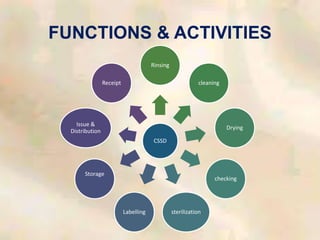
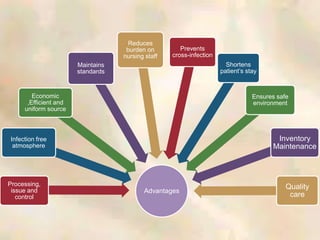
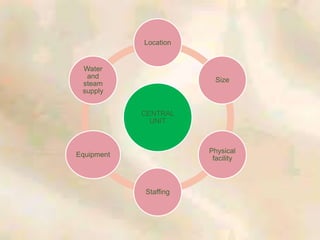
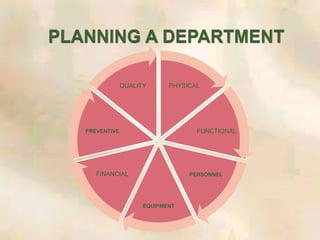
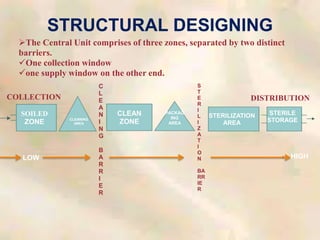
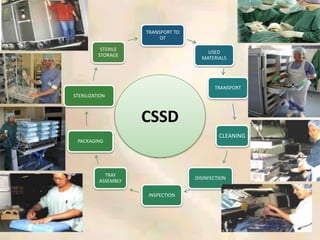
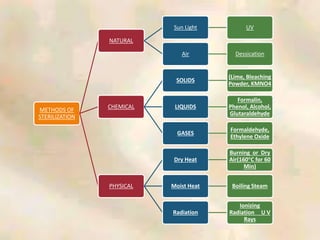
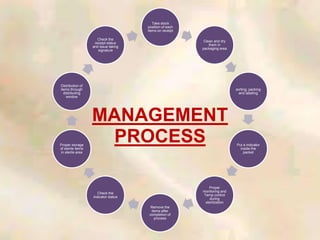
The document outlines the structure and processes of a Central Sterile Supply Department (CSSD) in a hospital, detailing its aim to provide sterile supplies and reduce infection rates. It describes the layout, equipment, staffing, and sterilization methods utilized to ensure an efficient and quality supply of sterile materials. Furthermore, it emphasizes the importance of quality control and proper management of sterilization processes to maintain safety and compliance within the hospital environment.