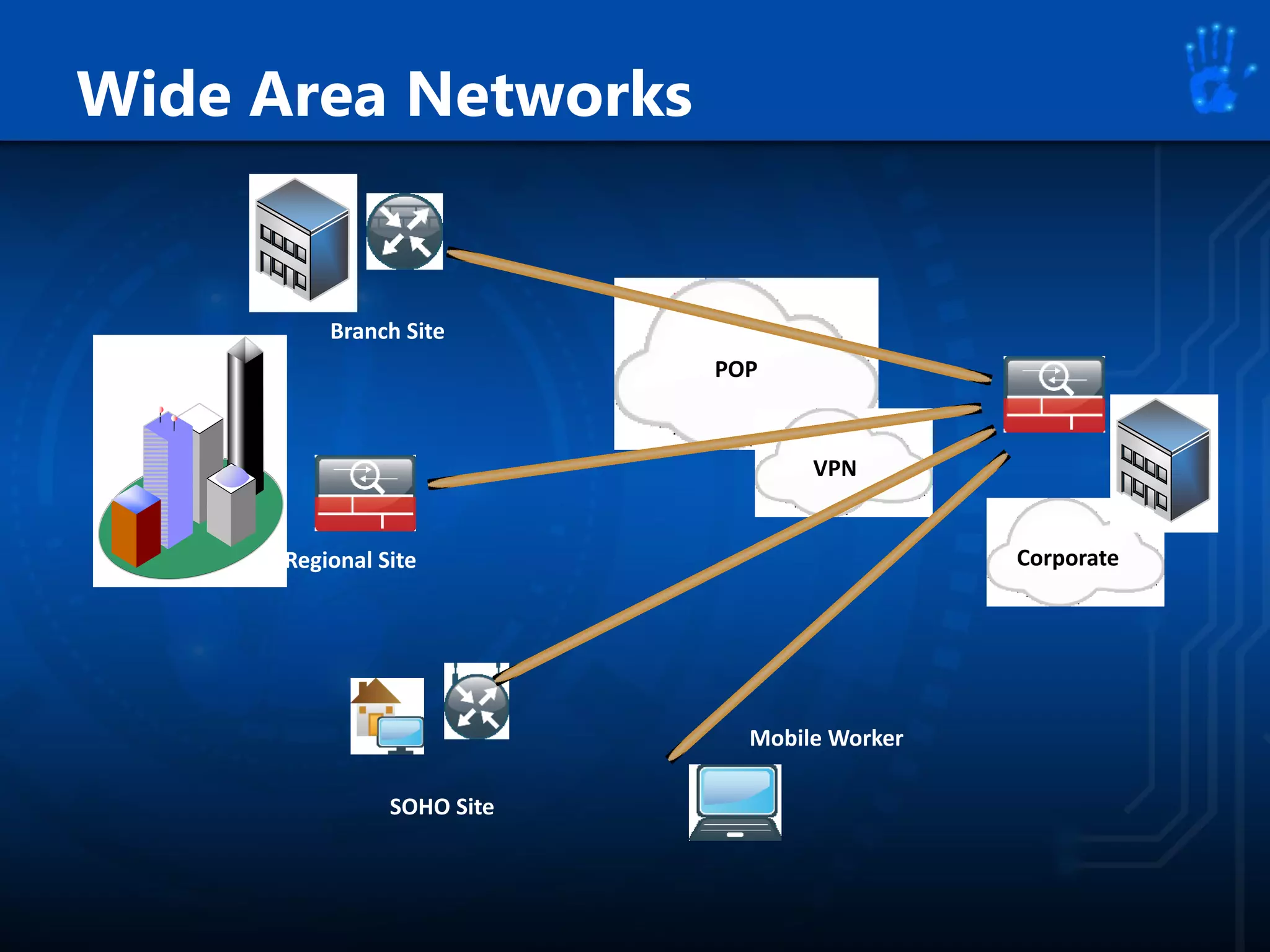
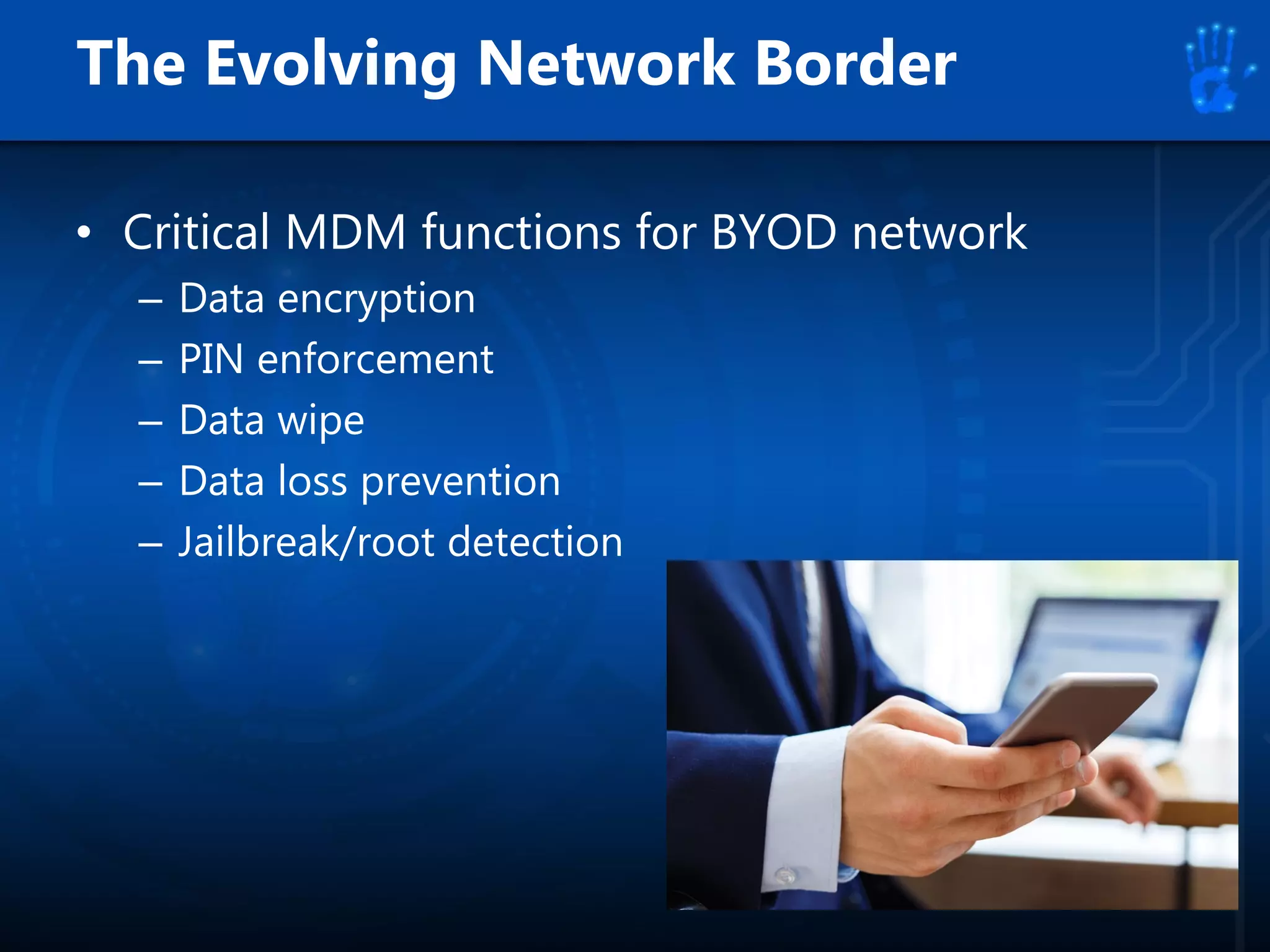
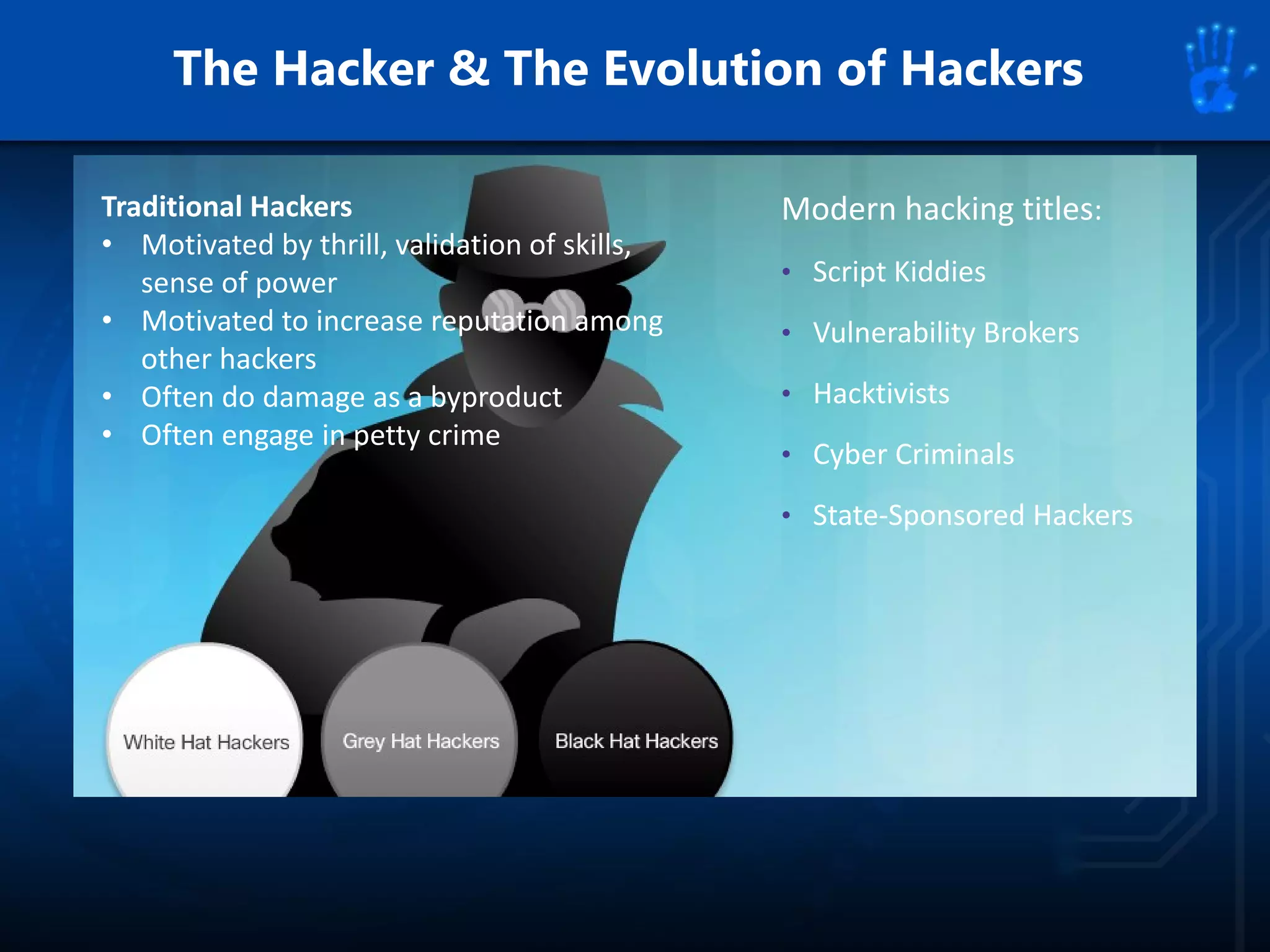
