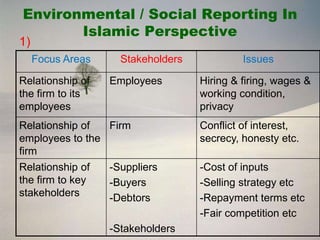
The document discusses social responsibility accounting (SRA), which involves voluntary reporting of non-financial information like employee welfare, environmental protection, and community initiatives. It notes challenges with SRA disclosure like a lack of legislation and uniform standards. The document also outlines objectives of SRA, areas of reporting, advantages, and ways to improve SRA disclosure practices.