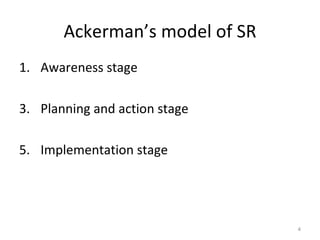
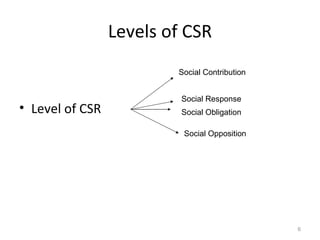
Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) refers to businesses operating ethically and sustainably to improve lives and society. Businesses need to be socially responsible for long term survival, public expectations, goodwill, laws and regulations, and a better operating environment. CSR models include Ackerman's awareness-planning-implementation stages and Carroll's economic-legal-ethical-discretionary responsibilities. CSR levels range from social opposition to social contribution. Main social responsibilities of businesses are to generate profit, employment, utilize resources, provide quality products and protect the environment. In India, companies like NTPC, BPCL, ACC, and Infosys demonstrate CSR through practices like community development, village adoption programs, education/health initiatives