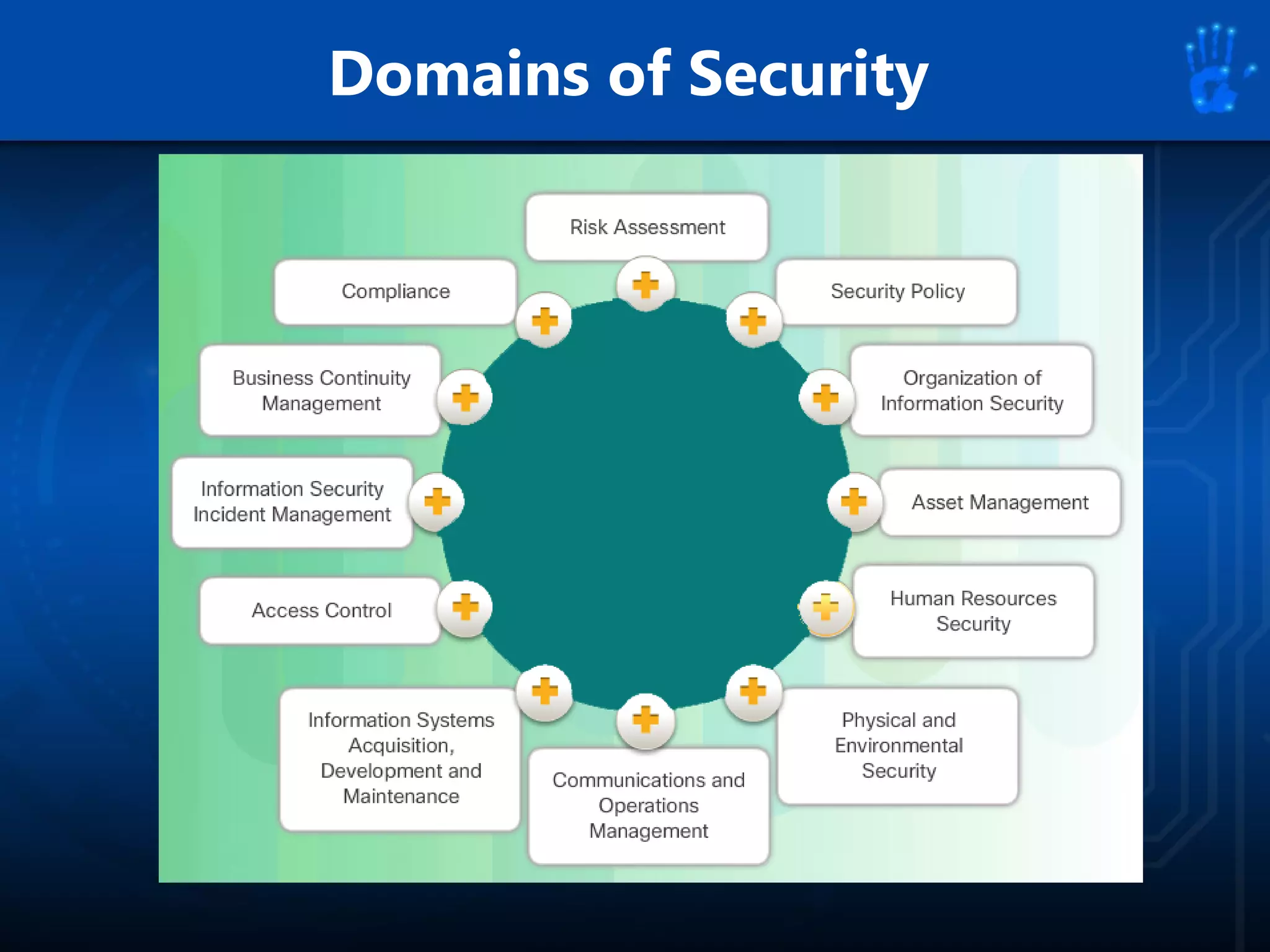
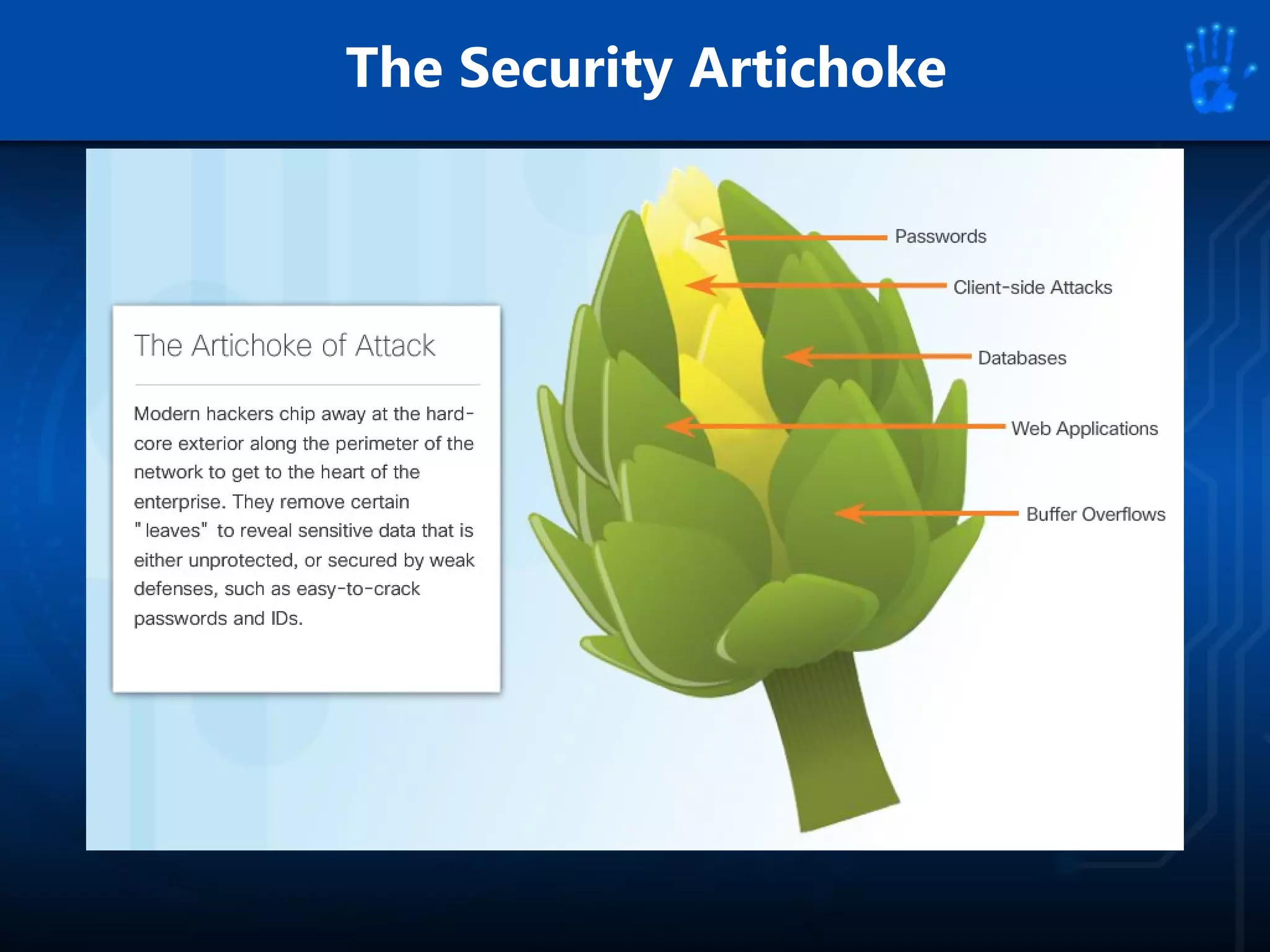
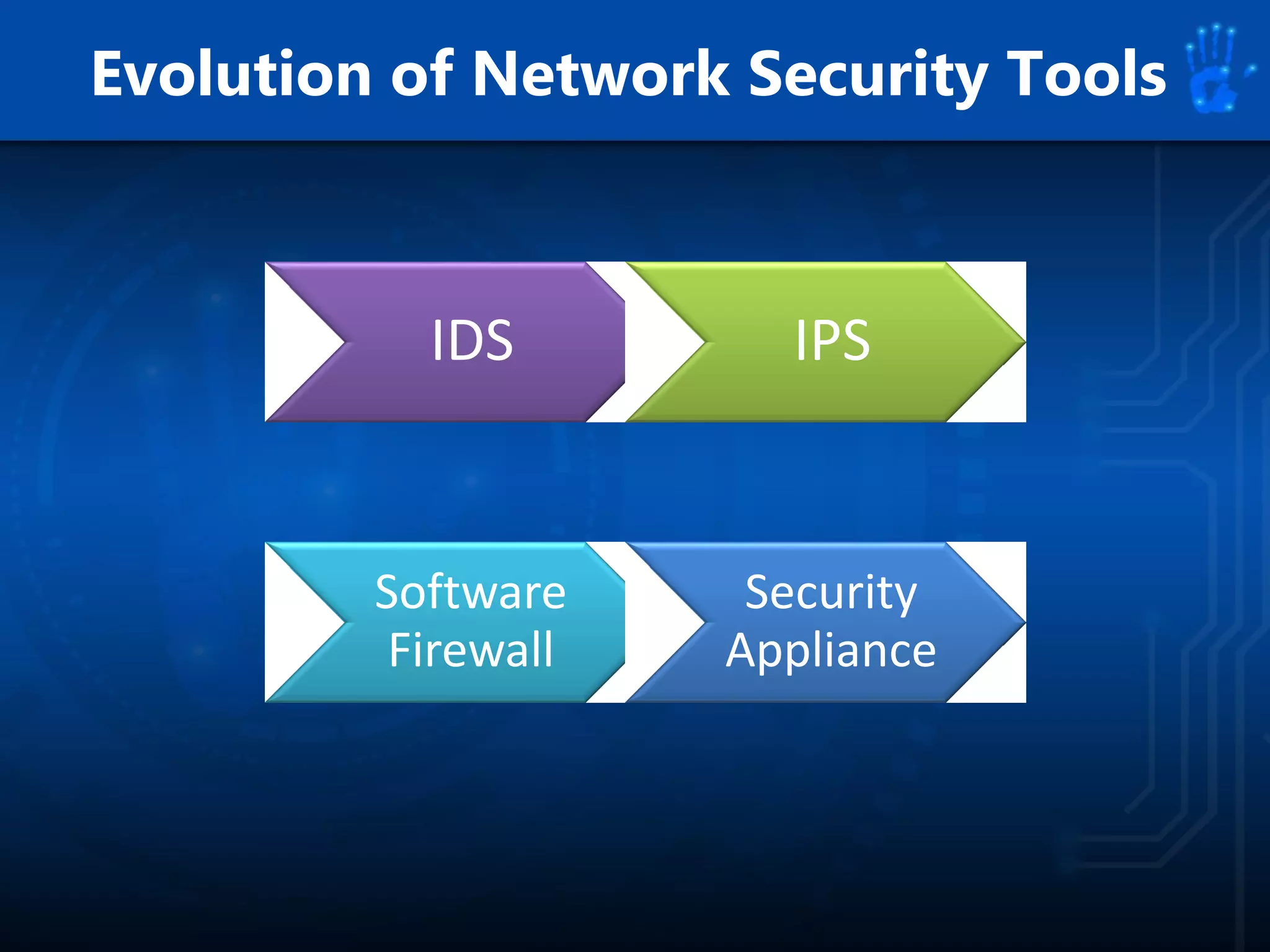
