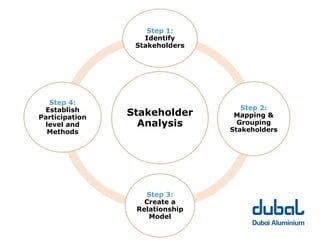
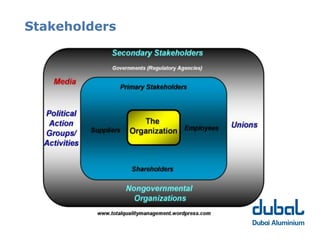
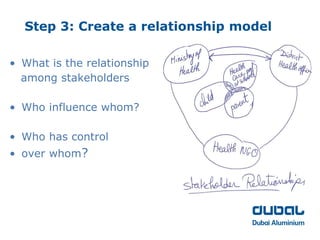
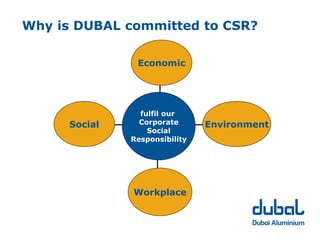
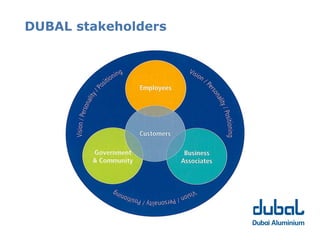
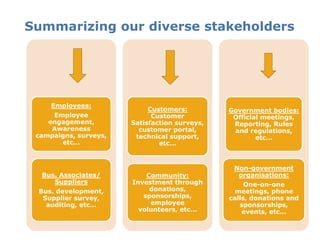
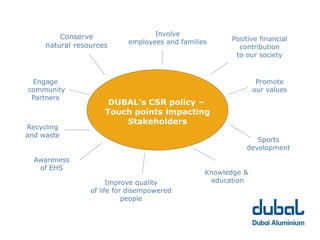
The 10th CSR Summit focused on selecting stakeholders and stakeholder engagement. Key points included identifying an organization's stakeholders, mapping and grouping stakeholders, and determining appropriate participation methods. It is important to engage with stakeholders through respectful dialogue and follow-through on commitments. DUBAL's stakeholders include employees, customers, government bodies, business associates/suppliers, and the community.