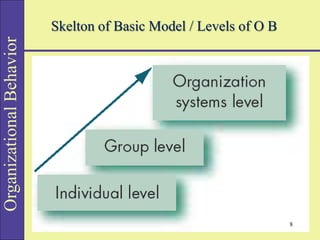
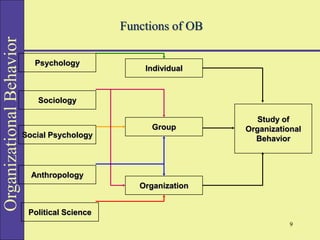
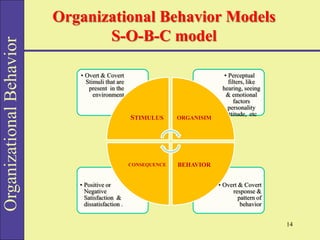
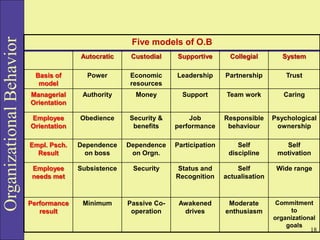
Organizational behavior (OB) studies the actions and interactions of individuals and groups within an organization, aiming to enhance performance and job satisfaction. It encompasses various concepts like behavior, perception, personality, and motivation, and employs multiple research methods to inform practices. Different models and approaches, such as human resource and system approaches, focus on improving organizational effectiveness by understanding the complexities of employee behavior.