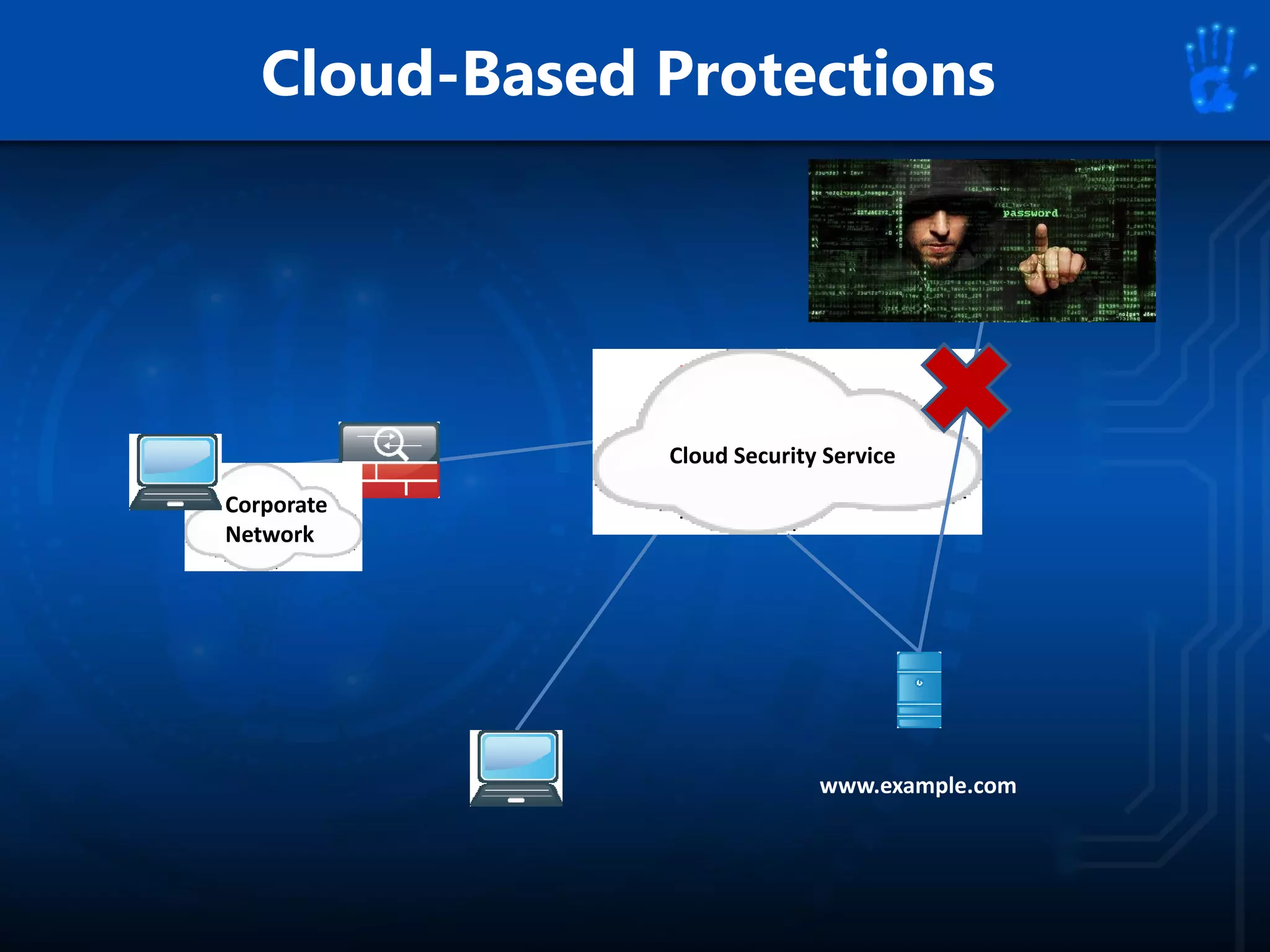
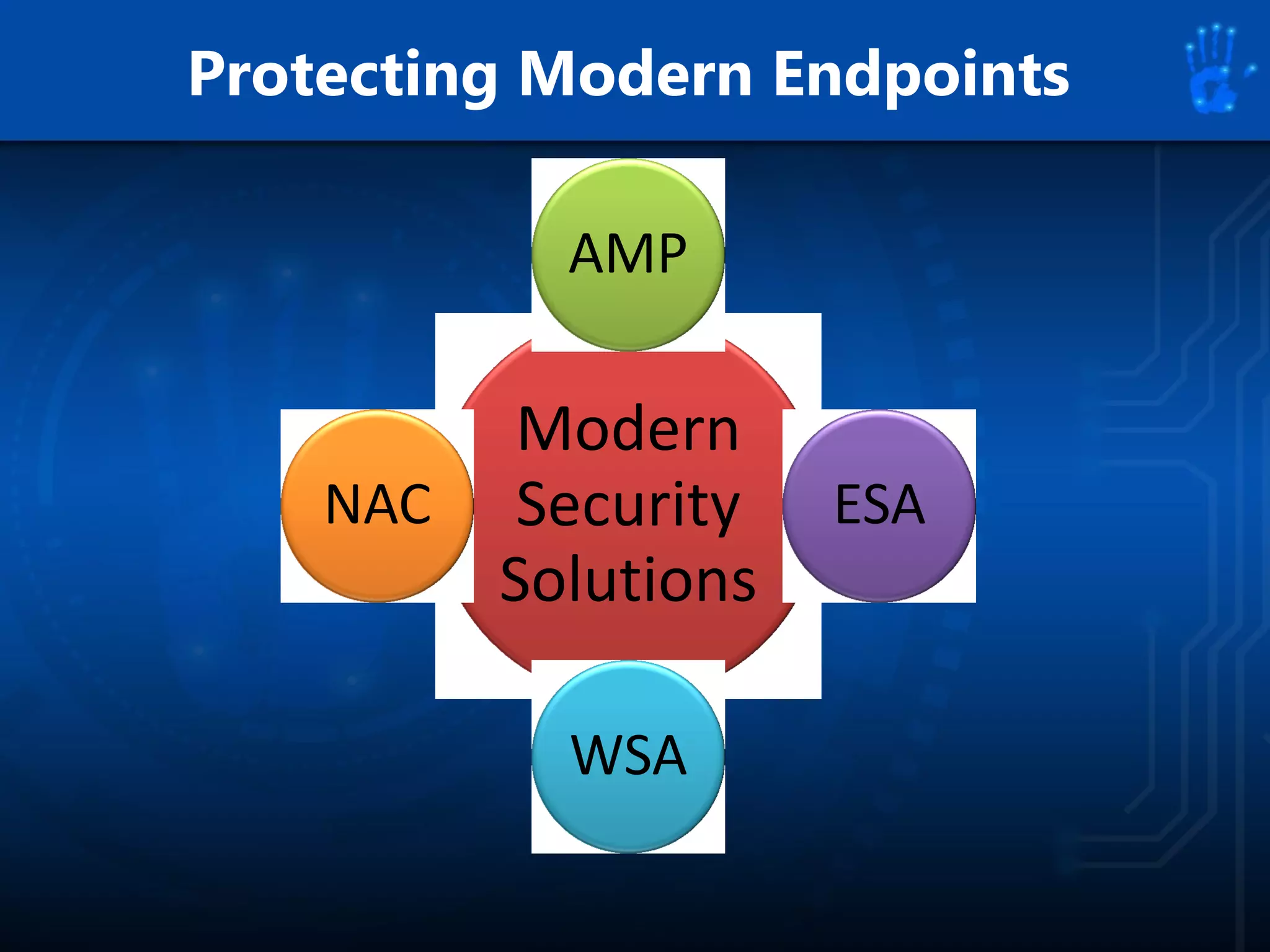
