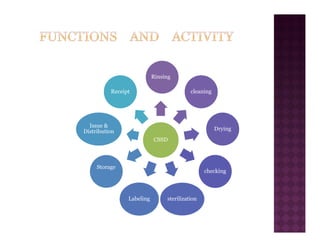
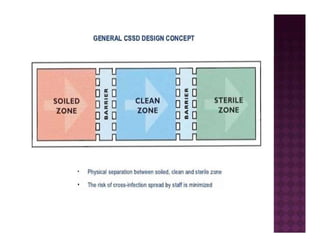
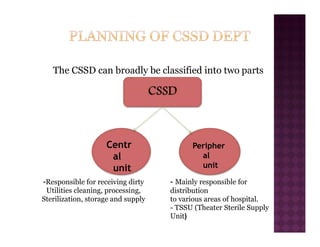
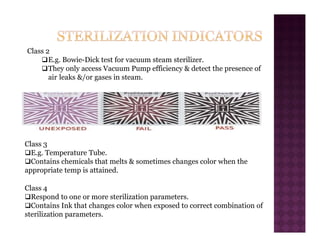
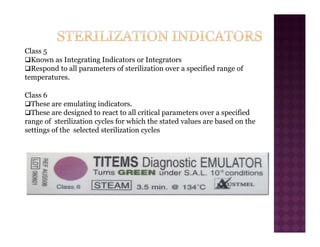
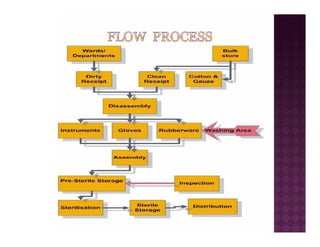
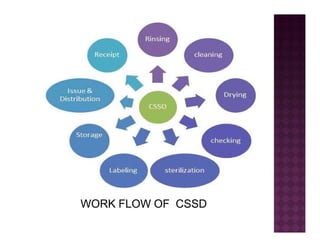
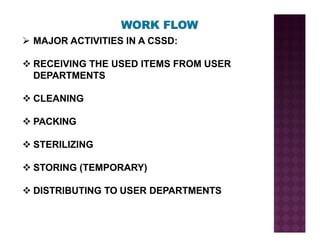
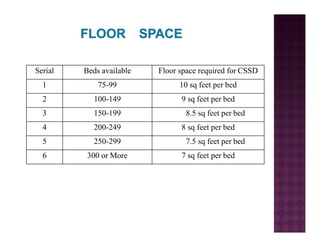
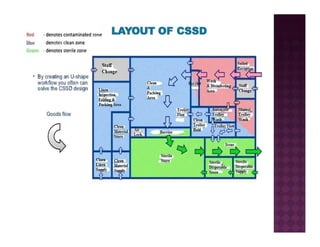
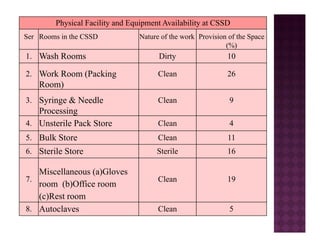
The Central Sterile Service Department (CSSD) provides sterile supplies to all hospital departments. It receives used medical items, cleans and disinfects them, packages them, and sterilizes critical items through processes like steam sterilization. The CSSD aims to reduce hospital infections through effective sterilization while avoiding costly duplicate equipment. It should be designed for efficient workflow with separate clean and dirty areas and proper ventilation. The CSSD benefits the hospital by ensuring a safe, infection-free environment and inventory maintenance while reducing the burden on nursing staff.