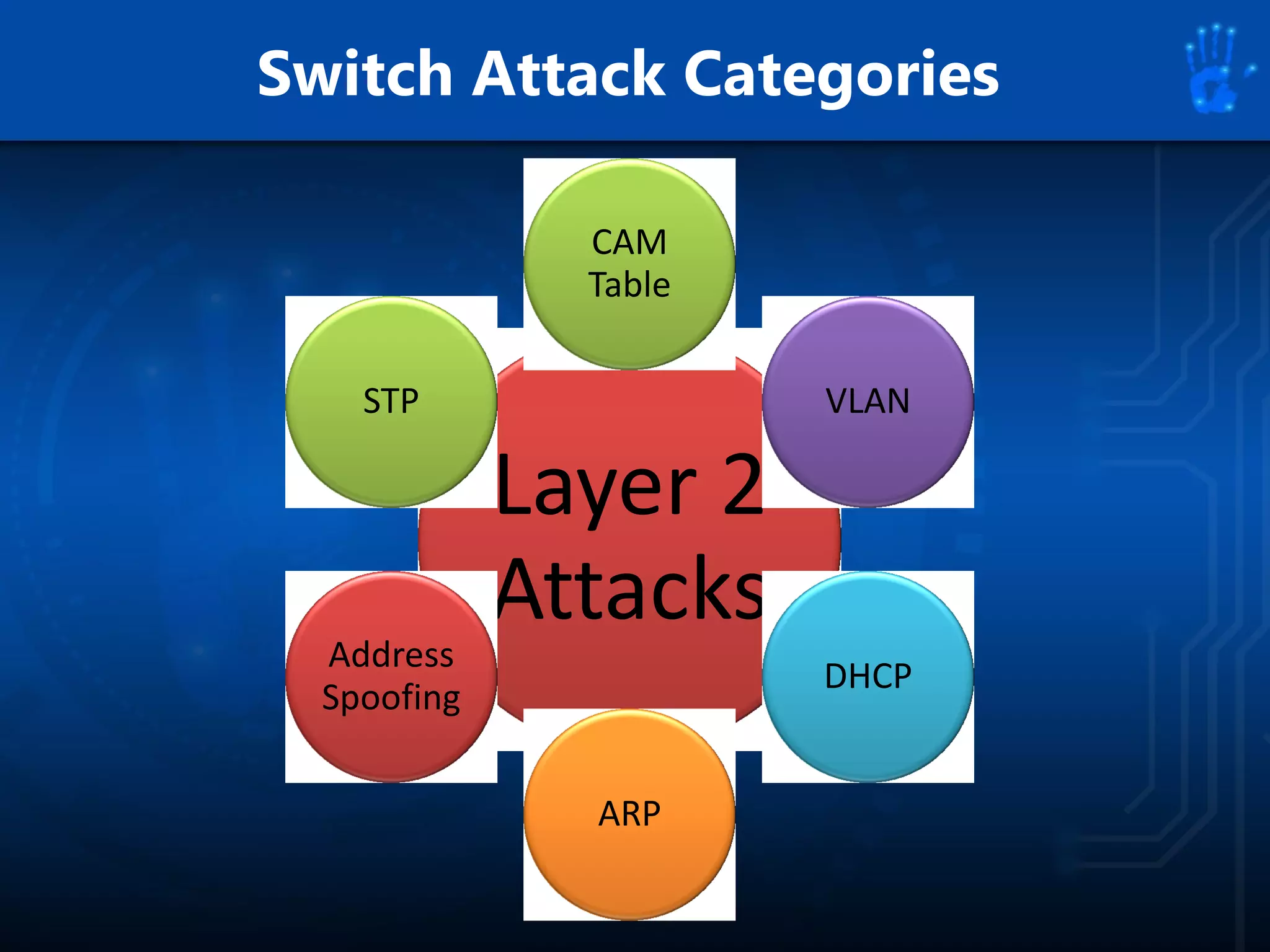
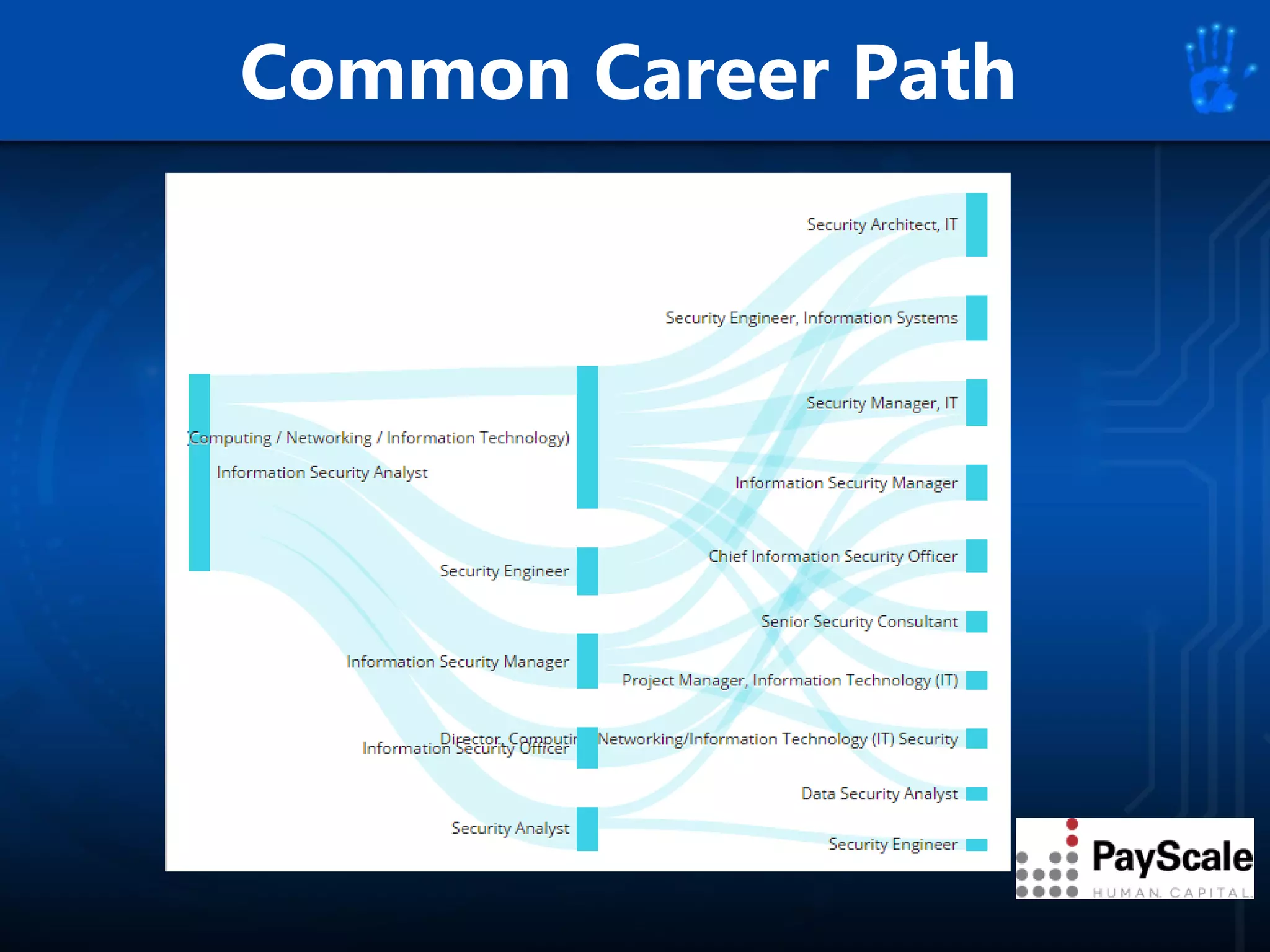
This document discusses information security as an academic field focused on developing professionals who can analyze organizational risks, plan security strategies, create security policies, and respond to threats to support organizational missions. It notes that those studying this field gain expertise in both security technologies and security management. The document then lists relevant courses and outlines the key components of the security management process: plan, protect, and respond.